Integration of Learning, Innovation, and SDGs Value in Pesantren: Sustainable Islamic Education Development
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/profetika.v26i02.11553Keywords:
learning innovation, sdgs, islamic education, development strategy, pesantrenAbstract
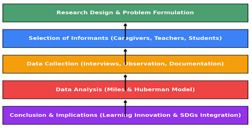
Objective: This study aims to examine the implementation of learning innovations and the integration of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) values in the Darul Ilmi Islamic Boarding School, as well as the strategies used in dealing with the digital era and the challenges that arise during the integration process. Theoretical framework: The theoretical framework of this research is based on the concept of sustainable Islamic education that integrates global values (SDGs), local wisdom, and Islamic principles as a foothold in the development of an Islamic boarding school education system that is adaptive to the changing times. Literature review: The literature review includes studies on pesantren education innovations, the integration of SDGs values in the learning system, and the transformation of sustainability value-based education, which is still limited, especially in the context of children's pesantren. Methods: This study uses a qualitative approach with data collection techniques in the form of in-depth interviews, direct observation, and documentation. The main informants consist of pesantren caregivers, accompanying teachers, and students who are selected purposively. Data analysis was carried out using the Miles and Huberman model: data reduction, data presentation, and a conclusion drawn. Results: The results show that SDGs-based learning innovations are implemented through contextual approaches that combine global, local, and Islamic values. This innovation has a positive impact on the quality of learning and social relevance of Islamic boarding schools, as well as improving the image of Islamic boarding schools in the community. Implications: Providing an adaptive and sustainable model of Islamic education in responding to global challenges. Novelty: Offers a new study on the integration of SDGs in children's boarding schools, which is still rarely discussed scientifically.
References
[1] P. Shenoy and T. Kumar, “A Platform for Model-based Learning and Gamification in Design Education,” Procedia CIRP, vol. 128, pp. 7–12, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2024.06.003.
[2] J. P. Davim, “Sustainable Development Goals: A Bibliometric Analysis,” J. Sustain. Res., vol. 7, no. 1, 2025, https://doi.org/10.20900/jsr20250008.
[3] J. J. González-Cortés, D. Cantero, and M. Ramírez, “Project-Based Learning in Bioprocess Engineering: MATLAB Software as a Tool for Industrial-Scale Bioreactor Design,” Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ., vol. 33, no. 1, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1002/cae.22811.
[4] S. Sarwenda, H. Rahim, D. Rosyada, A. Zamhari, and A. Salim, “Development of digital entrepreneurship programs in pesantren in Indonesia,” in Religion, Education, Science and Technology towards a More Inclusive and Sustainable Future: Proceedings of the 5th International Colloquium on Interdisciplinary Islamic Studies (ICIIS 2022), Lombok, Indonesia, 19-20 October 2022, London: Routledge, 2024, pp. 273–278. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003322054-46.
[5] Z. Fuady and M. Daud, “Fiqh Across Madhhabs : An Alternative to Pesantren Students ’ School of Thought Exclusivism in the Post-Truth Era. The schools of thought ( madhhabs ) within fiqh ( Islamic jurisprudence ) are one of the ijtihad products explored by qualified Muslim jurists,” Maz. J. Pemikir. Huk. Islam, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 143–168, 2021, [Online]. Available: https://journal.uinsi.ac.id/index.php/mazahib/article/view/3081/pdf
[6] A. Salim, I. Suyuti, M. Gafarurrozi, L. Badriah, and N. M. S. A. B. N. Abdullah, “Transformation of State Religious School Competence: An Analysis of the 1975 Joint Ministerial Decree and Its Implications in Indonesia,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 442–460, 2024, https://doi.org/10.14421/jpai.v21i2.9481.
[7] S. Huda, N. Tadjuddin, A. Sholihuddin, H. Kato, and K. Cengiz, “Character and Adab Education in Indonesia, Turkey, and Japan: A Comparative Study,” Islam. Guid. Couns. J., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 1–17, 2023, https://doi.org/10.25217/igcj.v6i1.2973.
[8] Yuhelmi et al., “Practicality of syntax soft skill-based learning (Ss-BL): a new model in web-based entrepreneurship learning,” Data Metadata, vol. 3, 2024, https://doi.org/10.56294/dm2024.407.
[9] J. Zhang, J. Wu, X. Sun, Y. Yang, and M. Zhou, “Technology-Enabled Project-Based Learning: Let Every Child Embrace ‘Good Learning,’” Lecture Notes in Educational Technology, vol. Part F1761. pp. 93–99, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6225-9_11.
[10] E. Levin, A. Rixon, and M. Keating, “How can a ‘sense of belonging’ inform your teaching strategy? Reflections from a core business unit. A practice report,” Student Success, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 71–78, 2019, https://doi.org/10.5204/ssj.v10i2.1307.
[11] M. Situmorang, M. Sinaga, M. Sitorus, and A. Sudrajat, “Implementation of Project-based Learning Innovation to Develop Students’ Critical Thinking Skills as a Strategy to Achieve Analytical Chemistry Competencies,” Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res., vol. 56, no. 1, pp. S41–S51, 2022, https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.56.1s.41.
[12] Sudir, M. F. Hidayatullah, M. Yusuf, and Subagya, “Total Quality Management (TQM) in Islamic Boarding Schools: Teacher and Principal Perspectives,” Educ. Process Int. J., vol. 15, no. 1, 2025, https://doi.org/10.22521/edupij.2025.15.136.
[13] S. Anam, I. N. S. Degeng, N. Murtadho, and D. Kuswandi, “The moral education and internalization of humanitarian values in pesantren,” J. Educ. Gift. Young Sci., vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 815–834, 2019, https://doi.org/10.17478/jegys.629726.
[14] K. Muthrofin, H. Ikmal, and E. Wahyudi, “The Implementation of Islamic Religious Education (PAI) in Shaping the Profile of Rahmatan lil alamin Students in a Madrasah,” Educ. J. Educ., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 370–381, 2023, [Online]. Available: http://staimnglawak.ac.id/ejournal/index.php/educatio/article/view/1182%0Ahttp://staimnglawak.ac.id/ejournal/index.php/educatio/article/download/1182/383
[15] E. Fatmawati, B. Suharto, M. Dahlan, W. K. Suhma, and A. Yudiawan, “Challenges of Educational Management in the Islamic Higher Education Sector Based on Pesantren,” J. Educ. Soc. Res., vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 105–118, 2023, https://doi.org/10.36941/jesr-2023-0151.
[16] S. S. Maulida, C. Nursaniah, and L. H. Sari, “Study of implementation of the eco-pesantren concept at Dayah Terpadu Inshafuddin, Banda Aceh,” IOP Conf. Ser.. Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 1290, no. 1, p. 12037, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1290/1/012037.
[17] A. Misno, K. L. Rochman, A. Idi, D. Maharani, and Hanna, “Development of Islamic education (PAI) curriculum based on anti-corruption fiqh,” Int. J. Psychosoc. Rehabil., vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 2434–2446, 2020, https://doi.org/10.37200/IJPR/V24I3/PR201891.
[18] A. Kholiq, “Strengthening Anticorruption Character at Elementary Schools in Indonesia: Study on Instructional Practices by In-Service Islamic Education Teachers,” Al Ibtida J. Pendidik. Guru MI, vol. 9, no. 2, p. 355, 2022, https://doi.org/10.24235/al.ibtida.snj.v9i2.11579.
[19] E. Nurtawab and D. Wahyudi, “Restructuring Traditional Islamic Education in Indonesia: Challenges for Pesantren Institution,” Stud. Islam, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 55–81, 2022, https://doi.org/10.36712/sdi.v29i1.17414.
[20] C. He, Z. Jiang, and Y. Yi, “Developing an Online Teaching Platform for Practice in Prosthetics and Orthotics,” in 2024 17th International Convention on Rehabilitation Engineering and Assistive Technology, i-CREATe 2024 and World Rehabilitation Robot Convention, WRRC 2024 - Proceedings, 2024, pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/i-CREATe62067.2024.10776193.
[21] S. Suwendi, C. B. Gama, M. F. F. Farabi, F. Fuady, and A. Arman, “Roles and Challenges of Pesantren Intellectual Networks,” J. Ilm. Islam Futur., vol. 24, no. 2, p. 453, 2024, https://doi.org/10.22373/jiif.v24i2.23134.
[22] Sahri and A. U. Hali, “Building Character in Sufism-Based Students in Madrasah West Kalimantan,” Nazhruna J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 240–252, 2023, https://doi.org/10.31538/nzh.v6i2.2974.
[23] M. Mahfudz and S. Sukarno, “The effect of ex-add learning techniques on critical thinking skills and pedagogic competence of Islamic education students,” J. Educ. Learn., vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 221–228, 2023, https://doi.org/10.11591/edulearn.v17i2.20782.
[24] M. Fukushima and T. Ohji, “Macroporous ceramics for the sustainable development goals (SDGs): Review,” Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 660–680, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.14261.
[25] Mutammam, D. Anggraeni, A. Afroni, Sutrisno, A. Zubaidah, and G. Irfanullah, “Adaptation and Transformation of Pesantren Education in Facing The Era of Muslim Society 5.0,” Nazhruna J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 705–726, 2024, https://doi.org/10.31538/nzh.v7i3.114.
[26] A. M. Alfoudari, C. M. Durugbo, and F. M. Aldhmour, “Understanding socio-technological challenges of smart classrooms using a systematic review,” Comput. Educ., vol. 173, p. 104282, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2021.104282.
[27] D. Susanto, Risnita, and M. S. Jailani, “Teknik Pemeriksaan Keabsahan Data Dalam Penelitian Ilmiah,” J. QOSIM J. Pendidikan, Sos. Hum., vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 53–61, 2023, https://doi.org/10.61104/jq.v1i1.60.
[28] H. Zukriadi, Sulaiman, U., “Aneka Macam Penelitian,” SAMBARA J. Pengabdi. Kpd. Masy., vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 36–46, 2023, https://doi.org/10.58540/sambarapkm.v1i1.157.
[29] W. Yuliani, “Metode Penelitian Deskriptif Kualitatif Dalam Perspektif Bimbingan Dan Konseling,” QUANTA J. Kaji. Bimbing. dan Konseling dalam Pendidik., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 1–10, 2018, https://doi.org/10.22460/q.v2i1p21-30.642.
[30] S. Y. L. Tumangkeng and J. B. Maramis, “Kajian Pendekatan Fenomenologi : Literature Review,” J. Pembang. Ekon. Dan Keuang. Drh., vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 14–32, 2022, https://doi.org/10.35794/jpekd.41379.23.1.2022.
[31] R. Surayya, “Pendekatan Kualitatif Dalam Penelitian Kesehatan,” AVERROUS J. Kedokt. Dan Kesehat. Malikussaleh, vol. 1, no. 2, p. 75, 2018, https://doi.org/10.29103/averrous.v1i2.415.
[32] M. Mulyadi, “Penelitian Kuantitatif Dan Kualitatif Serta Pemikiran Dasar Menggabungkannya,” J. Stud. Komun. dan Media, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 128, 2013, https://doi.org/10.31445/jskm.2011.150106.
[33] M. Athoillah, A. S. Rahman, A. S. Firdaus, and M. A. Septiadi, “Policies and Practices of Religious Moderation in Pesantren,” J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 387–396, 2024, https://doi.org/10.15575/jpi.v10i2.27543.
[34] F. Soltau, “The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development: What are its implications for future generations?” in Giving Future Generations a Voice: Normative Frameworks, Institutions and Practice, Edward Elgar Publishing, 2021, pp. 108–126. https://doi.org/10.4337/9781839108259.00014.
[35] A. S. Bello, “Innovative Experiences in Teaching and Learning,” in Overcoming Challenges in Online Learning: Perspectives from Asia and Africa, London: Routledge, 2023, pp. 171–179. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003342335-20.
[36] J. Purnomo, S. Anantanyu, H. Saptaningtyas, and F. M. Mangunjaya, “Prophetic Approach in Environmental Education and Community Empowerment: a Case Study of Sustainable Pesantren Development,” Rev. Gest. Soc. e Ambient., vol. 18, no. 8, p. 6259, 2024, https://doi.org/10.24857/rgsa.v18n8-047.
[37] L. Anwar, C. Sa’dijah, I. R. Hidayah, and A. H. Abdullah, “Integrating Local Wisdom and Project-Based Learning to Enhance Critical Thinking, Collaboration, and Creativity in Mathematics Education: A Pilot Study with Eighth Grade Students in Malang,” International Conference of Mathematics Education, Learning and Application (ICOMELA). p. 40032, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0241446.
[38] Y. Agustina, Margana, N. H. P. S. Putro, and M. A. Nazri, “Designing English Instructions for Islamic Settings: A Needs Analysis in Indonesian Pesantren,” World J. English Lang., vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 373–382, 2023, https://doi.org/10.5430/wjel.v13n8p373.
[39] M. Mustaqim and A. Atabik, “Challenges in Implementing the Pesantren Endowment Fund: a Study of Presidential Regulation Number 82 of 2021 on Operational Funding of Pesantren,” J. Huk. Unissula, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 129–140, 2024, https://doi.org/10.26532/jh.v40i1.39042.
[40] Y. Huang, L. Liu, and L. An, “Are the Teachers and Students Satisfied: Sustainable Development Mode of Entrepreneurship Education in Chinese Universities?” Front. Psychol., vol. 11, 2020, https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01738.
[41] I. Mujahid, “Islamic orthodoxy-based character education: creating moderate Muslims in a modern pesantren in Indonesia,” Indones. J. Islam Muslim Soc., vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 185–212, 2021, https://doi.org/10.18326/ijims.v11i2.185-212.
[42] A. Ben-Eliyahu, “Sustainable learning in education,” Sustain., vol. 13, no. 8, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084250.
[43] S. Zainal, M. A. Manumanoso Prasetyo, C. M. Aziz Yaacob, and Y. Jamali, “Adopting Pesantren-Based Junior High School Programs: the Pesantren Changes Its Educational System Without Conflict,” J. Ilm. Islam Futur., vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 260–276, 2022, https://doi.org/10.22373/JIIF.V22I2.13525.
[44] Jusubaidi, T. Lindgren, A. Mujahidin, and A. C. Rofiq, “A Model of Transformative Religious Education: Teaching and Learning Islam in Pondok Modern Darussalam Gontor, Indonesia,” Millah J. Relig. Stud., vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 171–212, 2024, https://doi.org/10.20885/millah.vol23.iss1.art6.
[45] R. Basori, T. J. Raharjo, T. Prihatin, and A. Yulianto, “Maintaining Salafi Values Through Innovative Management Practices At Pesantren,” J. Pendidik. Islam, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 145–156, 2023, https://doi.org/10.15575/jpi.v9i2.25376.
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fitria Martanti, Ma’as Shobirin, Maskur, Moch Fatkhurronji, Ana Surjanto

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.












