Exploring EFL Students’ Perceptions of ‘Perplexity’ AI Use and Abuse in Indonesia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/sosial.v6i2.13059Keywords:
artificial intelligence, perplexity, academic integrity, digital literacy, ethical awarenessAbstract
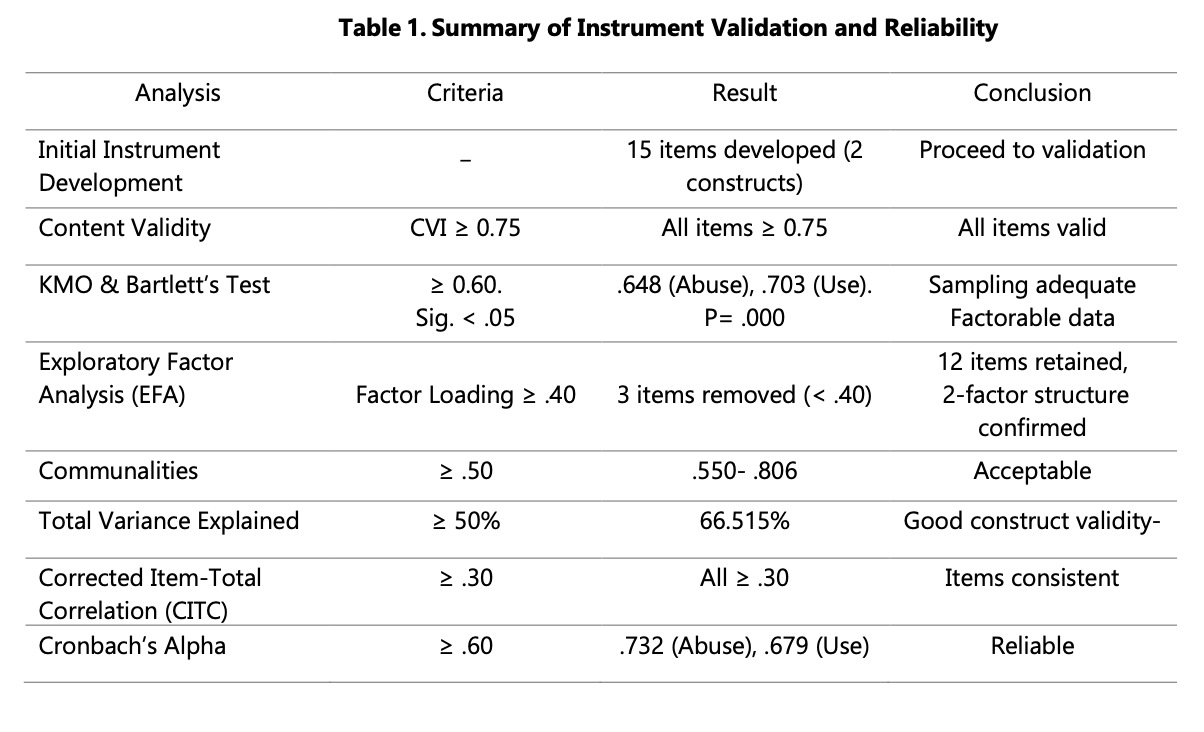
This study investigates English Education students’ perceptions of the use and potential abuse of Perplexity, an AI-based platform, in completing academic assignments. Employing a quantitative survey design, the study used a self-administered questionnaire consisting of 12 items measured using a five-point Likert scale. Data were obtained from 34 students at an Islamic Institute in Jambi Province, Indonesia. The instrument was validated by experts and tested for reliability using KMO, Bartlett’s Test, EFA, and Cronbach’s Alpha. The results indicate that students exhibit a strong awareness of ethical and academic implications in using Perplexity AI. Most participants acknowledged that while the tool enhances learning efficiency, excessive reliance may hinder creativity, critical thinking, and academic honesty. Students perceived Perplexity as both beneficial and potentially problematic if misused. The study underscores the need for Islamic higher education institutions to develop comprehensive AI ethics guidelines, integrate digital literacy and moral instruction into curricula, and promote responsible, value-based AI use that aligns technological advancement with academic integrity.
Downloads
References
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179-211. DOI: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)900 20-T
Alghamdi, A. H. (2024). Leadership in Islamic education: Integrating ethical values in the digital age. International Journal of Social and Human, 1(2), 136–143. https://doi.org/10.59613/ecwa6z62
Aulia, D. F., & Indrayadi, T. (2023). EFL Students’ Perception of MALL for Pronunciation Proficiency. Journal Educative: Journal of Educational Studies, 8(1), 01. https://doi.org/10.30983/educative.v8i1.6213
Chan, C. K. Y., & Hu, W. (2023). Students’ voices on generative AI: perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00411-8
Cresswell, J. W. and C. J. D. (2022). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches (6th ed.). SAGE Publications.
Grájeda, A., Córdova, P., Córdova, J. P., Laguna-Tapia, A., Burgos, J., Rodríguez, L., Arandia, M., & Sanjinés, A. (2024). Embracing artificial intelligence in the arts classroom: understanding student perceptions and emotional reactions to AI tools. Cogent Education, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2024.2378271
Holmes, W., Bialik, M., & Fadel, C. (2022). Artificial intelligence in education: Promises and implications for teaching and learning. Center for Curriculum Redesign. https://curriculumredesign.org/wp-content/uploads/AI-in-Education-CCR.pdf
Ivanov, S., Soliman, M., Tuomi, A., Alkathiri, N. A., & Al-Alawi, A. N. (2024). Drivers of generative AI adoption in higher education through the lens of the Theory of Planned Behaviour. Technology in Society, 77, 102521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2024.102521
Johnston, H., Wells, R. F., Shanks, E. M., Boey, T., & Parsons, B. N. (2024). Student perspectives on the use of generative artificial intelligence technologies in higher education. International Journal for Educational Integrity, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40979-024-00149-4
Johri, A., Hingle, A., & Schleiss, J. (2024). Misconceptions, Pragmatism, and Value Tensions: Evaluating Students’ Understanding and Perception of Generative AI for Education.
Juan, L. X., Wu, T. Y., Veloo, P. K., & Supramaniam, M. (2022). Using extended TPB models to predict dishonest academic behaviors of undergraduates in a Chinese public university. SAGE Open, 12(4), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221140391
Kasneci, E.; Sessler, K.; Kuchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Kasneci, G. (2023). ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learning and Individual Differences, 103, 102274.
Lund, B., Mannuru, N. R., Teel, Z. A., Lee, T. H., Ortega, N., Simmons, S., & Ward, E. (2025). Student Perceptions of AI-Assisted Writing and Academic Integrity: Ethical Concerns, Academic Misconduct, and Use of Generative AI in Higher Education. Preprints. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202507.1882.v1
Nelson, A. S., Santamaría, P. V., Javens, J. S., & Ricaurte, M. (2025). Students’ Perceptions of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) Use in Academic Writing in English as a Foreign Language†. Education Sciences, 15(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15050611
Pitra, A., Purnama, S., Kartika Putra, T., Arifin, A., & Azizah, S. (2024). Exploration Of Students’ and Lecturers’ Perceptions Towards the Utilization of Generative Artificial Intelligence. Journal of English Language Learning (JELL), 8(2), 650–667.
Rahmawati, S., & Inayati, N. L. (2024). Utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) Perplexity as a digital literacy tool for Islamic Religious Education students. Iseedu Journal of Islamic Educational Thoughts and Practices, 8(2), 205–214. https://doi.org/10.23917/iseedu.v8i2.9001
Ranganathan, P., & Caduff, C. (2023). Designing and validating a research questionnaire - Part 1. Perspectives in Clinical Research, 14(3), 152–155. https://doi.org/10.4103/picr.picr_140_23
Reiss, M. J. (2021). The use of AI in education: Practicalities and ethical considerations. London Review of Education, 19(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.14324/LRE.19.1.05
Schei, O. M., Møgelvang, A., & Ludvigsen, K. (2024). Perceptions and Use of AI Chatbots among Students in Higher Education: A Scoping Review of Empirical Studies. In Education Sciences (Vol. 14, Issue 8). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080922
Sugiyono. (2017). Metode penelitian kuantitatif, kualitatif, dan R&D. Alfabeta.
Tan, M. J. T., & Maravilla, N. M. A. T. (2024). Shaping integrity: why generative artificial intelligence does not have to undermine education. In Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 7). Frontiers Media SA. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2024.1471224
Upara, S. (2023). From Real World to Classroom/2: Navigating English Language Learning through Autonomy- Supportive Instruction and Out-of-Class Resources in Thai EFL Context. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/372761218
Lubis, C.U., & Rahman Hz, B. I. (2024). Perplexity AI on the writing efficiency of EFL students in higher education: Students’ insight. ENGLISH FRANCA, 8(1), 167–178. https://doi.org/10.29240/ef.v8i1%20May.9982
Xu, W., & Ouyang, F. (2022). The application of AI technologies in STEM education: a systematic review from 2011 to 2021. In International Journal of STEM Education (Vol. 9, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-022-00377-5
Yeo, M. A. (2023). Academic integrity in the age of Artificial Intelligence (AI) authoring apps. TESOL Journal, 14(3), e716.
Zhang, S., Zhao, X., Zhou, T., & Kim, J. H. (2024). Do you have an AI dependency? The roles of academic self-efficacy, academic stress, and performance expectations on problematic AI usage behavior. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-024004670
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yanti Asmara, Toni Indrayadi, Reko Hary Putra

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.















