Waqf Literacy, Islamic Religiosity, Subjective Norm, Perceived Behavior Control, and Attitude on Muhammadiyah Citizens' Interest in Becoming Wakif
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/jisel.v7i02.5113Keywords:
Muhammadiyah, Interest, Waqif, Islamic Religiosity, Waqf LiteracyAbstract
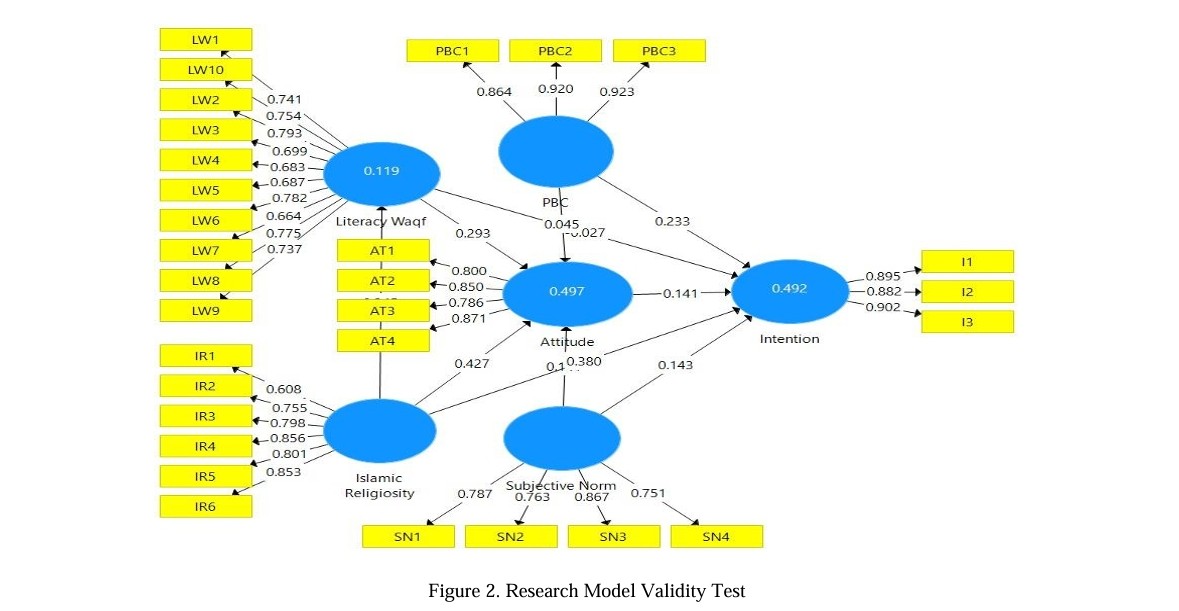
Muhammadiyah citizens consisting of Muhammadiyah members and those who work and study or attend Muhammadiyah organizations. There are interesting objects to analyze because Muhammadiyah can collect waqf assets, especially cash waqf of Rp 2.4 trillion per year. This is a very large amount. If invested productively, the results or profits can be channelled for the progress and prosperity of the Muhammadiyah organization and Muslims. This research aims to determine the influence of the variables Waqf Literacy, Islamic Religiosity, Subjective Norm, Perceived Behavior Control, and Attitude in influencing the interest of Muhammadiyah citizens to become wakif. The analytical method used is quantitative with a Structural Equation Model (SEM) approach. The software used is SmartPLS 3.0. The sample used was 188 respondents from 14 provinces in Indonesia. This research indicates that Muhammadiyah citizens' interest in becoming wakif can be directly influenced by the variables of Islamic Religiosity and their Perceived Behavior Control (PBC). However, the indirect influence on Muhammadiyah's citizens' interest is insignificant. This result can be seen from the research results that the variables Islamic Religiosity, Waqf Literacy, Subjective Norm, PBC, and Attitude do not significantly influence the interest of Muhammadiyah citizens in becoming wakif. One of the causes of this insignificance is the direct influence between the Attitude variable and interest insignificantly. So, the implications of this research were increasing Islamic Religiosity and PBC in Muhammadiyah citizens becoming waqif. Implications for further research include adding or replacing variables that influence people's interest in becoming a waqif, are trust and transparency
Downloads
References
Ajzen, I. (1991). The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50, 179–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2018.1493416
Amin, H. (2022). An analysis of online sadaqah acceptance among university graduates in Malaysia. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 15(6), 1019–1034. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMEFM-01-2019-0020
Arianty, E., Ahmad, R., & Amalia, E. (2023). Strategy To Increase Waqf Intentions Through CWLS For Institutional Waqif As An Effort To Optimiza CWLS Fundraising. Proceeding of 3rd International Conference On Islamic Economics, Islamic Finance, & Islamic Law (ICIEIFIL) in Conjunction with 3rd International Conference on Islamic and Muhammadiyah Studies (ICIMS) 11-12 January 2023.
Baber, H. (2020). Intentions to participate in political crowdfunding- from the perspective of civic voluntarism model and theory of planned behavior. Technology in Society, 63(October), 101435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101435
Badan Pusat Statistik. (2022). Statistik Indonesia : Statistical Yearbook Of Indonesia 2022. In Statistik Indonesia 2022. Badan Pusat Statistik. https://www.bps.go.id/publication/2020/04/29/e9011b3155d45d70823c141f/statistik-indonesia-2020.html
Badan Wakaf Indonesia. (2010). Peraturan Badan Wakaf Indonesia Nomor 4 Tahun 2010 Tentang Pedoman Pengelolaan dan Pengembangan Harta Benda Wakaf.
Bosnjak, M., Ajzen, I., & Schmidt, P. (2020). The theory of planned behavior: Selected recent advances and applications. Europe’s Journal of Psychology, 16(3). https://doi.org/10.5964/ejop.v16i3.3107
Fahruroji. (2019). Wakaf Kontemporer. Badan Wakaf Indonesia.
Fawwaz, M. F. A., Juliana, J., Cakhyaneu, A., Muhammad, M., & Marlina, R. (2021). Waqf as Alternative Financing Resource for Infrastructure Development in Indonesia: Analytical Hierarchy Process Approach. Jurnal Kajian Peradaban Islam, 3(2), 50–58. https://doi.org/10.47076/jkpis.v3i2.53
Furqon, A. (2020, November 5). Selamat Datang Nazhir Wakaf Uang Persyarikatan Muhammadiyah. Tarjih.or.Id, 1–6. https://tarjih.or.id/selamat-datang-nazhir-wakaf-uang-persyarikatan-muhammadiyah
Ghozali, I. (2014). Structurar Equation Modeling, Metode Alternatif dengan Partial Least Square. Badan Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2013). Multivariate Data Analysis (7th Editio). Pearson.
Hamdani, T. (2020). Tak Disangka , Aset Tanah Muhammadiyah Capai 21 Juta Meter Persegi. DetikFinance. https://finance.detik.com/properti/d-5314359/tak-disangka-aset-tanah-muhammadiyah-capai-21-juta-meter-perseg
Haron, H., Mat Nor, F., Johari, F., Misbah, H., & Shafii, Z. (2023). Factors influencing the behavioural intention to accept benefidonor concept among stakeholders of Waqf. Journal of Islamic Accounting and Business Research, ahead-of-p(ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/JIABR-06-2022-0146
Huda, N., Hulmansyah, H., & Rini, N. (2018). Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Perilaku Konsumsi Produk Halal Pada Kalangan Mahasiswa Muslim. EKUITAS (Jurnal Ekonomi Dan Keuangan), 2(2), 247–270. https://doi.org/10.24034/j25485024.y2018.v2.i2.3944
Iman, A. K. N., Najiyah, F., & Asshiddiqi, M. (2021). Unfolding the possibility to develop share-waqf in Indonesia through the concepts, opportunities & challenges. Journal of Islamic Economic Laws, 4(1), 45–60. https://doi.org/10.23917/jisel.v4i1.12510
Johan, Z. J., Hussain, M. Z., Mohd, R., & Kamaruddin, B. H. (2020). Muslims and non-Muslims intention to hold Shariah-compliant credit cards: a SmartPLS approach. Journal of Islamic Marketing, ahead-of-p(ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-12-2019-0270
Kassim, M., Embi, N. A. C., Haron, R., & Ibrahim, K. (2023). The determinants of cash waqf re-endow intention in Malaysia. Al-Uqud : Journal of Islamic Economics, 7(1), 126–137. https://journal.unesa.ac.id/index.php/jie/article/view/17508
Komite Nasional Ekonomi dan Keuangan Syariah. (2021). Policy Brief : Business Process Re-engineering Wakaf Uang (Issue 2020).
Larasati, A., Hati, S. R. H., & Safira, A. (2018). Religiusitas dan Pengetahuan Terhadap Sikap dan Intensi Konsumen Muslim untuk Membeli Produk Kosmetik Halal. Esensi: Jurnal Bisnis Dan Manajemen, 8(2), 105–114. https://doi.org/10.15408/ess.v8i2.7459
Masrizal, M., Huda, N., Harahap, A., Trianto, B., & Sabi’u, T. T. (2023). Investigating the Determinants of Cash Waqf Intention: an Insight From Muslims in Indonesia. Journal of Islamic Monetary Economics and Finance, 9(1), 17–38. https://doi.org/10.21098/jimf.v9i1.1607
Muharromah, S., Huda, N., Muslikh, & Rini, N. (2021). Factors That Influence Public Interest In Choosing Islamic Bank Financing Products. Jurnal Organisasi Dan Manajemen, 17(1), 53–66. https://doi.org/10.33830/jom.v17i1.1085.2021
Mujahidah, A. S., & Rusydiana, A. S. (2023). Indonesian Muslim Youth - Factors Influencing Intention to Perform Cash Waqf. International Journal of Islamic Economics and Finance (IJIEF), 6(1), 53–72. https://doi.org/10.18196/ijief.v6i1.13964
Mutmainah, L., Ela Fauziyyah, N., Zadid Taqwa, K., & Wahyudi Indrawan, I. (2022). Cash Waqf Linked Blue Sukuk (CWLBS) For Sustainable Marine Ecosystem: a Conceptual Model (BWPS No. 3/PKTD/BWI/XI/2022).
Rini, N., Huda, N., & Anshori, M. (2023). Prioritas Masalah dan Solusi Pengembangan Wakaf Saham dari Aspek Nazhir. Jurnal EKOBIS: Ekonomi, Bisnis & Manajemen, 13(1), 56–76.
Rini, N., Huda, N., Anshori, M., Darodjatun, M. A. S. S., Zaenudin, Fofana, M., & Harumain, Y. A. S. (2024). Problems, Solutions, and Strategies For Developing Stock Waqf in Indonesia. Jurnal Ekonomi & Keuangan Islam, 10(1), 15–28. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.20885/JEKI.vol10.iss1.art2
Rizal, H., & Amin, H. (2017). Perceived Ihsan, Islamic Egalitarianism and Islamic Religiosity Towards Charitable Giving of Cash Waqf. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 8(4), 669–685. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-05-2015-0037
Sahal, A., Huda, N., & Setianingrum, A. (2020). Analisis Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Masyarakat Muslim Melakukan Wakaf Saham. Ekspansi: Jurnal Ekonomi, Keuangan, Perbankan Dan Akuntansi, 12(1), 43–64.
Saifudin, S., & Puspita, R. E. (2020). Predicting the Intention of Millennial Moslems to Visit Halal Tourism. Equilibrium: Jurnal Ekonomi Syariah, 8(1), 129. https://doi.org/10.21043/equilibrium.v8i1.7322
Sapir, A. S. M., Ruslan, R. N., & Tarusan, S. A. A. (2023). Examining the Demographic Factors Influencing Malaysians ’ Attitudes Toward Cash Waqf. International Journal of Business & Economic Studies, 5(1), 61–75. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.54821/uiecd.1117797
Suhaili, N. A., & Palil, M. R. (2017). Crowdfunding : A Collaborative Waqf Based Internet Platform. Kuala Lumpur International Islamic Studies and Civilisations Conference -: Al Maqasid As -Syariah as the Guiding Principles of the Past, Present and Future Life", 2(5), 41–46.
Utomo, S. B., Masyita, D., & Hastuti, F. (2020). Why Cash Waqf Fails to Meet the Expectation: Evidence from Indonesia. Working Paper OJK, August. https://ojk.go.id/id/data-dan-statistik/research/working-paper/Documents/WP-20-02.pdf
Zakaria, M. Z., Salleh, A. Z., Hasbullah, M., Ismail, A. M., & Jalil, M. A. A. (2019). Exploring Waqf-Based Takaful Fund As Financial Aid For The B40 Group in Malaysia. Al-Shajarah: Journal of the International Institute of Islamic Thought and Civilization (ISTAC), November, 149–168. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.31436/shajarah.v0i0.927.
Zawawi, A. A., Mariyanti, T., & Sari, S. N. (2023). Factors That Influence The Intention of The Millenial Community to do Waqf With a Modification Theory Planned Behavior Approach. APTISI Transactions on Management (ATM), 7(1), 41–53.
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Islamic Economic Laws

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



















