Main Article Content
Abstract
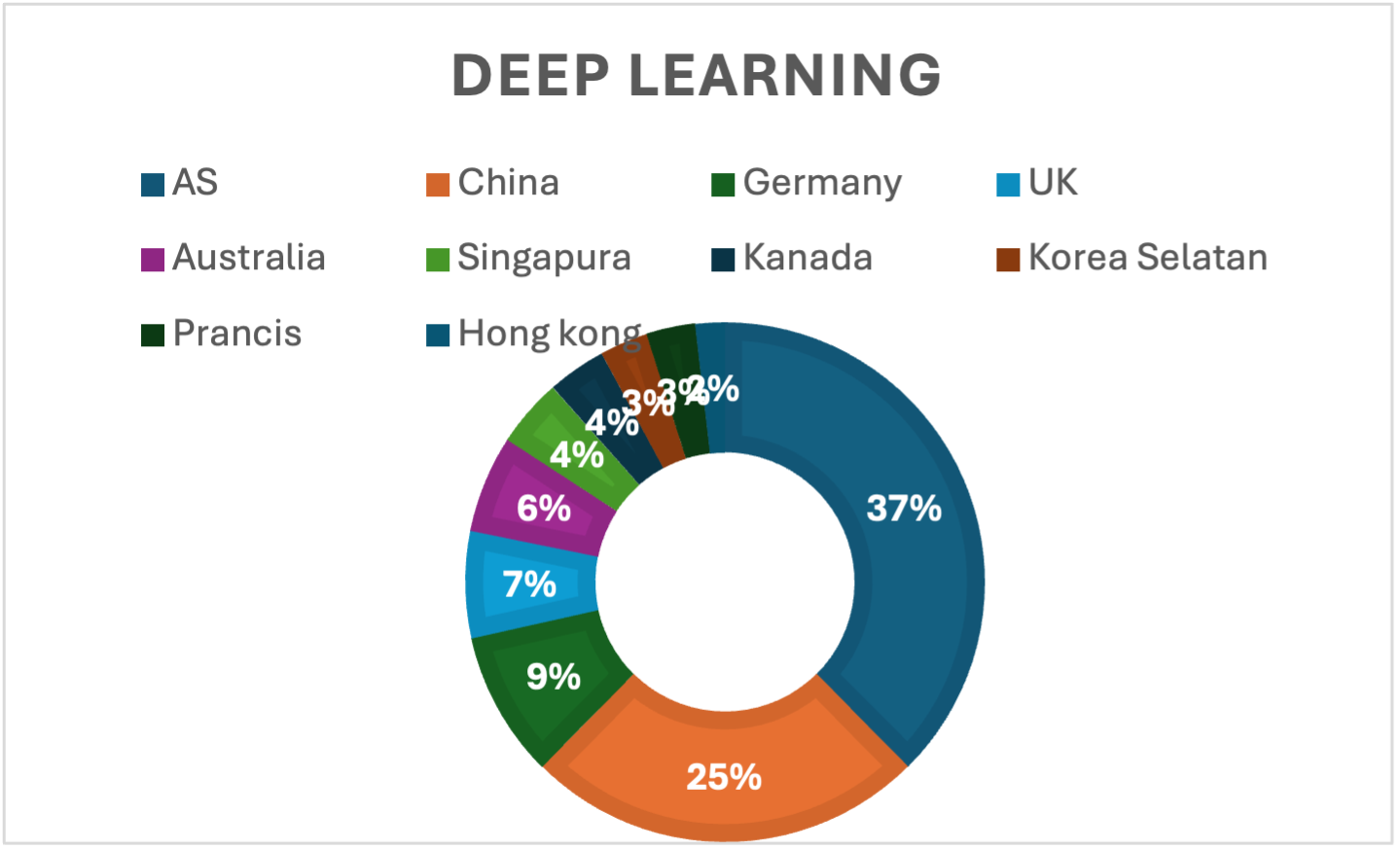
This study aims to evaluate the development, topic interconnections, and global research directions in the field of Deep Learning during the period 2019–2024, while also examining its implications for teaching statistical mathematics in the digital era. A bibliometric approach was used to analyze publication trends, citation patterns, and keyword relationships with the assistance of VOSviewer software. Data were obtained from the Scopus database using the main keywords “Deep Learning,” “Neural Networks,” and “Artificial Intelligence.” The results indicate that peak research activity occurred in 2022 with a significant surge in citations, followed by a decline in 2023–2024, marking a phase of research stabilization. Network analysis revealed that topics such as computer vision, medical imaging, and unsupervised learning dominate, while emerging trends like federated learning and edge computing are beginning to develop toward privacy and computational efficiency. Geographically, the United States and China are the main contributors to scientific publications, followed by Germany, the United Kingdom, and Australia. These findings highlight that the core success of Deep Learning is fundamentally grounded in statistical mathematics, particularly in optimization and probabilistic modeling. Accordingly, the implications for teaching statistical mathematics involve reorienting curricula toward applied, data-driven contexts emphasizing probabilistic thinking, algorithmic reasoning, and the integration of computational tools. Such an approach encourages students to bridge theoretical understanding with real-world problem solving in artificial intelligence and data science.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2025 Prima Crismono, Muhammad Akhyar Aji Saputra, Saman Hudi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
References
- Abdussamad, S. N. (2025). Statistika dalam era teknologi informasi. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/397783699_STATISTIKA_DALAM_ERA_TEKNOLOGI_INFORMASI/link/691eb7cec2a8e047ef3e3669/download?_tp=eyJjb250ZXh0Ijp7ImZpcnN0UGFnZSI6Il9kaXJlY3QiLCJwYWdlIjoicHVibGljYXRpb24iLCJwcmV2aW91c1BhZ2UiOiJfZGlyZWN0In19
- Abramson, J. (2024). Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature, 630(8016), 493–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07487-w
- Alzubaidi, L. (2021). Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. Journal of Big Data, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8
- Apriadi, E. A., Julianto, R., Dwiatmoko, F., Bisri, M., & Mukaromah, H. (2025). KECERDASAN BUATAN Teori, Implementasi, dan Aplikasi di Era Digital. Eko Aziz Apriadi. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=YtKOEQAAQBAJ
- Aria &, & Cuccurullo. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 4(11), 959–957. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
- Arrieta, A. B. (2020). Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Information Fusion, 58, 82–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012
- Bergmann, P. (2019). MVTEC ad-A comprehensive real-world dataset for unsupervised anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vol. 2019, pp. 9584–9592). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00982
- Buslaev, A. (2020). Albumentations: Fast and flexible image augmentations. Information (Switzerland), 11(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/info11020125
- Crismono, P. C. (2024). Metode Penelitian Pendidikan : Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, Ptk, dan Penelitian Pengembangan (F. Hanifiyah & I. Erdiansyah (eds.)). KHD Production.
- Deswita, R., & Ningsih, F. (2025). Innovation in Inferential Statistics Learning : Predict , Observe , and Explain ( POE ) -Based Teaching Materials to Optimizing Adaptive Reasoning. Journal of Ultimate Research and Trends in Education, 7(3), 194–212. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.31849/v7.I3
- Dong, X. (2020). A survey on ensemble learning. In Frontiers of Computer Science (Vol. 14, Issue 2, pp. 241–258). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-019-8208-z
- Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285–296. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
- Floridi, L. (2020). How to Design AI for Social Good: Seven Essential Factors. Science and Engineering Ethics, 26(3), 1771–1796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-020-00213-5
- Fuller, A. (2020). Digital Twin: Enabling Technologies, Challenges and Open Research. IEEE Access, 8, 108952–108971. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2998358
- Gou, J. (2021). Knowledge Distillation: A Survey. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129(6), 1789–1819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01453-z
- Hannun, A. Y. (2019). Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nature Medicine, 25(1), 65–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0268-3
- Istenič, A. (2021). Shifting to digital during COVID-19: are teachers empowered to give voice to students? In Educational Technology Research and Development (Vol. 69, Issue 1, pp. 43–46). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-021-09956-9
- Kaplan, A. (2020). Rulers of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of artificial intelligence. Business Horizons, 63(1), 37–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2019.09.003
- Khan, A. I. (2020). CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest x-ray images. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105581
- Lee, J. (2020). BioBERT: A pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics, 36(4), 1234–1240. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz682
- Lee, K. (2019). Meta-learning with differentiable convex optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vol. 2019, pp. 10649–10657). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01091
- Lei, Y. (2020). Applications of machine learning to machine fault diagnosis: A review and roadmap. In Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing (Vol. 138). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106587
- Liu, M. (2022). Research on the Impact of the Emotional Expression of Kindergarten Teachers on Children: From the Perspective of the Class Micro-Power Relationship. Frontiers in Psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.808847
- Marhawati, Mahmud, R., Nurdiana, Astuty, S., & Setyawan, D. A. (2022). STATISTIKA TERAPAN. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362127504_Statistika_Terapan/link/660d7d81f5a5de0a9ff761df/download?_tp=eyJjb250ZXh0Ijp7ImZpcnN0UGFnZSI6InB1YmxpY2F0aW9uIiwicGFnZSI6InB1YmxpY2F0aW9uIn19
- Mehrabi, N. (2022). A Survey on Bias and Fairness in Machine Learning. In ACM Computing Surveys (Vol. 54, Issue 6). https://doi.org/10.1145/3457607
- Mulianah, Thalib, A., Habsyi, R., & Ahmad, A. (2025). Pengaruh Kecerdasan Logis Matematis , Interpersonal , Visual Spasial , Dan Eksistensial Terhadap Prestasi Belajar Transformasi Geometri. Jurnal Ilmiah Matematika, 6(2), 668–680. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.63976/jimat.v6i2.1103
- Nishio, T. (2019). Client Selection for Federated Learning with Heterogeneous Resources in Mobile Edge. In IEEE International Conference on Communications (Vol. 2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICC.2019.8761315
- Nurazizah, E., & Jana, P. (2022). PENGEMBANGAN LKPD MATEMATIKA BERBASIS OPEN ENDED PROBLEM BERORIENTASI LITERASI. Jurnal Gammath, 7(2), 133–142.
- Pouyanfar, S. (2019). A survey on deep learning: Algorithms, techniques, and applications. In ACM Computing Surveys (Vol. 51, Issue 5). https://doi.org/10.1145/3234150
- Qin, S. J. (2019). Advances and opportunities in machine learning for process data analytics. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 126, 465–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.04.003
- Sattler, F. (2020). Robust and Communication-Efficient Federated Learning from Non-i.i.d. Data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 31(9), 3400–3413. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2944481
- Sebastian, A. (2020). Memory devices and applications for in-memory computing. In Nature Nanotechnology (Vol. 15, Issue 7, pp. 529–544). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0655-z
- Shorten, C. (2019). A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. Journal of Big Data, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0197-0
- Siddique, N. (2021). U-Net and Its Variants for Medical Image Segmentation: A Review of Theory and Applications. IEEE Access, 9, 82031–82057. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3086020
- Tan, M. (2019). Mnasnet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vol. 2019, pp. 2815–2823). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00293
- Tekdal, M. (2021). Trends and development in research on computational thinking. Education and Information Technologies, 26(5), 6499–6529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10617-w
- Vamathevan, J. (2019). Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development. In Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (Vol. 18, Issue 6, pp. 463–477). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0024-5
- van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
- Veličković, P. (2019). Deep graph infomax. In 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2019. https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85083950577&origin=inward
- Wang, L. (2020). COVID-Net: a tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Scientific Reports, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76550-z
- Wang, Q. (2020). ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 11531–11539). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155
- Wu, W. (2019). PointCONV: Deep convolutional networks on 3D point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vol. 2019, pp. 9613–9622). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00985
- Wu, Z. (2019). Wider or Deeper: Revisiting the ResNet Model for Visual Recognition. Pattern Recognition, 90, 119–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.01.006
- Wu, Z. (2021). A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 32(1), 4–24. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2978386
- Xiong, G. (2021). ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Research, 49. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab255
- Zhang, Y. (2021). TransFuse: Fusing Transformers and CNNs for Medical Image Segmentation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) (Vol. 12901, pp. 14–24). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_2
- Zhou, J. (2020). Graph neural networks: A review of methods and applications. In AI Open (Vol. 1, pp. 57–81). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aiopen.2021.01.001
References
Abdussamad, S. N. (2025). Statistika dalam era teknologi informasi. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/397783699_STATISTIKA_DALAM_ERA_TEKNOLOGI_INFORMASI/link/691eb7cec2a8e047ef3e3669/download?_tp=eyJjb250ZXh0Ijp7ImZpcnN0UGFnZSI6Il9kaXJlY3QiLCJwYWdlIjoicHVibGljYXRpb24iLCJwcmV2aW91c1BhZ2UiOiJfZGlyZWN0In19
Abramson, J. (2024). Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature, 630(8016), 493–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07487-w
Alzubaidi, L. (2021). Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. Journal of Big Data, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8
Apriadi, E. A., Julianto, R., Dwiatmoko, F., Bisri, M., & Mukaromah, H. (2025). KECERDASAN BUATAN Teori, Implementasi, dan Aplikasi di Era Digital. Eko Aziz Apriadi. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=YtKOEQAAQBAJ
Aria &, & Cuccurullo. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 4(11), 959–957. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Arrieta, A. B. (2020). Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Information Fusion, 58, 82–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012
Bergmann, P. (2019). MVTEC ad-A comprehensive real-world dataset for unsupervised anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vol. 2019, pp. 9584–9592). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00982
Buslaev, A. (2020). Albumentations: Fast and flexible image augmentations. Information (Switzerland), 11(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/info11020125
Crismono, P. C. (2024). Metode Penelitian Pendidikan : Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, Ptk, dan Penelitian Pengembangan (F. Hanifiyah & I. Erdiansyah (eds.)). KHD Production.
Deswita, R., & Ningsih, F. (2025). Innovation in Inferential Statistics Learning : Predict , Observe , and Explain ( POE ) -Based Teaching Materials to Optimizing Adaptive Reasoning. Journal of Ultimate Research and Trends in Education, 7(3), 194–212. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.31849/v7.I3
Dong, X. (2020). A survey on ensemble learning. In Frontiers of Computer Science (Vol. 14, Issue 2, pp. 241–258). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-019-8208-z
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285–296. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Floridi, L. (2020). How to Design AI for Social Good: Seven Essential Factors. Science and Engineering Ethics, 26(3), 1771–1796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-020-00213-5
Fuller, A. (2020). Digital Twin: Enabling Technologies, Challenges and Open Research. IEEE Access, 8, 108952–108971. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2998358
Gou, J. (2021). Knowledge Distillation: A Survey. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129(6), 1789–1819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01453-z
Hannun, A. Y. (2019). Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nature Medicine, 25(1), 65–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0268-3
Istenič, A. (2021). Shifting to digital during COVID-19: are teachers empowered to give voice to students? In Educational Technology Research and Development (Vol. 69, Issue 1, pp. 43–46). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-021-09956-9
Kaplan, A. (2020). Rulers of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of artificial intelligence. Business Horizons, 63(1), 37–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2019.09.003
Khan, A. I. (2020). CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest x-ray images. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105581
Lee, J. (2020). BioBERT: A pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics, 36(4), 1234–1240. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz682
Lee, K. (2019). Meta-learning with differentiable convex optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vol. 2019, pp. 10649–10657). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.01091
Lei, Y. (2020). Applications of machine learning to machine fault diagnosis: A review and roadmap. In Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing (Vol. 138). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106587
Liu, M. (2022). Research on the Impact of the Emotional Expression of Kindergarten Teachers on Children: From the Perspective of the Class Micro-Power Relationship. Frontiers in Psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.808847
Marhawati, Mahmud, R., Nurdiana, Astuty, S., & Setyawan, D. A. (2022). STATISTIKA TERAPAN. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362127504_Statistika_Terapan/link/660d7d81f5a5de0a9ff761df/download?_tp=eyJjb250ZXh0Ijp7ImZpcnN0UGFnZSI6InB1YmxpY2F0aW9uIiwicGFnZSI6InB1YmxpY2F0aW9uIn19
Mehrabi, N. (2022). A Survey on Bias and Fairness in Machine Learning. In ACM Computing Surveys (Vol. 54, Issue 6). https://doi.org/10.1145/3457607
Mulianah, Thalib, A., Habsyi, R., & Ahmad, A. (2025). Pengaruh Kecerdasan Logis Matematis , Interpersonal , Visual Spasial , Dan Eksistensial Terhadap Prestasi Belajar Transformasi Geometri. Jurnal Ilmiah Matematika, 6(2), 668–680. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.63976/jimat.v6i2.1103
Nishio, T. (2019). Client Selection for Federated Learning with Heterogeneous Resources in Mobile Edge. In IEEE International Conference on Communications (Vol. 2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICC.2019.8761315
Nurazizah, E., & Jana, P. (2022). PENGEMBANGAN LKPD MATEMATIKA BERBASIS OPEN ENDED PROBLEM BERORIENTASI LITERASI. Jurnal Gammath, 7(2), 133–142.
Pouyanfar, S. (2019). A survey on deep learning: Algorithms, techniques, and applications. In ACM Computing Surveys (Vol. 51, Issue 5). https://doi.org/10.1145/3234150
Qin, S. J. (2019). Advances and opportunities in machine learning for process data analytics. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 126, 465–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.04.003
Sattler, F. (2020). Robust and Communication-Efficient Federated Learning from Non-i.i.d. Data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 31(9), 3400–3413. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2944481
Sebastian, A. (2020). Memory devices and applications for in-memory computing. In Nature Nanotechnology (Vol. 15, Issue 7, pp. 529–544). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0655-z
Shorten, C. (2019). A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. Journal of Big Data, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0197-0
Siddique, N. (2021). U-Net and Its Variants for Medical Image Segmentation: A Review of Theory and Applications. IEEE Access, 9, 82031–82057. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3086020
Tan, M. (2019). Mnasnet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vol. 2019, pp. 2815–2823). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00293
Tekdal, M. (2021). Trends and development in research on computational thinking. Education and Information Technologies, 26(5), 6499–6529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10617-w
Vamathevan, J. (2019). Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development. In Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (Vol. 18, Issue 6, pp. 463–477). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0024-5
van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Veličković, P. (2019). Deep graph infomax. In 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2019. https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85083950577&origin=inward
Wang, L. (2020). COVID-Net: a tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Scientific Reports, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76550-z
Wang, Q. (2020). ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 11531–11539). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155
Wu, W. (2019). PointCONV: Deep convolutional networks on 3D point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Vol. 2019, pp. 9613–9622). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00985
Wu, Z. (2019). Wider or Deeper: Revisiting the ResNet Model for Visual Recognition. Pattern Recognition, 90, 119–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.01.006
Wu, Z. (2021). A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 32(1), 4–24. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2978386
Xiong, G. (2021). ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Research, 49. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab255
Zhang, Y. (2021). TransFuse: Fusing Transformers and CNNs for Medical Image Segmentation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) (Vol. 12901, pp. 14–24). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_2
Zhou, J. (2020). Graph neural networks: A review of methods and applications. In AI Open (Vol. 1, pp. 57–81). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aiopen.2021.01.001