Peer Review Process
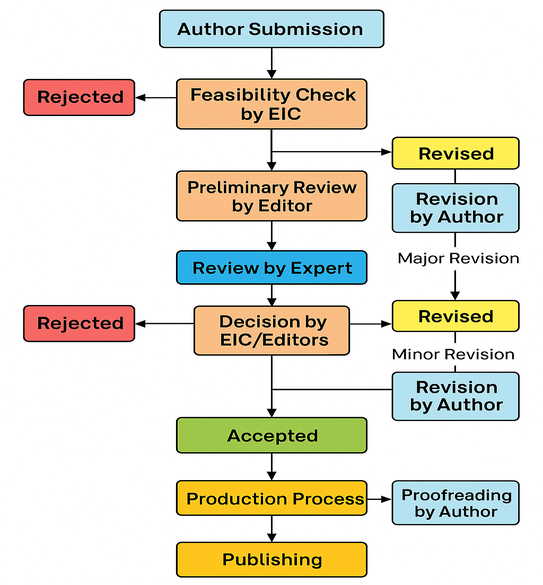
1. Author Submission
The review process begins with the submission of the manuscript by the author through the journal's online submission system. At this stage, the author ensures that the manuscript complies with the journal's submission guidelines, including formatting, referencing style, originality checks (plagiarism), and ethical declarations.
2. Feasibility Check by Editor-in-Chief (EIC)
Once submitted, the manuscript undergoes an initial screening by the Editor-in-Chief (EIC) to assess its general suitability for the journal. This feasibility check includes:
- Relevance to the journal’s aims and scope,
- Compliance with formatting and submission standards,
- Basic quality of English and presentation,
- Originality and novelty.
If the manuscript does not meet these preliminary criteria, it is desk rejected without external peer review. If deemed feasible, it proceeds to the editorial review.
3. Preliminary Review by Editor
The manuscript then undergoes a preliminary editorial assessment, often by associate or section editors. Here, the content is reviewed more closely for:
- Theoretical foundation and contribution to knowledge,
- Clarity of research questions or hypotheses,
- Methodological soundness and validity,
- Coherence of analysis and findings,
- Academic writing quality.
If minor or moderate improvements are needed, the editor may request the author to revise before sending it for peer review. This is known as editorial revision. The author then resubmits the revised manuscript for further consideration.
4. Peer Review by Experts
Following satisfactory preliminary evaluation, the manuscript is sent for external peer review by two or more subject-matter experts, in a double-blind review format. The reviewers assess the manuscript in depth, focusing on:
- Originality and novelty of the study,
- Validity and reliability of the research design and methodology,
- The significance of the results,
- Appropriateness of data analysis and interpretation,
- Strength and clarity of the conclusions,
- Relevance of literature review and citations.
5. Decision by EIC or Editorial Board
Upon receiving reviewer feedback, the EIC or editorial board makes a formal decision:
- Accept without changes (rare),
- Request revision (major or minor) based on peer review:
Based on the decision:
- For major revision, the manuscript may require significant reworking and may be sent back to reviewers for a second round of review.
- For minor revision, the manuscript is returned to the editor after author revision for quick final review.
The revision loop continues until the editor is satisfied that the manuscript meets publication standards.
- Reject if the manuscript fails to meet scholarly standards.
If revisions are requested, the author is expected to respond carefully to each reviewer comment and submit a revised manuscript along with a response letter detailing the changes made.
6. Final Acceptance
Once all required revisions are satisfactorily addressed and approved by the editorial team, the manuscript is officially accepted for publication. An acceptance letter is typically issued to the author as a formal notification.
7. Proofreading and Production Process
After acceptance, the manuscript enters the production stage, which includes:
- Copyediting: Language, grammar, and formatting adjustments,
- Typesetting: Layout and formatting as per journal standards,
- Proofreading by the author, where the author is invited to check the final layout and suggest minor corrections if necessary.
8.Publishing
Upon completion of production and author proofreading, the article is published online in the assigned journal issue. The publication may be open-access or subscription-based, depending on the journal’s policy.



















