Effectiveness of the Talaqqi Method in Children's Scripture Memorization within the SDGs Framework: A Case Study in Indonesian Elementary Schools
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v25i03.8667Keywords:
holy scripture memorization, talaqqi method, tone technique, children, sdgsAbstract
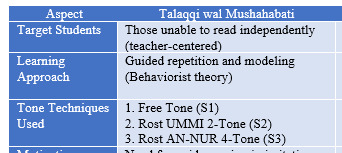
Objective: This study aims to describe the methods of memorizing the Holy Scripture, identify similarities and differences in implementation, and assess the effectiveness of these methods in elementary school settings. Grounded in a case study design, the research was conducted in three Indonesian elementary schools that actively implement Holy Scripture memorization programs. Theoretical framework: The theoretical framework guiding this study integrates behavioral and humanistic learning theories, which emphasize structured repetition, teacher modeling, and personalized emotional engagement. Literature review: The literature on Quranic memorization highlights the importance of oral transmission and teacher-student interaction, particularly through the talaqqi method. However, few studies have provided a comparative analysis across different schools using this method within the broader context of child education and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Methods: Data were collected from teachers, students, and parents through interviews, observations, and document analysis. The data were then processed using the descriptive-interpretative model proposed by Miles, Huberman, and Saldana, involving data reduction, display, and conclusion drawing. Results: The findings reveal three main outcomes: (1) all schools apply two core memorization methods—talaqqi wal mushahabati and talaqqi wal istiqlali—each utilizing three tone techniques: free tone, UMMI two-tone rost, and AN-NUR four-tone rost; (2) all schools shared a common approach grounded in behaviorist-humanist integration; and (3) differences were observed in tone applications, which influence students’ engagement and retention. Implications: The implication of this study suggests that the talaqqi method is highly effective for elementary-level students, as it aligns with their psychological development and supports consistent memorization outcomes. Novelty: The novelty of this research lies in its integration of traditional Islamic pedagogy—specifically the talaqqi method—with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), offering a unique framework for promoting inclusive, equitable, and quality religious education for children in elementary schools within a modern global development context.
References
[1] S. Hidayat and A. Ashiddiqi, “Metode I‘Rāb Al-Qur’an Dan Konvensional Sebagai Pembelajaran Bahasa Arab Bagi Non Arab Di Ponpes Al Madinah Boyolali,” Profetika J. Stud. Islam, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 123–135, May 2019, https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v19i2.8119.
[2] A. K. N. dan A. K. Pasmadi, “Implementasi Metode Al-Qosimi Dalam Menghafal Al-Qur’an Anak Usia Dini di Taud Al-Bayyan Krajan Kulon Kaliwungu Kendal,” J. Didakta Islam., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 61–85, 2022.
[3] T. Rahayu, J. Subando, M. Fatimah, A. F. Haq Rumaf, and A. K. Hussain Solihu, “Optimization of Teaching Strategies of Tahfidz Teachers To Improve the Quality and Quantity of Student’s Memorization of the Qur’an,” Profetika J. Stud. Islam, vol. 24, no. 02, pp. 259–268, 2023, https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v24i02.1976.
[4] Muthoifin et al., “An Interfaith Perspective on Multicultural Education for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs),” J. Lifestyle SDG’S Rev., vol. 4, no. 3, p. e01720, Sep. 2024, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v4.n03.pe01720.
[5] M. Sa’adah and U. Hasanah, “The Common Goals of BAZNAS’ Zakat and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) according to Maqasid Al-Sharia Perspective,” Al-Ihkam J. Huk. dan Pranata Sos., vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 302–326, 2021, https://doi.org/10.19105/AL-LHKAM.V16I2.4990.
[6] S. Anwar, S. Ali, A. Labib, and yasinta Rahmawati, “Penerapan Metode Muri-Q Pada Hafalan Al-Qur’an di Rumah Tahfizh Al-Furqon Pringsewu,” Ensiklopedia J. Pendidik. dan Inov. Pembelajaran Saburai, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 8–14, 2021, https://doi.org/10.24967/esp.v1i01.1351.
[7] I. Fauji, E. F. Fahyuni, A. Muhid, and Z. N. Fahmawati, “Implementing Child-Friendly Teaching Methods To Improve Qur’an Reading Ability,” J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 69–78, 2020, https://doi.org/10.15575/jpi.v6i1.8078.
[8] N. R. R. Rashid, I. Venkat, F. Damanhoori, N. Mustaffa, W. Husain, and A. T. Khader, “Towards Automating the Evaluation of Holy Quran Recitations: A Pattern Recognition Perspective,” in Proceedings - 2013 Taibah University International Conference on Advances in Information Technology for the Holy Quran and Its Sciences, NOORIC 2013, School of Computer Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Pulau Pinang, 11800, Malaysia: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2015, pp. 424–428. https://doi.org/10.1109/NOORIC.2013.88.
[9] S. Suwardi, S. Anif, W. Waston, and Y. O. Owa-Onire Uthman, “Tasmi’ Bil Ghoib Assessment Model of the Qur’an for Children: Case Study in Multicity,” Profetika J. Stud. Islam, vol. 24, no. 02, pp. 343–353, 2024, https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v24i02.1696.
[10] D. Baharuddin, “Tas’ir dalam Perespektif Maqashid Al-Syariah,” Fak. Syariah dan Ekon. Islam IAIN Ambon, 2017.
[11] B. M. Sugiyanto, A. Anshori, and M. Muthoifin, “Implementasi Pembelajaran Al-Qur’an Metode Littaqwa Di Sdit Nur Hidayah Surakarta Dan Metode Karimah Di Mi Nurul Karim Karanganyar Tahun Ajaran 2019/2020,” Profetika J. Stud. Islam, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 86–95, 2020, https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v21i1.11062.
[12] S. Z. Nisa, “Pembelajaran tahfidzul qur’an melalui metode Pakistani roudlotul qur’an cilacap,” p. 66, 2022.
[13] M. Nur, R. Maksum, N. S. B. Elmanaya, and M. Gamal, “Conception and Implementation of One Day One Verse at PMI Dea Malela,” vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 88–96, 2023, https://doi.org/10.61455/sicopus.v1i02.11.
[14] T. Sanyoto, N. Fadli, R. Irfan Rosyadi, and M. Muthoifin, “Implementation of Tawhid-Based Integral Education to Improve and Strengthen Hidayatullah Basic Education,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult., vol. 1, no. 01, pp. 30–41, 2023, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v1i01.31.
[15] A. F. Bintoro, I. Rosyadi, and A. Alqahoom, “Muri-Q Method for Learning to Read, Memorize and Tahsin Al-Qur ’ an : A New Perspective,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult., vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 172–181, 2023, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v1i03.72.
[16] J. Lobbestael and A. Arntz, “Emotional hyperreactivity in response to childhood abuse by primary caregivers in patients with borderline personality disorder,” J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry, vol. 48, pp. 125–132, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2015.03.005.
[17] M. Ali et al., “Tracking Education Transformation Towards Sustainable Development Goals: a Bibliometric Review on the Influence of Socioeconomic Factors in the Education Ecosystem,” J. Lifestyle SDG’S Rev., vol. 5, no. 1, 2025, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v5.n01.pe03295.
[18] D. M. Putri, “The Impact of Social Inequality on Educational Quality in Indonesia: Challenges and Policy Recommendations,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult., vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 43–56, 2025, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v3i01.248.
[19] N. U. Isaac, “Early Childhood Care Education ( ECCE ) and National Security,” Solo Int. Collab. Publ. Soc. Sci. Humanit., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 282–293, 2024, https://doi.org/10.61455/sicopus.v2i03.203.
[20] M. Abuzar, L. Yafi, I. Afiyah, and I. Amelia, “Strategy and Implementation of Islamic Personality Development through the Internalization of Religious Values at Madrasah Aliyah Dakka, Bangladesh,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 167–180, 2024, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v2i02.201.
[21] A. Haironi and Muthoifin, “Implementasi Metode Taḥfīẓul Qur’an ‘Sabaq, Sabqi, Manzil’ Di Marhalah Mutawasithah Dan Tsanawiyah Putri Pondok Pesantren Imam Bukhari Tahun Pelajaran 2010-2014,” UMS, 2016.
[22] M. Muthoifin, I. Amelia, and A. B. Eprahim Ali, “Islamic accounting: Ethics and contextualization of recording in Muamalah transactions,” Multidiscip. Rev., vol. 7, no. 8, 2024, https://doi.org/10.31893/multirev.2024132.
[23] S. Trihariyanto, E. Supriyanto, M. Muthoifin, and Z. ’Uyun, “Strategi Pembelajaran Inovatif Pendidikan Agama Islam Dengan Media Powerpoint Dalam Meningkatkan Mutu Pendidikan Di Sdit Muhammadiyah Sinar Fajar Cawas Dan Sd Muhammadiyah Pk Bayat,” Profetika J. Stud. Islam, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 109–120, 2020, https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v21i1.11653.
[24] M. Apriantoro, A. Suryaningsih, and M. Muthoifin, “Bibliometric Analysis of Research Development of Economic Dispute Settlement,” EUDL Eur. Union Digit. Libr., 2023, https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.19-10-2022.2329068.
[25] M. Muthoifin, “The phenomenon of the rise of online transactions : A case study Tokopedia. com and Bukalapak. com,” Multidiscip. Rev., 2024, https://doi.org/10.31893/multirev.2024133.
[26] S. N. Asia, M. Muthoifin, M. S. Apriantoro, A. Amrin, S. Sya’roni, and R. Irfan Rosyadi, “Analysis of Islamic Economic Law on Fishing Pool Business in Indonesia,” Demak Univers. J. Islam Sharia, vol. 1, no. 01, pp. 01–09, 2023, https://doi.org/10.61455/deujis.v1i01.7.
[27] S. Rochanah, A. R. Ridha, and A. Nirwana, “Development Teacher ’ s Performance of Construct Reliability and Avarice Variance Extracted Measurement Instruments of Certified Islamic Education Teacher ’ s,” Int. J. Relig., vol. 3538, no. 10, pp. 3828–3849, 2024, https://doi.org/10.61707/xzjvmb82.
[28] A. N. Andri Nirwana, Mahmudulhassan, F. D. Marshal, Muthoifin, and N. Fadli, “Human Rights and Social Justice in Quranic Contexts: A Global Trend,” Leg. J. Ilm. Huk., vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 453–471, 2024, https://doi.org/10.22219/ljih.v32i2.35088.
[29] E. B. G. Suwoko, Waston, Bambang Setiaji, Muthoifin, Huda Kurnia Maulana, “Family Education To Improve The Quality Of Human Resources And Sustainable Development In Samarinda,” Rev. Gestão Soc. e Ambient., vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 1–19, 2024, https://doi.org/10.24857/rgsa.v18n6-011.
[30] S. Uddin Ahmed Khondoker, “Understanding the Essence of Islamic Education: Investigating Meaning, Essence, and Knowledge Sources,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult. E, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 27–36, 2024, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v2i01.115.
[31] M. M. N. Muthoifin, “Outsourcing System in View of Islamic Law : Study on Employees at Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Social Science (ICONETOS 2020), Atlantis Press, 2021, pp. 91–95, https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.210421.015.
[32] N. Muthoifin, “Mengungkap Isi Pendidikan Islam Perspektif Al- Qur ’ an Surat Al -Ashr Ayat 1-3,” in The 7th University Research Colloqium 2018 STIKES, 2018, pp. 206–218.
[33] H. Haerul, I. Iqra, B. M. A. Muhammad Hamad Al-Nil, and R. Mahmoud ELSakhawy, “The Role of the Teacher in Instilling Tauhid-Based Education in Students in the Perspective of the Qur’an,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult., vol. 1, no. 01, pp. 50–57, 2023, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v1i01.35.
[34] U. A. Maidugu, A. Ahmad, and A. Sadeeq, “Islam and Morality : The Teachings of Al-Ihsan from the Qur ’ an and Hadith and its Effects on Muslim Ummah,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 181–194, 2024, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v2i03.199.
[35] A. Mahmud, “Multicultural Democratic and Tolerant : Qur ’ anic Perspectives and Islamic Education at the Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult., vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 205–220, 2024, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v1i03.82.
[36] Y. M. Fauzin and M. T. Affandi, “Professional Teachers and Bright Students in the View of the Qur’an and Prophetic Education,” Solo Univers. J. …, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 182–194, 2023, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v1i03.71
[37] M. Ari Kurniawati, “Effective Qur ’ an Learning Strategies to Strengthen Children s Memorization with Zahrawain Method,” Solo Univers. J. Islam. Educ. Multicult., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 37–48, 2024, https://doi.org/10.61455/sujiem.v2i01.104.
[38] A. Rohman, B. Mubaroka, and Q. Butlam, “Methodology of Tafseer Al-Qurtubi: Sources, Styles and Manhaj,” QiST J. Quran Tafseer Stud., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 180–202, 2023, https://doi.org/10.23917/qist.v2i2.1451.
[39] H. A. Said and N. Ferdiani, “Methodology of the Qur ’ an and Its Tafsir By the Ministry,” Stud. Islam., vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 1–29, 2022, https://doi.org/10.24239/jsi.v20i1.689.
[40] A.-S. Fathullah Al Haq Muhamad Asni, “Methodology Analysis In The Unification Of Usul Al-Fiqh Methods,” Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci., vol. 7, no. 7, p. 262, 2017, https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarbss/v7-i7/3093.
[41] A. Mahmud and H. Ilyas, “Islam and Tolerance Education for the Sustainable Development Goals ( SDGs ),” Profetika J. Stud. Islam, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 387–404, 2024, https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v25i02.8510.
[42] I. Busti and R. Saputra, “The Axiological Foundations of Knowledge : A Comparison of Western and Islamic Perspectives and Their Integration in Supporting the Achievement of SDGs,” Profetika J. Stud. Islam, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 421–432, 2024, https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v25i02.8528.
[43] Muthoifin, N. Yaman, I. Rosyadi, Isman, Masithoh, and I. Afiyah, “Fostering The Ummah ’ S Economy Through The Stock-investment System : The Views Of The Mui For Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs),” J. Lifestyle SDG’S Rev., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–19, 2024, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v4.n00.pe01685.
[44] S. Mahendra, E. Kubota, A. N. F. MS, T. Dwiyanti, and F. I. Syafirah, “Policy for Improving Digital Literature in Indonesia SDGs Based,” Proc. Ser. Phys. Form. Sci., vol. 3, pp. 18–24, 2022, https://doi.org/10.30595/pspfs.v3i.259.
[45] E. H. Mohamed and W. H. El-Behaidy, “An Ensemble Multi-label Themes-Based Classification for Holy Qur’an Verses Using Word2Vec Embedding,” Arab. J. Sci. Eng., vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 3519–3529, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05184-0.
[46] I. Nursidik and E. Komarudin, “Methodology of the Book of the Holy Qur ’ an and The Massage of Qur ’ an : A Comparative Study of the Book of Tafsir by A . Yusuf Ali and Muhammad Asad,” Mashadiruna J. Ilmu Al-Qur’an dan Tfasir, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 11–18, 2023, https://doi.org/10.15575/mjiat.v2i1.20129.
[47] A. Komariah and E. Rochmawati, “The Effect of Listening to the Holy Qur’an and a Back Massage on Fatigue and Quality of Life for Participants Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Quasi-Experimental Study,” J. Relig. Health, vol. 62, no. 6, pp. 4334–4346, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-022-01664-9.
[48] L. M. Alqaryouti, “Euphemism in the Translations of Surah Al Nisa ’ a in the Holy Quran,” vol. 23, pp. 44–50, 2016.
[49] M. S. Farid, “Revisiting the aims of Catholic missionary education in Bangladesh: the case of Holy Cross Congregation,” Int. Stud. Cathol. Educ., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 148–166, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1080/19422539.2022.2146390.
[50] A. Zangoueinezhad and A. Moshabaki, “Human resource management based on the index of Islamic human development: The Holy Quran’s approach,” Int. J. Soc. Econ., vol. 38, no. 12, pp. 962–972, 2011, https://doi.org/10.1108/03068291111176329.
[51] A. O. Adeleke, N. A. Samsudin, A. Mustapha, and N. M. Nawi, “A group-based feature selection approach to improve classification of Holy Quran verses,” in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, A. J.H., G. R., D. M.M., and N. N.M., Eds., Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Parit Raja, Batu Pahat, 86400, Johor, Malaysia: Springer Verlag, 2018, pp. 282–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72550-5_28.
[52] A. Fatah, “Dimensi Keberhasilan Pendidikan Islam Program Tahfidz Al-Qur’an,” Edukasia J. Penelit. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 335–356, 2014, https://doi.org/10.21043/edukasia.v9i2.779.
[53] P. Studi, M. Pendidikan, A. Islam, S. Pascasarjana, and U. M. Surakarta, “Implementasi Program Tahfidzul Qur ’ an Dengan Metode Tabarak Dan Metode Zahrawain,” 2021.
[54] M. M. A. Sholeh, Waston, A. Nirwana, and M. Mahmudulhassan, “The Reasons of Lifelong Education for the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): The Islamic Epistemology Perspective,” J. Lifestyle SDGs Rev., vol. 5, no. 2, p. e02988, Nov. 2024, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v5.n02.pe02988.
[55] A. Viviani, “Inclusion and education for sustainable development: The experience of the University of Siena,” Perspect. Educ., vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 132–145, 2022, https://doi.org/10.18820/2519593X/pie.v40.i3.9.
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Suwardi, Endang Fauziyati, Syamsul Hidayat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.












