Optimization of Artificial Intelligence in Islamic Religious Education: Opportunities and Challenges in Learning Evaluation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/suhuf.v37i2.11015Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence , Learning evaluation, Islamic education, Sharia values, Digital transformationAbstract
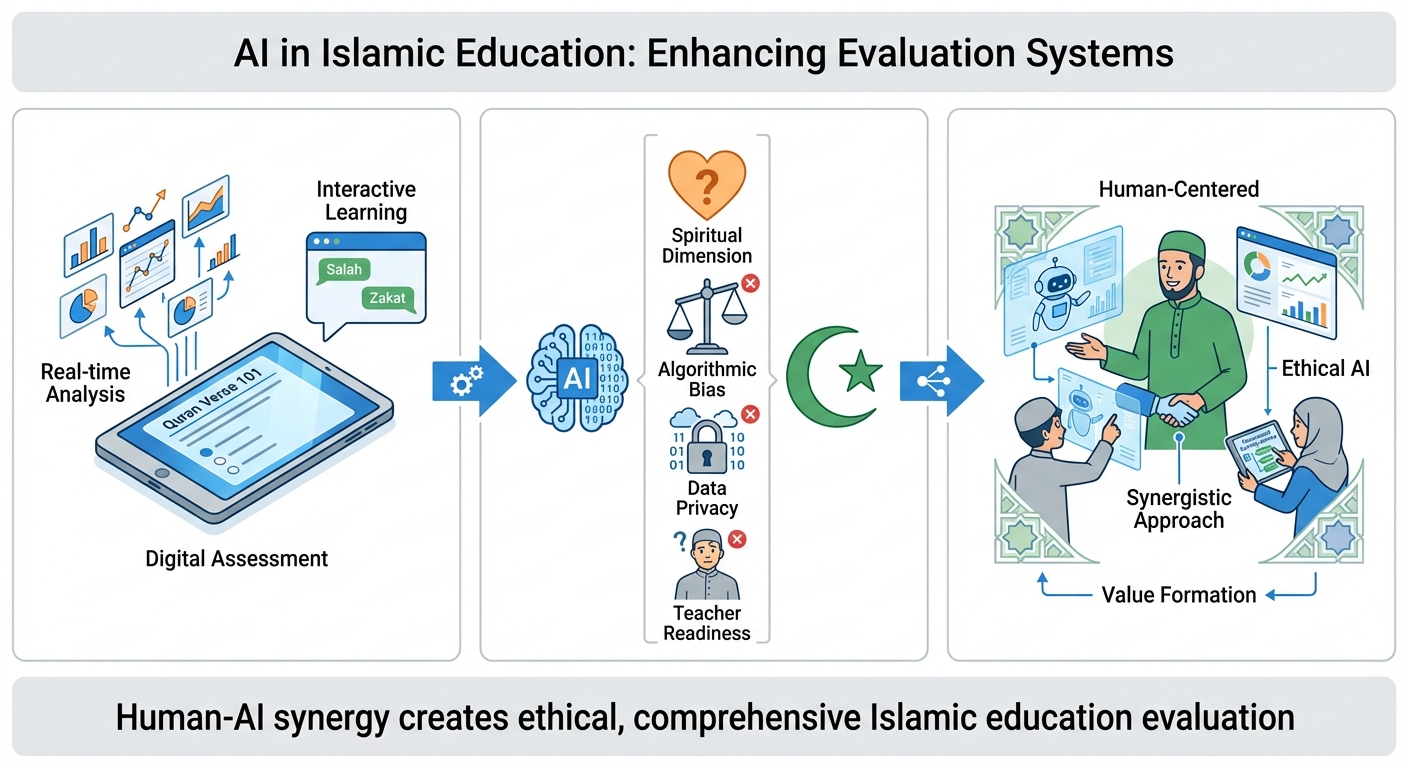
In the era of digital transformation, artificial intelligence (AI) has become important innovation in the world of education, including in the evaluation of learning Islamic Religious Education. This research aims to examine the optimization the application of AI in Islamic Religious Education evaluation, the challenges faced, and the future potential the future. With a qualitative approach based on literature review, this research analyzing literature related to the application of AI in the context of Islamic education. Results The study shows that AI is capable of enhancing the effectiveness of evaluating cognitive aspects. Cognitive through digital quizzes and real-time data analysis systems, as well as starting reaching affective and psychomotor aspects with technology such as chatbots, facial recognition, and virtual reality. However, a number of challenges also arise, among others, the limitations of AI in capturing the spiritual dimension, the potential for algorithmic bias algorithmic, ethical and data privacy issues, as well as teacher readiness and infrastructure. In
the future, AI has great potential to become a comprehensive and personal, if the application of AI in learning and evaluation can be supervised in an ethical and still making teachers the central figure in the formation of values and character. This research recommends a synergy between technology developers, educators, and Sharia experts in developing a human-centered AI-based evaluation system and in accordance with Islamic values.
Downloads
References
[1] F. R. Hakim, “Implementasi Model Pembelajaran Interaktif Pada Mata Pelajaran Pendidikan Agama Islam (Pai) Dalam Meningkatkan Prestasi Dan Motivasi Belajar Siswa [Implementation of an Interactive Learning Model in Islamic Religious Education (PAI) Subjects to Improve St,” 2021. [Online]. Available: https://tesis.riset-iaid.net/index.php/tesis/article/view/79
[2] W. Holmes, M. Bialik, and C. Fadel, Artificial Intelligence in Education. Promise and Implications for Teaching and Learning. Boston: Center for Curriculum Redesign, 2019.
[3] M. Sholeh, E. F. Rusydiyah, and M. Y. Abu Bakar, “Integration of AI Chatbots in Islamic Religious Education: Potential and Challenges from a Doctoral Student Perspective,” AL-ISHLAH J. Pendidik., vol. 16, no. 2, Jun. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.35445/alishlah.v16i2.5409.
[4] L. Hakim and M. R. Azizi, “Otoritas Fatwa Keagamaan Dalam Konteks Era Kecerdasan Buatan (Artificial Intelligence/Ai) [The Authority of Religious Fatwas in the Context of the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Era],” Ar-Risalah Media Keislam. Pendidik. dan Huk. Islam, vol. 21, no. 2, p. 164, Oct. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.69552/ar-risalah.v21i2.2101.
[5] M. Khasanah, “Tantangan Penerapan Teknologi Digital dalam Pendidikan Islam: Memanfaatkan Inovasi untuk Meningkatkan Mutu Pembelajaran [Challenges in the Implementation of Digital Technology in Islamic Education: Leveraging Innovation to Improve the Quality of Learning],” Lead. J. Manaj. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 282–289, (Indonesia), Nov. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.32939/ljmpi.v2i2.4240.
[6] Z. Alamin, Ihwan, Fathir, Dahlan, and Musmuliadin, “Integrasi Teknologi Pembelajaran Berbasis AI untuk Meningkatkan Keterlibatan Belajar Siswa di Madrasah Aliyah [Integration of AI-Based Learning Technology to Enhance Student Engagement in Madrasah Aliyah],” J. Pengabdi. Kpd. Masy., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 83–91, (Indonesia), May 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.63866/pemas.v2i2.87.
[7] M. I. Ismail, Evaluasi Pembelajaran. PT. RajaGrafindo Persada, 2021.
[8] J. G. Hedberg and T. C. Reeves, E-learning evaluation. 2015. doi: 10.4324/9https://doi.org/781315760933-28.
[9] H. Widodo, Evaluasi Pendidikan. Yogyakarta: UAD PRESS, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://books.google.co.id/books?id=sEFXEAAAQBAJ
[10] A. S. Munna and M. A. Kalam, “Teaching and learning process to enhance teaching effectiveness: literature review,” Int. J. Humanit. Innov., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–4, Feb. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.33750/ijhi.v4i1.102.
[11] M. Bakri, “Paradigma Islam tentang Pengembangan Pendidikan Islam [The Islamic Paradigm on the Development of Islamic Education ],” Islam. J. Stud. Keislam., vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 426, (Indonesia), Jan. 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.15642/islamica.2013.7.2.426-444.
[12] R. Sholihah, “Penggunaan Artificial Intelligence (Ai) Dalam Peningkatan Kualitas Pembelajaran Pendidikan Agama Islam [The Islamic Paradigm on the Development of Islamic Education ],” J. Jar. Penelit. Pengemb. Penerapan Inov. Pendidik., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 207–218, (Indonesia), Dec. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.59344/jarlitbang.v10i2.164.
[13] N. P. R. N. Asta, A. Aribowo, M. Saputra, N. Najmuddin, and P. Pahmi, “The Effect of Using Digital Learning Applications on Student Achievement in Elementary Schools,” J. Emerg. Technol. Educ., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 21–35, Feb. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.70177/jete.v2i1.735.
[14] L. Susanti, M. F. Al Khoiron, A. Nurhuda, and M. Al Fajri, “The Reality of Tarbiyah, Ta’lim, and Ta’dib in Islamic Education,” SUHUF, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 11–19, Nov. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.23917/suhuf.v35i2.22964.
[15] P. R. Brandao, “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Modern Society,” AI, vol. 6, no. 8, p. 190, Aug. 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6080190.
[16] D. Labhane, D. Indumathy, K. Palani, K. Lakshmi, and D. Vincent, “Big Data Analytics In Education: Transforming Student Learning And Institutional Practices,” Cah. MAGELLANES-NS, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 5214–5226, Sep. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.2632573.
[17] Daria Anisova, “Leveraging AI in Education: Exploring Big Data and Related Applications,” Svitla. Accessed: Oct. 23, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://svitla.com/blog/leveraging-ai-in-education-exploring-big-data-and-related-applications/
[18] N. Nur, Karakteristik Penelitian Kualitatif, vol. 1. 2024.
[19] M. Zed, Metode penelitian kepustakaan. Yayasan Pustaka Obor Indonesia, 2008.
[20] D. Sugiyono, “Metode penelitian kuantitatif dan R&D,” Bandung Alf., vol. 33, 2010.
[21] J. W. Creswell, “Research designs. Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches,” 2009.
[22] Imam Maulana Hidayat and Fitri Hilmiyati, “Konsep Evaluasi Pendidikan Dalam Perspektif Islam [The Concept of Educational Evaluation in the Islamic Perspective ],” J. Paris Langkis, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 309–318, (Indonesia), Dec. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.37304/paris.v5i1.17566.
[23] Nur Hadi Ihsan, Fachri Khoerudin, and A. Amir Reza, “Konsep Insan Kamil Al-Jilli Dan Tiga Elemen Sekularisme [The Concept of Insan Kamil by Al-Jilli and the Three Elements of Secularism ],” al-Afkar, J. Islam. Stud., vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 48–65, (Indonesia), Oct. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.31943/afkarjournal.v5i4.323.
[24] J. Syarif, N. Huda, and D. Hermina, “Integrasi Teknologi Dalam Evaluasi Pendidikan Islam,” J. Eval. Pendidik., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 101–111, Dec. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.21009/jep.v15i2.51060.
[25] W. Holmes, M. Bialik, and C. Fadel, “Artificial intelligence in education,” in Data ethics : building trust : how digital technologies can serve humanity, Globethics Publications, 2023, pp. 621–653. doi: https://doi.org/10.58863/20.500.12424/4276068.
[26] A. M. Vieriu and G. Petrea, “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on Students’ Academic Development,” Educ. Sci., vol. 15, no. 3, p. 343, Mar. 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15030343.
[27] P. Boddington, Towards a code of ethics for artificial intelligence. Springer, 2017.
[28] H. Fauzan, “Pemikiran Maqashid Syariah Al-Tahir Ibn Asyur [The Thought of Maqashid Shariah by Al-Tahir Ibn Ashur ],” al-Mawarid J. Syariah dan Huk., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 101–114, (Indonesia), Jul. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.20885/mawarid.vol5.iss1.art7.
[29] F. Karim, “Ihya Ulum-id-Din. ( Fazlul Karim, Trans.),” 1993, Ahmad Printing Corporation Karachi, Karachi. [Online]. Available: https://www.ghazali.org/books/ihya-v1.pdf
[30] A. Jobin, M. Ienca, and E. Vayena, “The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines,” Nat. Mach. Intell., vol. 1, no. 9, pp. 389–399, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-019-0088-2.
[31] N. Rahmi, “Sejarah dan Perkembangan Maqashid Syariah Serta Karya Ulama Tentangnya Sebelum Imam Syatibi [The History and Development of Maqashid Shariah and the Works of Scholars on It Before Imam al-Shatibi ],” J. AL-AHKAM, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 54–69, (Indonesia), Jul. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.15548/alahkam.v14i1.6143.
[32] N. Nursaid, Z. Smith, and A. Dhakal, “Development of Islamic economics and practices in Indonesia (2013-2023): opportunities and challenges,” Revenue J. Manag. Entrep., vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 89–101, Dec. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.61650/rjme.v1i1.323.
[33] N. Badri and B. Kusuma Riasti, “Pembuatan Media Pembelajaran Interaktif Pada SMK Negeri Tiga Jepara Dengan Materi Power Point 2007 [Creation of Interactive Learning Media at SMK Negeri 3 Jepara Using PowerPoint 2007 Materials ],” J. Speed-Sentra Penelit. Eng. dan Edukasi, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 73–78, (Indonesia), 2012, [Online]. Available: https://download.garuda.kemdikbud.go.id/article.php?article=268839&val=7112&title=Pembuatan Media Pembelajaran Interaktif Pada SMK Negeri Tiga Jepara Dengan Materi Power Point 2007
[34] B. Baharuddin, S. Sahidin, A. Kholilah, and F. A. Yanuar, “Pendidikan Islam dalam Era Kecerdasan Buatan: Membangun Peradaban Berbasis Etika dan Teknologi di Indonesia [Islamic Education in the Era of Artificial Intelligence: Building a Civilization Based on Ethics and Technology in Indonesia ],” JIIP - J. Ilm. Ilmu Pendidik., vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 3782–3791, (Indonesia), Apr. 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.54371/jiip.v8i4.7432.
[35] W. Kritandani, R. Aryani, and T. Rakasiwi, “A Report Review: Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Teaching and Learning,” Int. Res. Educ. J., vol. 6, no. 2, p. 245, Jun. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.17977/um043v6i2p245-253.
[36] W. Fitri, N. Nasril, S. N. Elvina, S. M. Basra, and R. A. Syifa, “Overview of character education design in senior high schools with boarding school in Indonesia,” COUNS-EDU Int. J. Couns. Educ., vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 35–47, Sep. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.23916/0020240949330.
[37] B. P. Woolf, Building Intelligent Interactive Tutors. Elsevier, 2009. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-373594-2.X0001-9.
[38] R. Nurhayati, T. Nur, S. P, N. Adillah, Agustina, and M. Urva, “Dinamika Pembelajaran Pendidikan Agama Islam Berbasis Artificial Intelligence (AI) [Dynamics of Islamic Religious Education Learning Based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) ],” Pros. Semin. Nas. Fak. Tarb. dan Ilmu Kegur. IAIM Sinjai, vol. 3, pp. 1–7, (Indonesia), Oct. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.47435/sentikjar.v3i0.3131.
[39] Amalia Dwi Fitriani, “Implementasi Teknologi AI (Artificial Intelligence) Pada Pembelajaran Pendidikan Agama Islam [Implementation of AI (Artificial Intelligence) Technology in Islamic Religious Education Learning ],” Wildan J. Pendidik. dan Pengajaran - STAI Bani Saleh, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 70–84, (Indonesia), Aug. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.54125/wildan.v3i2.47.
[40] H. Xuan, C. Guo, and J. Dai, “Do innovation and entrepreneurship vitality enhance university-industry collaboration? Roles of financial development and educational investment,” Int. Rev. Econ. Financ., vol. 103, p. 104412, Oct. 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iref.2025.104412.
[41] I. A. B. Arif, R. Ricky, and Y. K. Yahdi, “The Role of Islamic Religious Education in the Formation of the Character of the Millennial Generation,” Alhamdulillah J. Agama Islam, vol. 2, no. 02, pp. 33–38, Dec. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.54209/alhamdulillah.v2i02.304.
[42] R. Kasman and A. Madjid, “Opportunities and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence and Their Implications in Islamic Education,” Intiqad J. Agama dan Pendidik. Islam, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 1–13, Jun. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.30596/19308.
[43] H. Noor, Muhdi, G. N. Kartika, and Herlinawati, “Peluang Dan Tantangan Pendidikan Agama Islam Di Era Artificial Intelligence,” Sibatik J., vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 801–810, 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.54443/sibatik.v4i6.2813.
[44] S. K. Owusu, J. B. Zimpa, F. A. Atta, and M. Darling, “Evaluating the Impact of AI-Personalized Learning Systems in Higher Education; Examining how They Affect Academic Performance across Different Age Groups at Kumasi Technical University,” J. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. Neural Netw., vol. 29, no. 45, pp. 19–29, Aug. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.55529/jaimlnn.45.19.29.
[45] M. Theodoratou and M. Argyrides, “Neuropsychological Insights into Coping Strategies: Integrating Theory and Practice in Clinical and Therapeutic Contexts,” Psychiatry Int., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 53–73, Feb. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/psychiatryint5010005.
[46] F. Raza, AI in Education: Personalized Learning and Adaptive Assessment. 2023. doi: https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.24796.77446.
[47] M. A. Salim and R. B. Aditya, “Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Islamic Education: Trends, Methods, and Challenges in the Digital Era,” J. Mod. Islam. Stud. Civiliz., vol. 3, no. 01, pp. 74–89, Jan. 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.59653/jmisc.v3i01.1368.
[48] K. I. Vorobyeva, S. Belous, N. V. Savchenko, L. M. Smirnova, S. A. Nikitina, and S. P. Zhdanov, “Personalized learning through AI: Pedagogical approaches and critical insights,” Contemp. Educ. Technol., vol. 17, no. 2, p. 574, Apr. 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.30935/cedtech/16108.
[49] Y. Guo and Y. Wang, “Exploring the effects of artificial intelligence application on EFL students’ academic engagement and emotional experiences: A mixed-methods study,” Eur. J. Educ., pp. 1–15, Oct. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.111/ejed.12812.
[50] N. Nurhayati, “Tantangan dan Peluang Guru Pendidikan Agama Islam di Era Globalisasi,” J. Ilm. Iqra’, vol. 7, no. 1, Feb. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.30984/jii.v7i1.605.
[51] H. Ying, A. Pranolo, Z. Nuryana, and A. I. Syafitri, “Emerging trends in the evolution of neuropsychology and artificial intelligence: A comprehensive analysis,” Telemat. Informatics Reports, vol. 16, p. 100171, Dec. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teler.2024.100171.
[52] O. A. Meyer, M. K. Omdahl, and G. Makransky, “Investigating the effect of pre-training when learning through immersive virtual reality and video: A media and methods experiment,” Comput. Educ., vol. 140, p. 103603, Oct. 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103603.
[53] C. Halkiopoulos and E. Gkintoni, “Leveraging AI in E-Learning: Personalized Learning and Adaptive Assessment through Cognitive Neuropsychology—A Systematic Analysis,” Electronics, vol. 13, no. 18, p. 3762, Sep. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183762.
[54] M. A. Abdullah, Islamic studies di perguruan tinggi: Pendekatan integratif-interkonektif. Pustaka Pelajar, 2006.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Awalia Rina Rahmawati, Risfita Wulandari, Maulida Ade Suryani Sadaruddin, Triono Ali Mustofa, Hamdan Chedimae

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


















