An Overview of Parents' Knowledge About Accident Prevention in Toddler
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/bik.v16i1.1014Keywords:
knowledge, injury, toddlerAbstract
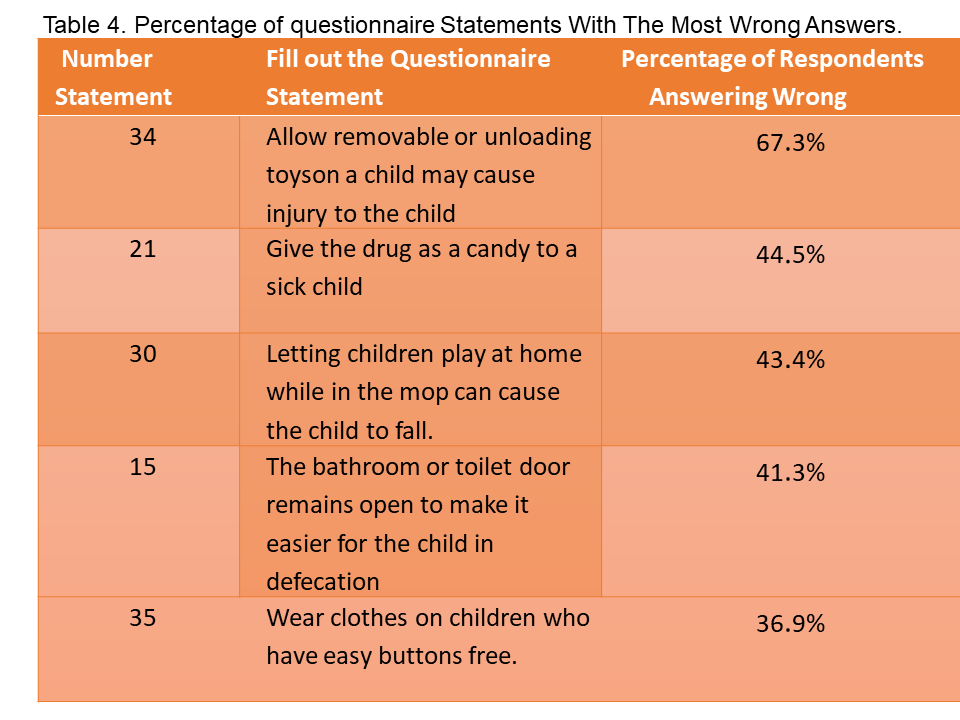
The World Health Organization (WHO) states that no less than 875,000 children under the age of 18 worldwide die from injuries. The results of the 2018 Basic Health Research reported that the national prevalence of injury was 9.2%, with the highest prevalence of injury occurring in the home and environment with a percentage of 44.7%. In Central Java province alone, the percentage of injury incidence is 9.3%, this figure is higher than the national average rate of injury. Toddler injuries can actually be prevented with good supervision from parents, but these parents must also have good knowledge about handling injuries to children. Objective: This study aims to determine the level of parental knowledge about Accident Prevention in Toddler in the Gambirsari Health Center Work Area Method: This research type is a descriptive analytic study. The group studied were parents in the Gambirsari Health Center Working Area who had toddlers (aged 1-3 years), this study will describe the description of mothers' knowledge about accident prevention in toddlers in the Gambirsari Health Center Surakarta Work Area. Results: Based on the results of this study it can be concluded that the research subjects have the most age in the age range of 26-35 years (59%), the subjects of this study have the highest percentage of types of education at the high school level (57%), the subjects in this study the most work as IRT or housewives (74%), the highest percentage of toddlers is male sex toddler (60%), and 61% of the subjects have more than 1 children. Conclusion: Questionnaire statements with the most incorrect answers were found in statement point number 34 of 67.3%
Downloads
References
Ahmed, Naseer, Ijaz, Sundas., Manzoor, Sommaya., & Sajjad, Sana. (2021). Prevalence of self?medication in children under?five years by their mothers in Yogyakarta city Indonesia (Prevalensi pengobatan sendiri pada anak balita oleh ibunya di kota Yogyakarta Indonesia). Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care: Volume 10 : Issue 8. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2457_20
Al?Bshri, Soad Abdulrhman., and Jahan, Saulat. (2021). Prevalence of home related injuries among children under years old and practice of mothers toward first aid in Buraidah, Qassim (Prevalensi cedera terkait rumah pada anak di bawah tahun dan praktik pertolongan pertama ibu di Buraidah, Qassim). Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care. 10:3. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2265_20
Carlsson, Anna., Karlsson E, Dejin., Håkansson, & Udén G (2006). Compliance with child accident precautions by Child Health nurses. J Child Health Care. (Kepatuhan terhadap tindakan pencegahan kecelakaan anak oleh perawat Kesehatan Anak). 10(2):149–59. https://doi.org/10.1177/1367493506062554
Carlsson, Anna., Anna, Karin Dykes., Annkristin, Jansson., & Bramhagen, Ann?Cathrine. (2016). Mothers’ awareness towards child injuries and injury prevention at home: an intervention study (Kesadaran ibu terhadap cedera anak dan pencegahan cedera di rumah: studi intervensi). BMC Res Notes: 9:223. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-016-2031-5
Gustina. (2016). Description of Mother's Education Level, Occupation and Knowledge of Weighing Children Aged 0-5 Years in the Work Area of the Paal X Health Center, Jambi City, 2015 (Gambaran Tingkat Pendidikan, Pekerjaan dan Pengetahuan Ibu Terhadap Penimbangan Anak Usia 0-5 Tahun di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Paal X Kota Jambi Tahun 2015). Scientia Journal. Vol 5. No. 01
Handayani, Purba. (2020). Our Writing Foundation (Ilmu Kesehatan Anak) (1st ed.). Yayasan Kita Menulis.
Hastuti (2017). Relationship Knowledge About Anticipation Of Injury With Practice of Injury Prevention in Toddler Age Children in Rw 01, Manggahang Village, Jelekong Community Health Center, Bandung Regency (Hubungan Pengetahuan Tentang Antisipasi Cedera Dengan Praktik Pencegahan Cedera Pada Anak Usia Toddler Di Rw 01 Kelurahan Manggahang Wilayah Puskesmas Jelekong Kabupaten Bandung). Jurnal Keperawatan Komprehensif (Comprehensive Nursing Journal), 3(1), 52–62. https://doi.org/10.33755/jkk.v3i1.85
Hidayat, Aziz Alimul. (2010). Quantitative Paradigm Health Research Methods (Musrifatul Uliyah (ed.); 1st ed.) (Metode Penelitian Kesehatan Paradigma Kuantitatif (Musrifatul Uliyah (ed.); 1st ed.). Health Books Publishing.
Jaeyana, Imah. (2012). An overview of the level of knowledge of mothers under five about weighing toddlers at Posyandu Perum Boro Mukti Permai Banyuurip Purworejo (Gambaran Tingkat Pengetahuan Ibu Balita Tentang Penimbangan Balita di Posyandu Perum Boro Mukti Permai Banyuurip Purworejo). Jurnal Komunikasi Kesehatan.
Marcdante, Karen., Kliegman, R., Jenson, H., & Behrman, R. (2011). Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics (6th Ed). IDAI. 2014 (Alih Bahasa), Indonesia: Elsevier.
Ministry of Health (Riskesdas). (2013). Ministry of Health Research and Development Agency of the Republic of Indonesia in 2013 (Badan Penelitian danp Pengembangan Kesehatan Kementerian RI tahun 2013).
Ministry of Health (Riskesdas). (2018). Republic of Indonesia Ministry of Health Research and Development Agency in 2018 (Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan Kementerian RI tahun 2018).
Murhayati, A. (2021). Keperawatan Jiwa Mengenal Kesehatan Mental (1st ed.).
Ahlimedia Press.
Novieastari. (2020). Dasar-Dasar Keperawatan. Elsevier.
Potter, P.A, and Perry, A.G. (2005). Nursing Fundamental Textbook: Concepts, Processes, and Practices (Buku Ajar Fundamental Keperawatan: Konsep, Proses,dan Praktik). Edisi 4. Jakarta: EGC.
Purwanto, Heri. (2006). Introduction to Human Behavior For Nursing (Pengantar Perilaku Manusia Untuk Keperawatan). Jakarta: EGC.
Saadati, M., Js, T., Rezapour, R., & R, A. K. (2020). Home injury prevention attitude and performance: a community-based study in a designated safe community (Sikap dan kinerja pencegahan cedera rumah: studi berbasis komunitas di komunitas aman yang ditunjuk). Journal of Injury and Violence Research, 12(2), 145-152. https://doi.org/10.5249/jivr.v12i2.1506.
Salami, Kabiru., and Adesanwo, Olusola. (2015). The practice of self-medication for treatment of illnesses for under-five children by mothers in Ibadan, Nigeria (Praktik pengobatan sendiri untuk pengobatan penyakit pada anak balita oleh ibu di Ibadan, Nigeria). Res J Drug Abuse 2:2-7. https://doi.org/10.7243/2057-3111-2-2
Siu, Godfrey., Batte1, Anthony., Tibingana, Brenda., Otwombe, Kennedy., Sekiwunga, Richard., & Paichadze, Nino. (2019). Mothers’ perception of childhood injuries, child supervision and care practices for children 0–5years in a peri-urban area in Central Uganda; implications for prevention of childhood injuries (Persepsi ibu tentang cedera masa kanak-kanak, praktik pengawasan dan pengasuhan anak untuk anak 0–5 tahun di daerah pinggiran kota di Uganda Tengah; implikasi untuk pencegahan cedera masa kecil). BMC Journal. 6:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40621-019-0211-1
World Health Organization (WHO). (2014). Injuries and violence the facts (Cedera dan kekerasan fakta). http://who.int/violence_injury_prevention/key_facts/VIP_keyfacts.pdf?ua=1.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Irdawati Irdawati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


















