Effective Pedagogical Approaches in Fostering Student Responsibility: A Qualitative Study at an Islamic Boarding School in Indonesia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/suhuf.v37i1.10123Keywords:
Responsibility improvement, Discipline in school, Islamic boarding school, Character building, Student responsibility attitudesAbstract
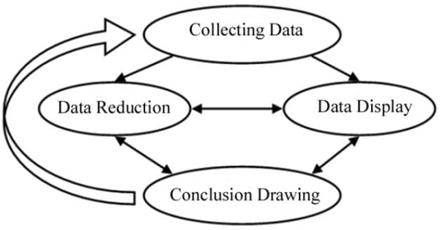
Student responsibility attitudes are important in shaping character and discipline in school. Teachers play a big role in fostering this attitude through the right approach. At SMA Terpadu Islam Hasanka Boarding School Palangka Raya, the teacher's approach is the key to increasing student responsibility for regulations in school activities. This study aims to describe the teacher's approach in improving students' attitude of responsibility at SMA Terpadu Islam Hasanka Boarding School, Palangka Raya. This research uses a qualitative method. The subjects of this study are two teachers, consisting of 1 teacher of Moral Faith and one teacher of Islamic Religious Education. Meanwhile, the informants in this study are the principal, vice principal for student affairs, and students. Data collection techniques include observation, interviews, and documentation. Data analysis is carried out qualitatively through four stages: data collection, data reduction, data presentation, and drawing a conclusion. The results of this study show that students of Hasanka Boarding School Palangka Raya Integrated Islamic High School generally have an attitude of responsibility towards school regulations, both in learning activities and outside of learning. In the classroom, students tend to complete assignments on time, be active, and be ready to learn, although some are still inconsistent. Outside of the classroom, students are quite disciplined in participating in activities such as congregational prayers, Qur'an halaqah, ceremonies, and extracurricular activities, although some have not fully complied with the rules of attributes. Teachers use persuasive, communicative, and personal approaches through example and guidance to foster student responsibility. This approach has proven to be effective in shaping students' attitudes of discipline and compliance with school rules.
Downloads
References
[1] F. Indah Merdisa, I. Moeis, A. Ananda, and M. Montessori, “Upaya Guru Terhadap Penanaman Karakter Tanggung Jawab dan Kepedulian dalam Konteks Civic Virtue Pada Pembelajaran PPKN,” J. Pendidik. Tambusai, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 9768–9777, Feb. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.31004/jptam.v8i1.13862.
[2] T. Thoriquttyas and N. Rohmawati, “How Far Artificial Intelligence influenced Mu’allim, Murabbi, and Mudarris? Transhumanism and Diffusion of Innovation Theory’s Perspective,” Suhuf Int. J. Islam. Stud., vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 139–154, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.23917/suhuf.v36i2.6302.
[3] I. Setiawan, “Boarding School Sebagai Solusi Penguatan Karakter Religius Siswa [Boarding Schools as a Means of Strengthening Students’ Religious Characte],” J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 66–85, (in Indonesia), 2021, [Online]. Available: https://journal.unipdu.ac.id/index.php/jpi/article/view/2734
[4] L. Lesnida, “Analisis Kompetensi Guru Sejarah Kebudayaan Islam (SKI) dalam Melaksanakan Pembelajaran Kurikulum 2013 Berbasis Sistem Kredit Semester di MAN 2 Model Medan [An Analysis of Islamic Cultural History (SKI) Teacher Competence in Implementing the 2013 Curricul,” Universitas Islam Negeri Sumatera Utara Medan, 2022. [Online]. Available: http://repository.uinsu.ac.id/20279/
[5] A. S. Salsabilah, D. A. Dewi, and Y. F. Furnamasari, “Peran guru dalam mewujudkan pendidikan karakter [The role of teachers in realizing character education.],” J. Pendidik. Tambusai, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 7158–7163, (in Indonesia), 2021, [Online]. Available: https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/96076891/483330066-libre.pdf?1671544835=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DPeran_Guru_Dalam_Mewujudkan_Pendidikan_K.pdf&Expires=1747623781&Signature=gYe8iONQVlXb5wBqJPXoKVMB6w19K9one1W2qRlnkabEXgeCQd2n
[6] I. M. Ulfi, “Peran Guru Akidah Akhlak dalam Membina Akhlak Peserta Didik di Kelas IX A MTs Negeri 1 Cilacap, Kabupaten Cilacap, Provinsi Jawa Tengah. [The Role of Aqidah Akhlak Teachers in Fostering the Morals of Students in Class IX A at MTs Negeri 1 Cilacap, Cilacap,” UNISAN, vol. 03, no. 07, pp. 635–645, (in Indonesia), 2024, [Online]. Available: https://journal.an-nur.ac.id/index.php/unisanjournal
[7] A. F. A. Ihsani and N. Febriyanti, “Pendidikan Karakter Melalui Islamic Boarding School di SMP Plus Ar-Rahmat Bojonegoro [Character Education Through Islamic Boarding School at SMP Plus Ar-Rahmat Bojonegoro.],” PAKAR Pendidik., vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 45–56, (in Indonesia), 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.24036/pakar.v18i2.187.
[8] F. Manurung, C. V. R. Sinaga, and E. Thesalonika, “Analisis Peran Guru untuk Membentuk Karakter Siswa pada Pembelajaran Tematik di Kelas V SDN 091556 Nagojor. [Analysis of the Role of Teachers in Shaping Student Character through Thematic Learning in Class V at SDN 091556 Nagojor. ],” Pedagog. J. Pedagog. dan Din. Pendidik., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 146–153, (in Indonesia), 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.30598/pedagogikavol10issue2page146-153.
[9] J. Topulu and L. K. Sianipar, “Upaya meningkatkan sikap tanggung jawab siswa kelas X IPA pada pembelajaran fisika dengan menggunakan penilaian antar teman [Efforts to Improve the Responsibility Attitude of Class X IPA Students in Physics Learning by Using Peer Assessment. ],” J. Pengemb. Pembelajaran dan Ris. Fis., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 84–91, (in Indonesia), 2023, [Online]. Available: https://ojs.uph.edu/index.php/JPPRF/article/view/6771
[10] R. Rohmadi and T. Yulindaputri, “Pengaruh Kompetensi Kepribadian Guru Terhadap Karakter Tanggung Jawab Siswa [The Influence of Teacher Personality Competence on Students’ Responsibility Character. ],” TSAQAFATUNA J. Ilmu Pendidik. Islam, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 84–95, (in Indonesia), 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.54213/tsaqafatuna.v5i2.204.
[11] O. Camerino, A. Valero-Valenzuela, Q. Prat, D. Manzano Sánchez, and M. Castañer, “Optimizing education: A mixed methods approach oriented to teaching personal and social responsibility (TPSR),” Front. Psychol., vol. 10, p. 440169, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01439.
[12] E. Z. Ariyani, I. W. Lasmawan, and I. P. W. M. Sujana, “Peran Guru dalam Penanaman Karakter Tanggung Jawab Melalui Pembelajaran Pendidikan Pancasila [The Role of Teachers in Instilling the Character of Responsibility Through Pancasila Education Learning. ],” EDU Soc. J. PENDIDIKAN, ILMU Sos. DAN Pengabdi. Kpd. Masy., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 468–472, (in Indonesia), 2025, doi: https://doi.org/10.56832/edu.v5i1.818.
[13] S. Hadi and N. Nurhaidah, “Meningkatkan Tanggung Jawab Belajar Siswa di Rumah Selama Covid 19 melalui Pendekatan Konseling Kelompok Realita:(Studi Kasus Siswa Kelas X1 SMA Negeri 2 Lambu) [Improving Student Learning Responsibility at Home During COVID-19 Through Reality Group Couns,” J. Bimbing. Dan Konseling Islam, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 112–130, (in Indonesia), 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.29080/jbki.2021.11.1.112-130.
[14] M. B. Miles, A. M. Huberman, and J. Saldana, Qualitative Data Analysis: A Methods Sourcebook., vol. 11, no. 1. 2019. [Online]. Available: http://scioteca.caf.com/bitstream/handle/123456789/1091/RED2017-Eng-8ene.pdf?sequence=12&isAllowed=y%0Ahttp://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2008.06.005%0Ahttps://www.researchgate.net/publication/305320484_SISTEM_PEMBETUNGAN_TERPUSAT_STRATEGI_MELESTARI
[15] M. Masluhah, K. R. Afifah, and M. Salik, “Pemikiran Muhammad Iqbal Tentang Pendidikan Karakter Dan Relevansinya Dengan Era Disrupsi [Muhammad Iqbal’s Thought on Character Education and Its Relevance to the Disruption Era],” Ta’allum J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 317–338, (in Indonesia), 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.21274/taalum.2021.9.2.317-338.
[16] E. Triyani, A. Busyairi, and I. Ansori, “Penanaman Sikap Tanggung Jawab Melalui Pembiasaan Apel Penguatan Pendidikan Karakter Siswa Kelas Iii [Instilling a Sense of Responsibility Through the Habit of Character Education Strengthening Flag Ceremony for 3rd Grade Students. ],” J. Kreat. J. Kependidikan Dasar, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 150–154, (in Indonesia), 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.15294/kreatif.v10i2.23608.
[17] S. Siswati, C. B. Utomo, and A. Muntholib, “Implementasi Pendidikan Karakter dalam Membentuk Sikap dan Perilaku Sosial Peserta Didik Melalui Pembelajaran Sejarah di SMA PGRI 1 Pati Tahun Pelajaran 2017/2018 [The Implementation of Character Education in Shaping Students’ Attitudes and Social Behavio,” Indones. J. Hist. Educ., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 1–13, (in Indonesia), 2018, doi: https://doaj.org/article/00a9902587ec405e9bc3b30adfbf276c.
[18] B. Kairienė, “The duties of a pupil: The implementation problem,” Pedagogika/Pedagogy, vol. 126, no. 2, pp. 130–142, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.15823/p.2017.24.
[19] N. P. Wardman, “‘So you can’t blame us then?’: gendered discourses of masculine irresponsibility as biologically determined and peer-pressured in upper-primary school contexts,” Gend. Educ., vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 796–812, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09540253.2016.1166178.
[20] M. Warne, Å. Svensson, L. Tirén, and E. Wall, “On time: a qualitative study of Swedish students’, parents’ and teachers’ views on school attendance, with a focus on tardiness,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, vol. 17, no. 4, p. 1430, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041430.
[21] G. S. Öztaş, G. Akçapınar, M. N. Hasnine, and E. Er, “Understanding High and Low-Performing Students’ Time Management Strategies through Assignment Submission Patterns,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 246, pp. 3503–3511, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2024.09.206.
[22] M. A. Gottfried, “The influence of tardy classmates on students’ socio-emotional outcomes,” Teach. Coll. Rec., vol. 116, no. 3, pp. 1–35, 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/016146811411600305.
[23] S. Anzorova, S. Niyazbekova, E. Torbik, M. Krupchak, and G. Zhumadilova, “ENSURING ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY IN THE FIELD OF EDUCATION IN MODERN CONDITIONS [Ensuring Environmental Safety in the Field of Education in Modern Conditions. ],” Reliab. Theory Appl., vol. 19, no. SI 6 (81), pp. 1660–1664, 2024, [Online]. Available: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/ensuring-environmental-safety-in-the-field-of-education-in-modern-conditions
[24] V. Gupta and S. Anand, “Water, sanitation, and hygiene facilities: enabling or impeding handwashing? An assessment of a primary school infrastructure in Palwal, India,” J. Water, Sanit. Hyg. Dev., vol. 13, no. 9, pp. 723–734, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.2166/washdev.2023.136.
[25] M. K. Sharma, R. Adhikari, E. van Tejlingen, B. Devkota, and S. P. Khanal, “Improved water, Sanitation and Hygiene Facilities at School and their effect on educational achievement in basic level students in Nepal,” Int. J. Heal. Promot. Educ., pp. 1–12, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/14635240.2024.2314459.
[26] F. Sultana, S. M. Khan, M. Rahman, P. J. Winch, S. P. Luby, and L. Unicomb, “Sustaining an elementary school-based hygiene intervention in Bangladesh by forming ‘hygiene committees’: A pilot study,” J. Water, Sanit. Hyg. Dev., vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 749–763, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.2166/washdev.2023.191.
[27] J. A. Simmons, “An environmental science approach to service-learning in biology,” in Life, Learning, and Community, Routledge, 2023, pp. 25–30. [Online]. Available: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781003445753-4/environmental-science-approach-service-learning-biology-jeffrey-simmons
[28] M. Mahbub and Y. S. Pambudi, “An analysis on the effect of school policy towards teachers’ participation in cleanliness program at schools receiving adiwiyata award in Surakarta city, Indonesia,” Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol., vol. 29, no. 5, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://eprints.iain-surakarta.ac.id/6226/
[29] N. Huda, B. S. Widodo, and M. Aseri, “Strategies for Strengthening Character Education in Islamic Boarding Schools Through Extracurricular Activities,” Munaddhomah J. Manaj. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 354–366, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.31538/munaddhomah.v5i3.1397.
[30] N. Fitriani, S. Anam, A. Maulana, and S. Sebgag, “Building Literacy of Early Age Students’ Language; Teacher Managerial Competence and Legal-Rational Authority of Boarding School Leaders,” Munaddhomah J. Manaj. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 41–50, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.31538/munaddhomah.v5i1.707.
[31] F. A. Orji and J. Vassileva, “Predicting the persuasiveness of influence strategies from student online learning behaviour using machine learning methods,” J. Educ. Comput. Res., vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 1410–1429, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/07356331231178873.
[32] A. Khatter, K. Thalaachawr, and M. Blyth, “Student engagement and fostering ownership of learning,” J. Appl. Learn. Teach., vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 291–302, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2024.7.1.38.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Lusi Kemala Sari , Zainap Hartati , Yuliani Khalfiah , Yusrin Halid

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


















