Improving Innovative Behavior Through Entrepreneurship Education in Economic Education Students Lambung Mangkurat University
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/jpis.v33i2.3395Keywords:
innovative behavior, entrepreneurship educationAbstract
The development of the times is increasingly rapid so it demands change in every individual, therefore innovative behavior is very important, especially for students so that they are able to face developments in the times and provide better changes for themselves and others. However, in reality the innovative behavior of students is still relatively low because they find it difficult to innovate. This research uses a quantitative approach with the type of expost facto research population amounted to 166 students using the probability sampling technique. The research instrument used observation and questionnaires with a likert scale, data analysis uses simple linear correlation. The test results of the t-test obtained a significance value of entrepreneurship education showing that the results of the t-test obtained a tcount value of 3,383 > ttable value of 1,980 meaning that the H1 hypothesis is accepted. Variable (X) entrepreneurship education on innovative variable (Y) has a positive influence, so hypothesis H0 is rejected. The calculated r value is 0.301. This means that the entrepreneurship education variable (X) has an effect on increasing innovative behavior (Y) by 30% which is categorized as relatively weak. The remaining 70% is influenced by other variables both internally and externally.
Downloads
INTRODUCTION
The development of an era that is increasingly rapid and modern, especially in the current era of globalization demands changes, one of which is the economy, therefore innovative behavior is very important, especially for students so that students after graduation are expected to be more innovative, have skills, and are proficient in seeing opportunities in the future. will come because as the next generation of the nation that can provide a better change. In line with what was said by (Handayani & Rahmah, 2020) that nowadays, students are increasingly required to be more innovative within a group or organization, this aims so that students can develop and compete in meeting and achieving goals. College graduates are expected to have competence in academic matters as well as contribute to the progress of the nation and the State by creating jobs (Baihaqi & Nurif, 2015) in (Asih et al., 2020:32).
Behavior is an act in the form of an action from a person in responding to something and then it becomes a habit because of the value that is believed. Human behavior is essentially an action or activity of a person, both observable and non-observable by human interaction with the environment which is manifested in the form of knowledge, attitudes and actions. Behavior can be interpreted more rationally as an organism's or a person's response to stimuli from outside the subject, this response is formed in two kinds, namely the passive form and the active form where the passive form is an internal response that occurs within humans and is not directly visible from other people. while the active form is when the behavior can be observed directly Triwibowo (2015) (in Subekti, et al., 2022).
Innovative behavior is a person's attitude in creating new and different innovations and providing added value to a product or method. Innovative behavior is a person's ability to apply creativity or produce creative ideas in solving problems and finding solutions so that an innovative person becomes more effective and efficient. always think critically, have high motivation, be optimistic, and carry out research and evaluation. Innovative behavior is closely related to innovation, innovation is a new way of thinking while innovation is the result of thinking from innovative behavior.
In facts there are factors in students in innovative behavior namely that awareness of innovation and entrepreneurial ability can be said to be low so it needs to be increased, motivation needs to be strengthened, innovative awareness and innovative abilities are the main processes of innovation activities, and are also influenced by innovation personality Ding (2017) (in Suwardi, et al., 2021: 71). There are also other factors in innovative behavior caused by environmental factors, the brain, thoughts and thoughts where thoughts and thoughts include more than memory and knowledge of the senses, feelings, intentions and motivations for action then lead to the four constituents of thinking as concepts, perceptions (the process of knowing or recognizing objective objects and events with the help of the senses), emotions, and goals Koutstaal & Binks (2015) (in Amalya, 2019: 45).
Based on the results of direct observations with 40 students of Economics Education Batch 2019/2020/2021 and data collection was collected via Google form which was distributed to representatives of each class. Students say that their innovative behavior tends to be low, because they find it difficult to create new products (innovations) caused by a lack of knowledge and skills regarding innovation. In addition, the results of the questionnaire also concluded that there were student internal factors, namely the lack of motivation and self-confidence in the success of the innovation to be realized, so that they prefer something that already exists rather than innovating.
Duening, Hisrich, & Lechter (2009: 71) explains that innovation is a talent or ability to apply creativity to solve problems, find opportunities, and have new and different ideas from before. The meaning of new and different is to be able to create a product that is new and different both in the form of goods and services or in processes such as ideas, methods and ways so that it has its own characteristics. Innovation is seen as an internal driver and is related to an entrepreneurial mindset (Suwardi et al., 2021). In line with what Zimmerer said (in Suryana, 2017: 74) Innovation is a person's creative ability to create opportunities in solving problems and can create opportunities to improve or enrich human life (innovation is the ability to apply creative solutions to those problems and opportunities to enhance or to enrich people's live).
Based on the problems described above, efforts that can support increased innovative behavior are through the Entrepreneurship Education program, such as entrepreneurship courses in universities because innovation is one of the driving forces for the development of entrepreneurial projects. Entrepreneurship education related to perceptions in encouraging innovation through entrepreneurship education is the main task of tertiary institutions. In line with what Pangesti (2018) said that entrepreneurship education is an important basis for continuing education for quality young people.
Entrepreneurship Education is a unit of study applied in tertiary institutions whose goal is that students are expected to be able to obtain it from a learning process that stimulates their analytical and psychomatic abilities so that they have a better experience through practice carried out in learning which is expected to be carried out in the real world. Susilaningsih (2015) says that entrepreneurship education in tertiary institutions is related to the formation of entrepreneurial character, an entrepreneurial mindset that is always creative and innovative, and is able to train students in creating added value (innovation) or good values (values), take advantage of opportunities, dare to taking risks, instilling knowledge, values, spirit, and entrepreneurial attitude to students so that they become independent, creative and innovative people. According to De Jong, & den Hartog (2003) (in Hidayat, et al., 2018) Innovative behavior is an individual activity that aims to introduce new and useful ideas related to processes, products or procedures. In line with what was said by Bruce, (1994); Jennsen, (2004) (in Helmy & Pratama, 2018) defines that innovative behavior is all individual action that leads to idea generating, idea promoting, and implementation of something new.
Hasan (2020) says that entrepreneurship education with several types of education and training processes, aims to influence individual attitudes, behaviors, values or intentions towards the concept of independent business as a career that can be realized in society. In line with what was said by Kaharudin & Djohan (2022: 290) that entrepreneurship education is a process to build an entrepreneurial spirit in a person so that he can increase a culture of creativity and innovation, by taking advantage of existing opportunities so that he can run a business effectively and efficiently. The innovative spirit of an entrepreneur is like having the courage to take into account and taking existing risks, being able to create products that are different or have added value and are different from those offered by competitors. Entrepreneurship education is organized with the aim that graduates can build businesses and create jobs. According to Suwardi, et al (2021: 79) the results of the study showed that the path analysis test obtained a standardized beta value of 0.224, a tcount of 2.823, and a significant value of 0.005, which is smaller than alpha (0.05). This means that entrepreneurship education directly influences significantly and positively on student innovation, with entrepreneurship education it can help students equip themselves to become independent, creative and innovative individuals.
Based on the description above, it can be concluded that students' innovative behavior is still low. Innovative behavior is very important for students, especially innovation in creating new products, so that this can influence students' future readiness in facing current developments. Therefore, efforts that can be applied to students to increase innovative behavior are through the role of entrepreneurship education so that they are more confident in new ideas for innovation that can provide new added value, so that they are able to develop and implement these innovations.
RESEARCH METHOD
The author uses a quantitative approach with the type of expost facto research, to test the increase in innovative behavior through entrepreneurship education programs for students of the faculty of teacher training and education of the University of Lampung. The population used in this research is economic education students class 2019/2020/2021 who have taken entrepreneurship courses, while the number of students is 166 students using the probability sampling technique. The number of samples was calculated using the slovin formula, totaling 117 students. The research instrument uses data collection techniques. Furthermore, when viewed from the methods or techniques of data collection, data collection techniques can be carried out by interviews, questionnaires, observation, and a combination of the three (Sugiyono, 2021). The distribution of questionnaires/questions carried out in this study used the survey method by sending questionnaires directly to students of the 2019/2020/2021 class of economics education who had taken entrepreneurship courses as well as the technique of distributing the questionnaire links listed on the Cloud system which in this case used Google Form media for filling out questionnaires, data analysis using simple linear correlation for data analysis using questionnaires (validity test and reliability test) then for analysis prerequisite tests using normality tests, linearity tests, and for hypothesis testing using (t-test and R-test Coefficient of Determinant).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Results
Validation and Reliability Results
Based on the validity test that has been carried out with the SPSS innovative variable above, it can be seen that the 23 questionnaire items that have been tested the results are 20 valid questions> 0.30 while 3 items are invalid because the results show <0.30 and for the entrepreneurship education variable all questions used are valid. Meanwhile, the results of the instrument reliability test or test with Alpha-Cronbach obtained values between 0.815 – 1.000 > 0.600, so it can be concluded that all questions in this study are reliable or consistent because the alpha value > r table value.
Classical Assumption Test
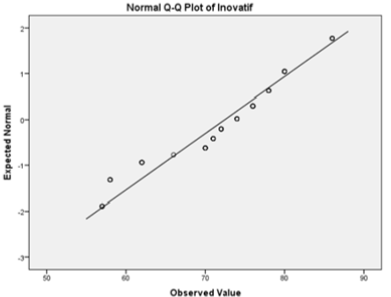
Based on the results carried out using (Q-Q plot) it can be seen that innovative entrepreneurial education data (Y) most of the data patterned around the diagonal line to the upper right, on this basis proves that the distribution of data is normally distributed both from innovative and educational behavior variables entrepreneurship.
The table above shows that the results of linearity testing obtained the significance value of entrepreneurial education to innovative 0.00 <0.05 means that the relationship of independent variables with the dependent variable is linear.
Hypothesis Test(t-test)
The table above shows that the results of the t test obtained a tcount value of 3,383 > a t-table value of 1,980 meaning that the H1 hypothesis is accepted: Variable (X) entrepreneurship education on innovative (Y) variable has a positive influence, so hypothesis H0 is rejected.
R Coefficient of Determinants
The calculated r value is 0.301. means that the entrepreneurship education variable (X) has an effect on increasing innovative behavior (Y) by 30% The remaining 70% is influenced by other variables both internally and externally based on research journals found a, such as: creativity, motivation, self-efficacy, and desire to succeed based on previous research journals.
Discussion
Based on the results of the questionnaire, it can be seen how the role of entrepreneurship education is that with entrepreneurship education, students can learn things related to renewal, students can feel confident in their abilities to develop innovative ideas in learning, with student entrepreneurship education can increase understanding of how to develop product innovation, add knowledge in creating creative and innovative products, with entrepreneurship education I get the knowledge to innovate, but have never directly practiced it, and entrepreneurship education can open students' minds to the importance of innovative behavior.
Economics education students have good innovative behavior such as being able to look for new opportunities to improve products and innovate, being able to create new products that are not yet on the market, being able to make innovations that are more effective and efficient, being able to make products in new ways, etc. but there are some things that must be at the level, such as don't give up easily if you experience failure in creating product innovations and so that you are better able to overcome obstacles when implementing product innovations.
The results showed that the t-test obtained a significance value of entrepreneurship education showing that the results of the t test obtained a tcount value of 3,383 > ttable value of 1,980 meaning that the H1 hypothesis is accepted. Variable (X) entrepreneurship education on innovative (Y) variable has a positive influence, so hypothesis H0 rejected. The calculated r value is 0.301. This means that the entrepreneurship education variable (X) has an effect on increasing innovative behavior (Y) by 30% which is categorized as relatively weak. The remaining 70% is influenced by other variables both internally and externally based on research journals found a, such as: creativity, motivation, self-efficacy, and desire to succeed based on previous research journals.
Researchers can also prove that the entrepreneurship education variable can be a significant predictor of increasing student innovative behavior, even though the increase is only 30%. These results illustrate that through programs, learning and assignments in entrepreneurship education are able to increase students' innovative behavior. In line with research conducted by Suwardi, et al (2021) concluded that through participation in learning, students are able to form learning networks in a good entrepreneurship education environment, use their influence to continuously obtain and exchange valuable resources through persuasion and collaboration, forming networks shared social resources, and improve self-professional skills. The effectiveness and conversion rate of innovative knowledge strengthens the perceived impact of entrepreneurship education on innovation. This means that the introduction of entrepreneurial opportunities can encourage students to recognize their entrepreneurial orientation with the help of entrepreneurship education obtained in college so that students are able to express their own creativity and innovation in entrepreneurial projects based on the transformation of innovative technology and creativity. Innovation is the driving force for the development of entrepreneurial projects (Kassean et al., 2015).
CONCLUSION
Based on research conducted, the role of entrepreneurship education on students' innovative behavior has a positive effect. Students feel more confident in their abilities to develop innovative ideas because entrepreneurship education teaches students how to innovate and add value to a product, increases creativity in creating creative products, and opens students' minds to the importance of innovative behavior. in entrepreneurship. Based on the results of the research conducted, it can be concluded that with the role of entrepreneurship education, ULM economics students have better innovative behavior, such as being able to look for new opportunities to improve products and innovate, being able to create new products that are not yet on the market, being able to carry out more effective innovations. and efficient, and able to make products in new ways.
The findings of this study contributed to an increase in student innovative behavior based on the results of the study showing that the results of the t test obtained a significance value of entrepreneurship education showing that the results of the t-test obtained a tcount value of 3,383 > a ttable value of 1,980 meaning that the H1 hypothesis is accepted. Variable (X) entrepreneurship education on the innovative (Y) variable has a positive influence, so the hypothesis H0 is rejected. The calculated r value is 0.301. means that the entrepreneurship education variable (X) has an effect on increasing innovative behavior (Y) by 30% categorized as relatively weak. The remaining 70% is influenced by other variables both from the student's internal self and from externally based on research journals found a, such as: creativity, motivation, efficacy self, and desire to succeed based on previous research journals.
References
Agung, A. I. G. L., & Made, P. N. (2016). The Effect of Entrepreneurship Education, Self Efficacy and Locus of Control on Entrepreneurial Intentions. Unud Management E-Journal, 5(2), 1160–1188.
Alfiyan, A., Qomaruddin, M., & Alamsyag, D. (2019). Bhayangkara University Jakarta Raya the Influence of Entrepreneurship Education and Academic Support on Student Entrepreneurial Intentions. Journal of Scientific Studies, 19(2), 175–181.
Amalya, I. D. (2019). Innovative Behavior in Entrepreneurial Students. Indonesian Psychological Research, 1(1), 40–46. https://doi.org/10.29080/ipr.v1i1.169.
Angrayni, A. (2019). Problems of Education in Indonesia. Ushuluddin and Da'wah Faculty of IAIN Ambon 2, 1–10. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/229361428.pdf.
Arikunto, S. (2019). Research Procedures: A Practice Approach. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Asih, W. M., Kamil, I., & Indrapriyatna, A. S. (2020). The Role of Entrepreneurship Education on Students' Innovative Behavior in Facing the Industrial Revolution 4.0. JMKSP (Journal of Management, Leadership and Educational Supervision), 5(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.31851/jmksp.v5i1.3513.
Datak, G., Sylvia, E. I., & Manuntung, A. (2018). The Influence of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Self Efficacy and Self Care Behavior of Hypertension Patients in Palangka Raya City. Surya Medika Journal, 3(2), 132–143. https://doi.org/10.33084/jsm.v3i2.113.
Ding, Y. -Y. (2017). The Constraints of Innovation and Entrepreneurship Education for University Students. Journal of Interdisciplinary Mathematics, 20(6–7), 1431–1434. https://doi.org/10.1080/09720502.2017.1382152.
Evidence, P., Long, P., Lunang, B., Mix, P., Services, P., Decisions, T., Travelers, B., Objects, P., Houses, W., Mande, G., & Coastal, R. (2019). EcoGen Department of Economic Education, Faculty of Economics, Padang State University. EcoGen 2(3), 5 September 2019, 338–350.
Firdausiah, S., & Etikariena, A. (2021). Innovative Work Behavior and Creative Self-Efficacy in Students. Psychology: Journal of Psychological Thought and Research, 26(1), 57–84. https://doi.org/10.20885/psikologika.vol26.iss1.art4.
Handayani, E. Y., & Rahmah, A. (2020). Relationship between Organizational Commitment and Innovative Behavior in Surabaya State University Students. Proceedings of the 2020 National Seminar, 228–234.
Harianti, A., Malinda, M., Nur, N., Suwarno, H. L., Margaretha, Y., & Kambuno, D. (2020). The Role of Entrepreneurship Education in Increasing Motivation, Competence and Growing Student Interests. Journal of Business and Entrepreneurship, 16(3), 214–220. https://doi.org/10.31940/jbk.v16i3.2194.
Harnani, N. (2020). Creative Entrepreneurship Learning Model Through Business Practices in Growing Student Creativity and Innovative (Study on Management Students at the Faculty of Business Economics, Winaya Mukti University, Bandung City). Sociohumanities, 22(1), 79–87. https://doi.org/10.24198/sosiohumaniora.v22i1.24510.
Harwiki, W. (2019). Entrepreneurship Education, Innovation Disruption, and Entrepreneurship Opportunities for DR. Sutomo Surabaya. Perwira, 2(1), 79–89.
Hasan, H. A. (2020). Entrepreneurship Education: Concepts, Characteristics, and Implications in Empowering Young Generation. Pilar Journal: Journal of Contemporary Islamic Studies, 11(1), 99–111.
Helmy, I., & Pratama, M. P. (2018). The Effect of Proactive Personality and Psychological Empowerment on Innovative Behavior Through Creative Self Efficacy. Journal of Probusiness, 11(2), 14–21.
Hidayat, A. S., Setiawan, Y., Alwi, M., & Nurdiana, E. (2018). The Role of Innovative Behavior as an Intervening Variable between Knowledge Creation and Competitive Advantage. Ecodemica Journal, 2(2), 203. https://ejournal.bsi.ac.id/ejurnal/index.php/ecodemica/article/view/4090/202-212.
Irwansyah, M. R., & Tripalupi, L. E. (2018). Testing the Effect of Entrepreneurship Education in the Formation of an Entrepreneurial Spirit Among Students. International Journal of Social Science and Business, 2(4), 251. https://doi.org/10.23887/ijssb.v2i4.16340
Januarti, D. W., Pratiknjo, M. H., & Mulianti, T. (2018). Student Behavior in Using Social Media at Sam Ratulangi University Manado. Unair Journal, 21, 1–20.
Sektiyaningsih, I. S., Hardianawati, & Aisyah, S. (2020). Analisis Pengaruh Pendidikan Kewirausahaan, Inovasi, dan Motivasi Berwirausaha Terhadap Minat Berwirausaha Pada Mahasiswa IBM ASMI Jakarta. JMBA - Jurnal Manajemen dan Bisnis, 06(02), 67–77.
Kaharudin, E., & Djohan, H. A. (2022). Pendidikan Kewirausahaan Bagi Mahasiswa. Jurnal Ekonomi Bisnis, Manajemen dan Akuntansi (JEBMAK), 1(3), 285-294.
Kan, A. U. & Murat, A. (2020). Investigation of Prospective Science Teachers' 21st Century Skill Competence Perceptions and Attitudes Toward STEM. International Online Journal of Educational Sciences, 10(4), 251-272.
Lestari, E., Siregar, G., Sijuang, N. A., Sirait, S. br., & Simanjuntak, S. S. D. (2022). Student Behavior of 2018 Stambuk Economic Education Study Program, Medan State University in Online Learning. LAKSMI SARI: Jurnal Pendidikan dan Humaniora, 2(1), 79-94.
Lubis, P. K. D. (2018). The Influence of Entrepreneurship Education and Entrepreneurship Skills on Entrepreneurial Motivation of Economic Education Students at Medan State University. Tradesman, 7(2), 95–101. https://doi.org/10.24114/niaga.v7i2.10756.
Makmum, A. S. (2017). Characteristics of Behavior and Personality in Adolescence. Indonesian Teacher Research Journal, 2(2), 17–23. https://jurnal.iicet.org/index.php/jpgi/article/view/220.
Ningsih, R. (2017). The Role of Entrepreneurship Education in Increasing Entrepreneurial Motivation for Students. Journal of the Role of Entrepreneurship Education in Increasing Entrepreneurial Motivation for Students, 2(3), 60.
Putri, N. L. W. W. (2017). The Effect of Entrepreneurship Education on Students' Interest in Entrepreneurship in Economic Education Students at Ganesha University of Education. Undiksha Journal of Economic Education, 9(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.23887/jjpe.v9i1.19998.
Rahman, A., Munandar, S. A., Fitriani, A., Karlina, Y., & Yumriani. (2022). Definition of Education, Education Science and Elements of Education. Al Urwatul Wutsqa: A Study of Islamic Education, 2(1), 1–8.
Ranto, two pril revelations. (2016). Building Entrepreneurial Behavior in Students Through Entrepreneurship Education. Jbma, 3(1), 79–86.
Setiti, S., & Ratumbuysang, M. F. N. G. (2019). Entrepreneurship Theory (Theory of entrepreneurship). CV. Artikata Publisher.
Sugiyono. (2013). Quantitative Research Methods, Qualitative, and R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta, CV.
Sugiyono. (2021). Educational Research Methods (Quantitative, Qualitative, R&D, Educational Research) (2nd ed.). Bandung: Alphabet.
Susilaningsih, S. (2015). Entrepreneurship Education in Higher Education: Is it Important for All Professions? Journal of Economia, 11(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.21831/economia.v11i1.7748.
Suwardi, D. M., Machmud, A., & Iswanti, I. (2021). The Role of Entrepreneurship Education on Mediated Student Innovation Introduction to Entrepreneurial Opportunities. Edunomic Journal of Economic Education, 9(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.33603/ejpe.v9i1.4595.
Taluke, D., Lakat, R. S. M., Sembel, A., Mangrove, E., & That, M. (2019). Analysis of Community Preferences in Mangrove Ecosystem Management in the Coastal District of Loloda, West Halmahera Regency. Spatial, 6(2), 531–540.
Utama, H. (2020). The Need to Innovate in Entrepreneurship. Journal of Management Tools, 12(2), 170–176. http://jurnal.pancabudi.ac.id/index.php/JUMANT/article/view/1129.
Wardani, N. T., & Dewi, R. M. (2021). The Influence of Motivation, Creativity, Innovation and Business Capital on Interest in Entrepreneurship. Jurnal Manajemen dan Kewirausahaan, 9(1), 77-93.
Wibowo, A. (2017). Impact of Entrepreneurship Education for Students. Asian Journal of Entrepreneurship and Family Business, 01(01), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.21632/ajefb.1.1.1-14.
Winda Novariana, N., & Andrianto, S. (2020). Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy and Entrepreneurial Intention: The Mediating Role of Innovative Behavior Among College Students in Yogyakarta. Motiva: Journal of Psychology, 2020(1), 26–34.
Wiyono, H. D. (2020). Creativity and Innovation in Entrepreneurship. Journal of USAHA, 1(2), 19–25. https://doi.org/10.30998/juuk.v1i2.503.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Jurnal Pendidikan Ilmu Sosial

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.













