Wearable upper limb motion assist robot for eating activity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/arstech.v1i1.28Keywords:
Activities of daily living , Degree of freedom, Motion assist robots, Upper limb rehabilitation robot, Task-specific, Wearable exoskeletonAbstract
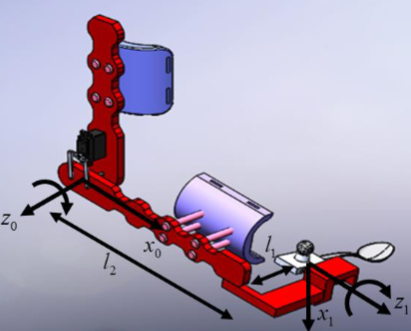
Many people all around the world are suffering from various types of disabilities and need to depend on others to perform activities of daily living. One of the essential daily living activities is eating. The disabled people should be able to eat their food independently at any time and place, without relying on the caregivers. This paper presents the development of a new wearable upper limb motion assist robot for helping the disabled to eat by themselves. The motion assists robot consists of two degrees of freedom (DOF) movement, focusing on the two most crucial upper limb movements in eating activity, which is the elbow flexion/extension and forearm pronation/supination. A light-weight material was used for the fabrication of the wearable motion assist robot, and Arduino was utilized as the microcontroller. The originality of the study was in terms of the design, operational sequence setting, and kinematic analysis of the wearable upper limb motion assist robot that was explicitly focusing on eating activity. The resulted prototype was portable, compact, light in weight, simple and low cost. The experimental results have proven that the proposed wearable upper limb motion assist robot for eating activity was successful in helping the users to perform the main upper extremity motions in eating. The success rate of the proposed system was 80%, and it took 6 seconds for the system to complete one feeding cycle.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Uzair Kashtwari, Norsinnira Zainul Azlan, Ifrah Shahdad

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










