Determinants of Green Credit and Their Influence on Banking Profitability in Indonesia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/reaksi.v9i1.3906Keywords:
Green credit, profitability, capital adequacy, credit risk, operating efficiency, bank sizeAbstract
Green finance involves efforts to internalize environmental externalities and adjust risk perceptions to encourage environmentally friendly investments and reduce those that are harmful to the environment. One form of green financial support is the provision of green credit by banks. This research aims to test the effect of green credit on bank profitability, and test the effect of capital adequacy, operational efficiency, credit risk and bank size on bank profitability. This research also examines the influence of capital adequacy, operational efficiency, credit risk and bank size on green credit. The population in this study are banks operating in Indonesia with a sample of all banks that have a commitment to green credit. To test the hypothesis, use panel data regression analysis. After conducting a model test, the best model was obtained, namely the fixed effect model. The results of research using the fixed effect model show that green credit in Indonesia is not influenced by bank capital adequacy, bank operational efficiency, bank liquidity, bank credit risk, and bank size. However, green credit has a significant positive effect on bank profitability in Indonesia. Another result is capital adequacy, which has a positive effect on profitability, while operational efficiency and bank size have a significant and negative effect on profitability, while credit risk has no effect on profitability.
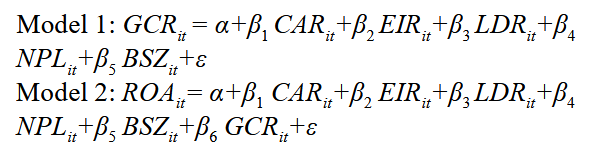
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Riset Akuntansi dan Keuangan Indonesia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



















