Strengthening IRE Teacher Competencies for Character Education and SDGs Realization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v26i03.14854Keywords:
ire, teachers' competency, character education, challenges, sdgsAbstract
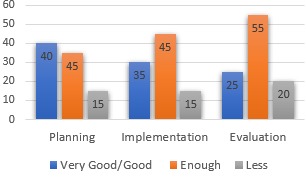
Objective: This study aims to examine the role of Islamic Religious Education (IRE) teachers' competencies in integrating character education to support the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 4 (Quality Education) and SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions), in Ogan Ilir Regency. Theoretical framework: The study draws on Lickona’s character education theory (cognitive, affective, conative dimensions) and Muslich’s teacher competency framework (pedagogic, professional, personality, social aspects) for integrating character education into IRE learning. Literature review: Previous research underscores the importance of character education, its integration challenges, and the essential role of IRE teachers as moral role models, though competencies in character education vary. Methods: A mixed-methods approach was used, involving quantitative (competency tests) and qualitative (interviews, observations, document analysis) data from 70 IRE teachers in Ogan Ilir Regency. Data were analyzed with SPSS and thematic coding. Results: The study found that IRE teachers' competencies in planning and implementing character education were generally adequate, but significant gaps existed in the evaluation of character education. Most teachers demonstrated sufficient competencies in integrating character values during planning and implementation phases, but the evaluation of character education was weak, with limited use of standardized assessment tools. Implications: The study highlights that IRE teachers face challenges such as limited time, resources, and training. Novelty: This research is among the first to analyze IRE teachers' competencies in integrating character education in Ogan Ilir Regency, offering new insights into how teacher competencies support sustainable development goals in education.
References
[1] M. Shaleh, Tobroni, Mundir, and Umiarso, “Development of a Holistic-Integrative Islamic Religious Education Curriculum in an Integrated Islamic School,” Eurasian J. Educ. Res., vol. 2024, no. 113, pp. 227–241, 2024, https://doi.org/10.14689/ejer.2024.113.13.
[2] M. Rahmat and M. W. B. H. M. Yahya, “The Impact of Inclusive Islamic Education Teaching Materials Model on Religious Tolerance of Indonesian Students,” Int. J. Instr., vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 347–364, 2022, https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2022.15120a.
[3] N. Y. Muthoifin, I. R. Isman, and M. Ishmah Afiyah, “Fostering The Ummah’s Economy Through The Stockinvestment System : The Views Of The Mui For Sustainable Development Goals ( SDGS ),” J. Lifestyle SDGs Rev., vol. 4, pp. 1–19, 2024, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v4.n00.pe01685.
[4] G. Maksum et al., “Religious values as foundations of education: Insights from teachers’ perspectives,” Res. J. Adv. Humanit., vol. 6, no. 3, 2025, https://doi.org/10.58256/tb06n075.
[5] Sukiman, U. Baroroh, A. S. Nugraheni, and A. Sama-Alee, “Innovation of the Internship Program and Its Implications for the Soft Skill Development of Prospective Islamic Religious Education Teachers at Sunan Kalijaga State Islamic University, Yogyakarta,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 165–185, 2024, https://doi.org/10.14421/jIRE.v21i1.7583.
[6] M. A. Rokhimawan, M. G. Aulia, I. Rifai, and S. L. Azahro, “The Correlation between Understanding the Independent Learning – Kampus Merdeka (MBKM) Curriculum with the Fulfillment of IRE Student Learning Rights,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 279–292, 2023, https://doi.org/10.14421/jIRE.v20i2.8049.
[7] J. Barus, Husaini, Ja’far, and U. M. Noor, “Islamic Higher Education In Post-Conflict Aceh: Generation Z Students, Religious Knowledge and Professional Interests,” Miqot J. Ilmu-ilmu Keislam, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 126–145, 2024, https://doi.org/10.30821/miqot.v48i1.836.
[8] A. Khanif, “Islamic Religious Education Learning Strategy for Alpha Generation,” Ascarya J. Islam. Sci. Cult. Soc. Stud., vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 36–45, 2023, https://doi.org/10.53754/iscs.v3i1.461.
[9] S. Rizal, S. Nahar, and M. Al Farabi, “Islamic Values: Integration in Learning Mathematics and Science at Man 2 Level 2022/2023 Academic Year,” Munaddhomah, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 732–745, 2023, https://doi.org/10.31538/munaddhomah.v4i3.653.
[10] M. B. Aziz, Fitriani, R. Nurhasanah, A. A. Abidin, F. Dwiyama, and M. Toha, “Cultural Heritage as a Driver of Educational Choices: Evaluating the Role of Bugis Values in the Selection of Islamic Private Schools in Indonesia,” Nazhruna J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 726–741, 2024, https://doi.org/10.31538/nzh.v7i3.110.
[11] F. Ismail, M. Astuti, D. Nasrudin, I. Wigati, and Zuhdiyah, “Assessment Model of Islamic Religious Education in the Psychomotor Domain during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia,” Eurasian J. Educ. Res., vol. 2022, no. 101, pp. 190–203, 2022, https://doi.org/10.14689/ejer.2022.101.011.
[12] M. A. H. Putra, E. Malihah, E. Wiyanarti, and W. Darmawan, “Religious Values in Hijaz Yamani Poetry: Integration of Spiritual Responsibility in Character Education,” Karsa, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 33–65, 2025, https://doi.org/10.19105/karsa.v33i1.18745.
[13] M. Sri Mega Indah Umi Zulfiani and I. Rosyadi, “Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Practices Of Shariaconsumer Cooperatives For Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Ethical Perspective,” J. Lifestyle SDGs Rev., vol. 4, pp. 1–20, 2024, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v4.n00.pe01752.
[14] A. Chairy, Istiqomah, and A. C. F. Nahdiyah, “Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) dan Pendidikan Islam di Perguruan Tinggi: Sinergi untuk Masa Depan,” Acad. J. Inov. Ris. Akad., vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 124–134, 2024, https://doi.org/10.51878/academia.v4i3.3631.
[15] M. Mulyadi, “Penelitian Kuantitatif Dan Kualitatif Serta Pemikiran Dasar Menggabungkannya,” J. Stud. Komun. dan Media, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 128, 2013, https://doi.org/10.31445/jskm.2011.150106.
[16] M. Z. Yasin and R. N. F. Amijaya, “Peningkatan Kemapuan Pengolahan Data Kuantitatif Menggunakan Aplikasi Stata,” J. Pengabdi. Masy. Appl., vol. 2, no. 1, p. 57, 2023, https://doi.org/10.19184/jpma.v2i1.39468.
[17] D. Indrawan and S. R. Jalilah, “Metode Kombinasi/Campuran Bentuk Integrasi Dalam Penelitian,” J. Stud. Guru dan Pembelajaran, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 735–739, 2021, https://doi.org/10.30605/jsgp.4.3.2021.1452.
[18] A. M. Isaac, “Changing the Relation of Science and Religion through Integrated Islamic Curricula: A Theoretical Position on Faith-Based Science Education,” Austral Comun., vol. 14, no. 2, 2025, https://doi.org/10.26422//aucom.2025.1402.isa.
[19] A. N. Suwarsono, Bambang Setiadji, Musa Asy’arie, Waston, Muthoifin, “The Future Of The Civilization Of The Ummah Is Reviewed From The Sociology Of Education For The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGS’ S ),” J. Lifestyle SDGs Rev., vol. 4, pp. 1–19, 2024, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v4.n00.pe01688.
[20] S. U. A. Khondoker, Waston, A. N. An, Mahmudulhassan, and Muthoifin, “The Role of Faith-Based Education in Bangladesh’s Multicultural System and Its Impact on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs),” J. Lifestyle SDG’S Rev., vol. 5, no. 2, 2025, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v5.n02.pe03472.
[21] M. Sholahuddin, “Integrating Religious and Economic Education for Sustainable Development Goals ( SDGs ): An Analysis of Entrepreneurial Models in Indonesian Pesantren,” Profetika J. Stud. Islam, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 287–302, 2024, https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v25i02.7801.
[22] A. Alimni, A. Amin, and D. A. Kurniawan, “The role of Islamic education teachers in fostering students’ emotional intelligence,” Int. J. Eval. Res. Educ., vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 1881–1892, 2022, https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v11i4.22116.
[23] S. S. Posangi, A. Lundeto, S. Labaso, H. Anwar, and M. Damopolii, “Enhancing Islamic Education Quality Through Educational Supervision and ICT,” J. Ilm. Peuradeun, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 1209–1234, 2025, https://doi.org/10.26811/peuradeun.v13i2.1955.
[24] N. Burhanuddin and D. Ilmi, “Typologies of Religious Moderation in Indonesian Higher Education Institutions,” J. Indones. Islam, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 455–479, 2022, https://doi.org/10.15642/JIIS.2022.16.2.455-479.
[25] H. L. Siregar, Syihabuddin, K. A. Hakam, and K. Komalasari, “Application of project-based learning (PJBL) in Islamic religious education courses (an alternative solution to the problem of learning IRE at PTU),” J. Crit. Rev., vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 21–28, 2020, https://doi.org/10.22159/jcr.07.01.05.
[26] A. Fakhruddin, S. Anwar, and M. R. Fajar Islamy, “Enhancing academic self-concept and historical literacy in Islamic studies through collaborative learning: a study on prospective Islamic Education teachers in Indonesia,” Cogent Educ., vol. 12, no. 1, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2025.2491871.
[27] M. T. Yani, M. Hazin, and Y. Hanafi, “Educational Experience Insertion Model of Religious Moderation and National Defence As Efforts To Prevent Radicalism and Communism Via Islamic Religious Education Instructions,” Artseduca, vol. 2023, no. 36, pp. 111–124, 2023, https://doi.org/10.6035/artseduca.3610.
[28] Nuhayati and A. Hamid, “Radicalism Prevention Through Islamic Religious Education Learning At Elementary School,” J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 109–126, 2020, https://doi.org/10.15575/jpi.v6i1.8352.
[29] Hamdi, S. U. Rizal, N. Hikmah, M. Syabrina, Sulistyowati, and Mualimin, “Developing Digital-Based Islamic Religious Education Teaching Modules on the Subject Matter of Duha Prayer in Elementary Schools,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 131–146, 2024, https://doi.org/10.14421/jIRE.v21i1.7520.
[30] M. Zainuddin, Mardianto, and H. Matsum, “Development of Game-Based Learning Media on Islamic Religious Education Materials,” Nazhruna J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 13–24, 2023, https://doi.org/10.31538/nzh.v6i1.2824.
[31] N. Hamid, Sutama, S. Hidayat, Waston, A. Nirwana, and Muthoifin, “Creative Leadership: an Implementing Study of Transformative Leadership Models in High School for Sustainable Development Goals,” J. Lifestyle SDG’S Rev., vol. 5, no. 1, 2024, https://doi.org/10.47172/2965-730X.SDGsReview.v5.n01.pe01686.
[32] A. Wedi, D. Mardiana, and Umiarso, “Digital Transformation Model of Islamic Religious Education in the AI Era: A Case Study of Madrasah Aliyah in East Java, Indonesia,” Int. J. Learn. Teach. Educ. Res., vol. 24, no. 8, pp. 842–863, 2025, https://doi.org/10.26803/ijlter.24.8.37.
[33] S. S. Susanti et al., “Innovative Digital Media in Islamic Religious Education Learning,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 40–59, 2024, https://doi.org/10.14421/jIRE.v21i1.7553.
[34] A. M. im Amaly, Y. Herdiana, U. Ruswandi, and B. S. Arifin, “the Necessity and Reality of Islamic Religious Education in Schools,” J. Ilm. Islam Futur., vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 1–19, 2023, https://doi.org/10.22373/jiif.v23i1.13190.
[35] A. M. Putri and A. P. Astutik, “TikTok as a Generation-Z Islamic Religious Learning Media During the Covid-19 Pandemic,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 273–294, 2021, https://doi.org/10.14421/jIRE.2021.182-04.
[36] M. A. Abdullah, “Islamic Religious Education Based on Religious Intersubjectivity: Philosophical Perspectives and Phenomenology of Religion,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 141–163, 2022, https://doi.org/10.14421/jIRE.2022.191-11.
[37] Masturin, “Development of Islamic Religious Education Materials Based on Religious Moderation in Forming Student Character,” Munaddhomah, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 346–355, 2022, https://doi.org/10.31538/munaddhomah.v3i4.310.
[38] M. I. Sholeh et al., “The Role of Teachers in Increasing Students’ Learning Motivation in Islamic Religious Education,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 421–441, 2024, https://doi.org/10.14421/jIRE.v21i2.8846.
[39] L. Affandi, M. Rahmat, and U. Supriadi, “A Thematic Digital Quran Learning Model in Islamic Religious Education,” J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 181–194, 2021, https://doi.org/10.15575/jpi.v7i2.15062.
[40] Reksiana, A. Nata, D. Rosyada, M. D. H. Rahiem, and A. R. Rafikjon Ugli, “Digital Extension of Digital Literacy Competence for Islamic Religious Education Teachers in the Era of Digital Learning,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 402 – 420, 2024, https://doi.org/10.14421/jIRE.v21i2.9719.
[41] M. Apriantoro, A. Suryaningsih, and M. Muthoifin, “Bibliometric Analysis of Research Development of Economic Dispute Settlement,” EUDL Eur. Union Digit. Libr., 2023, https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.19-10-2022.2329068.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Mariam Elbanna Mariam Elbanna, Endang Switri, M. Sirozi, Annisa Astrid, Rozi Irfan Rosyadi, Meguellati Achour

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.












