THE EFFECT OF ZNO/CUO-WATER- HYBRID NANOFLUID CONCENTRATION RATIO ON HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT COOLING SYSTEMS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/mesin.v25i1.2464Keywords:
heat transfer, nanofluids, hybrid nanofluids, Reynolds Number, convection coefficientAbstract
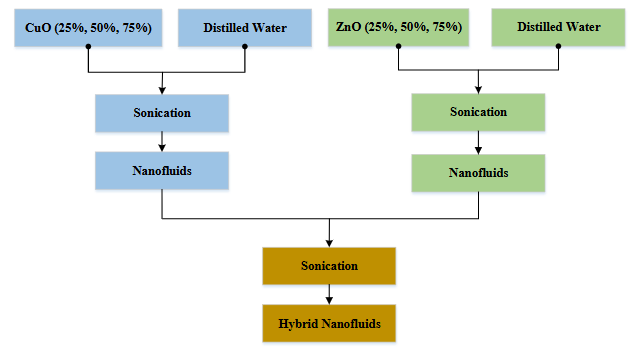
The use of hybrid nanofluids CuO-ZnO /distilled water as a cooling medium was tested in this study to determine the characteristics of convection heat transfer. The hybrid nanofluids preparation process was carried out first by dispersing the CuO and ZnO nanofluids using an ultrasonic cleaner for 3 hours and then allowed to settle for 24 hours. Furthermore, the CuO and ZnO nanofluids were mixed based on the stipulated ration of CuO:ZnO (25%:75%), (50%:50%) and (75%:25) with a volume fraction of 0.5% and agitated for 1 hour. Testing of the hybrid nanofluids CuO-ZnO/distilled water was carried out using a water block as an electronic cooling device with a flow rate variation of 0.7 – 1.9 l/min. From experimental results, the convection coefficient, as one of performance parameters of cooling device, and its relation to Reynolds numbers was able to be determined. Overall, the results show that the rate of heat transfer with the hybrid nanofluids is higher compared to distilled water. At a particular configuration of flowrate and nanoparticle ratio, the hybrid nanofluid has more than 2.5 times higher coefficient of convection than distilled water. In addition, the experiment revealed that the synthesized nanofluid created a temperature drop of around 40ᵒC across the water block at a heater power of 10 W.
Downloads
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Versions
- 2024-01-31 (4)
- 2025-01-12 (3)
- 2025-01-12 (2)
- 2024-01-30 (1)
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Devia Gahana Cindi Alfian, Arvin Ade Guna Meliala, T. M. Indra Riayatsyah, Dicky Januarizky Silitonga

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











