The Essential Role of Teacher Self-Efficacy and Teacher Acceptance for Differentiated Learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/ppd.v12i2.9215Keywords:
Differentiated LearningAbstract
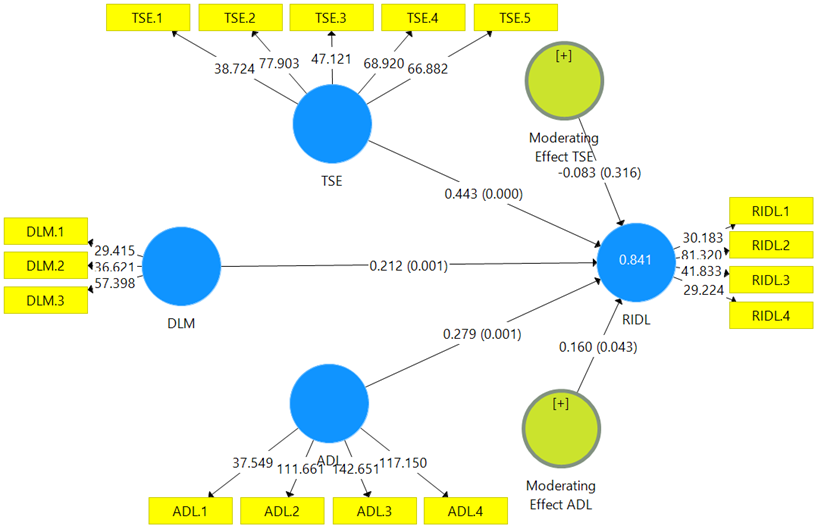
The heterogeneous characteristics of students require teachers to be creative in implementing innovative learning strategies that can meet the various needs of students. This study explores the influence of differentiated learning management on teacher readiness to implement differentiated learning, by analysing teacher self-efficacy and acceptance of differentiated learning as moderator variables. The study involved 162 Elementary School (ES) and Madrasah Ibtidaiyah (MI) teachers from 49 schools in three sub-districts, namely Tapos District, Depok City, Cimanggis District, Bogor Regency, and Kelapa Dua Wetan District, East Jakarta City, Indonesia. This research uses quantitative methods. Data collection used three instruments in the form of questionnaires, namely instruments to measure differentiated learning management (DLM), teachers’ readiness to implement differentiated learning (RIDL), teacher self-efficacy (TSE), and acceptance of differentiated learning (ADL). Data were analyzed using partial least squares structural equal modelling (PLS-SEM) with the help of SmartPLS 3 software. The results showed that differentiated learning management, self-efficacy, and teacher acceptance of differentiated learning had a direct and significant effect on teacher readiness to implement differentiated learning. This study has implications for the importance of core support, professional development, and other policies and resources to support teachers’ readiness to implement differentiated learning.
Downloads
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Husnul Khotimah, Nandang Hidayat, Nur Shahira Binti Abdul Rashid

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.