EFFECTS OF CONTINUOUS AND FRACTURED RIBS PLACED AT THE ENDWALL SURFACE UPSTREAM OF THE TURBINE-VANE LEADING-EDGE
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/mesin.v25i2.4349Keywords:
vane-blade, mid-stream, total pressure loss, heat transferAbstract
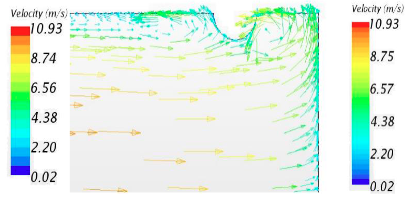
Total pressure loss, chaotic and heavy flow downstream of the turbine passage exit area are a few effects of the desired increase in inlet temperature input at the upstream part of the turbine vane passage. Huge amount of energy from the cross-flows near the middle of the vane actual chord are transported downstream by this chaotic flow which often results in aerodynamic loss and differential heat penalties. To compare the different arrangement, comparisons of the two geometries, the impact of adding various rib configurations upstream are studied for heat augmentation efficacies. The leading-edge rib(s) effects at the mid-stream of the vane passage are quantitatively examined in this work using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) technique. With the employment of Reynolds Averaged Navier-Stoke energy equations, the geometries are modelled choosing the appropriate boundary conditions. Polyhedral mesh is used with fifteen prism layer mesh at the endwall and vane surfaces to capture the flow physics close to the endwall area. Although the two configurations employed showed relative reduction in the total pressure loss coefficient, however, the fractured ribs produced superior outcomes of Nusselt number reduction of over 10% along the passage exit region. The data demonstrate a considerable difference in the overall pressure loss between the two configurations.
Downloads
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Versions
- 2024-07-31 (2)
- 2024-07-31 (1)
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Adeola Suhud Shote, Samson Abiodun Aasa , Olabode T Olakoyejo , Aderemi Musiliudeen Bamiduro

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











