Impact of Mobile Money Access on Household Expenditures: A Case Study from Kenya
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/jep.v25i2.24199Abstract
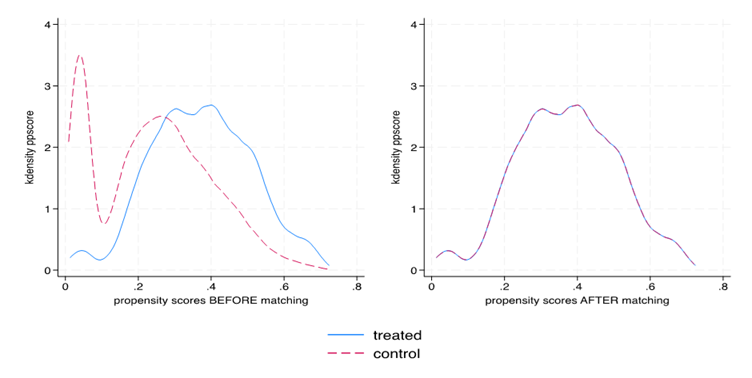
This paper investigates the impact of access to mobile money services on household expenditure patterns in Kenya – focusing on essential expenditures: food, rent, cellphone, and transport – using data from the 2021 FinAccess household survey, which includes 22,024 households (6,134 with mobile money access and 15,890 without), we employ propensity score matching (PSM) and inverse probability weighted regression adjustment (IPWRA) to address potential selection biases. The results demonstrate that access to mobile money services increases spending on food, cellphone, rent, and transport. This indicates that mobile money can be further promoted, and relevant stakeholders or policymakers may work to increase financial literacy. However, further research is necessary to assess the impacts of expanding mobile services on household welfare, especially in disadvantaged, remote, and vulnerable communities.
Downloads
Submitted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mussa Deme, Ghulam Dastgir Khan, MD. Abdul Bari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














