Self-Management Counseling Increases Compliance in Diabetes Mellitus Patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/bik.v18i2.8759Keywords:
compliance, Diabetes mellitus, Self-Management Counseling, Transtheoretical ModelAbstract
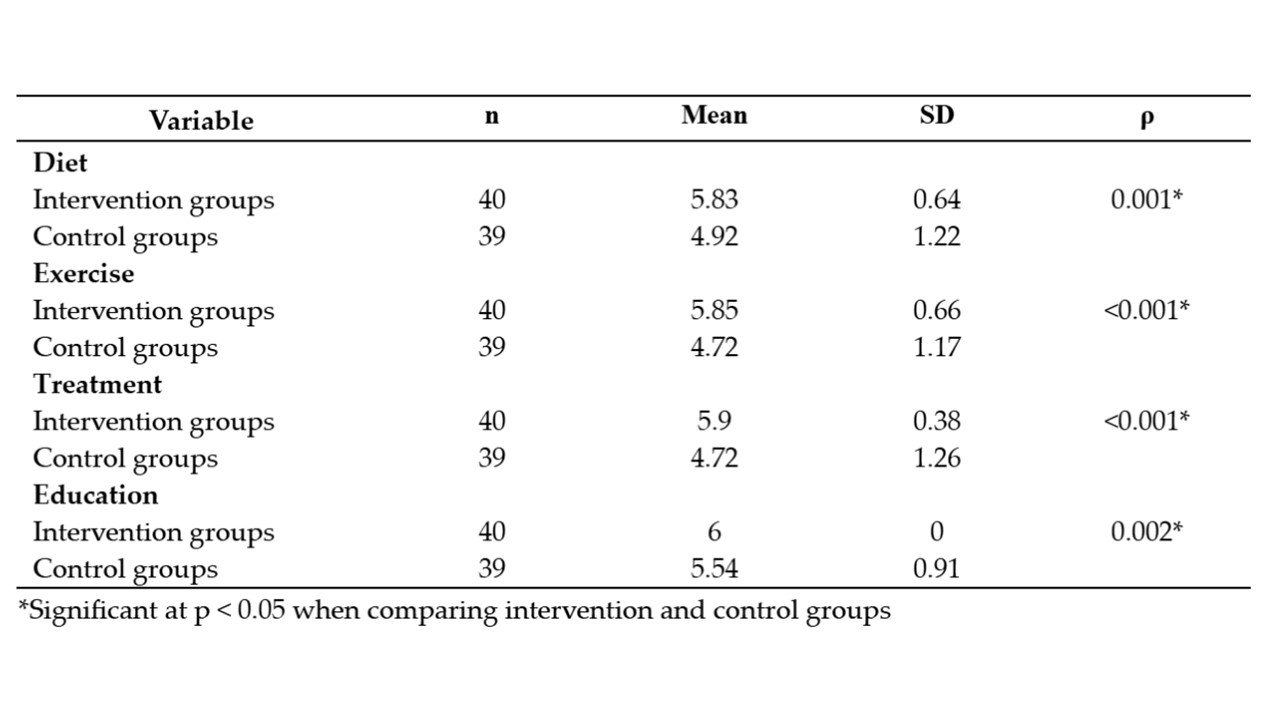
People with diabetes mellitus (DM) can experience various complications if they do not have a good lifestyle. People with DM must comply with medication, physical activity, diet, and education to improve a healthy lifestyle. One effort that can be made to improve compliance is to provide Self-Management Counseling (SMC) with the Transtheoretical Model (TTM) approach. This quasi-experimental study involved two groups of DM patients. 79 respondents were selected with the criteria of not having the disease and having diabetes for 2 years. Respondents were divided into an intervention group (40 people) and a control group (39). The results showed that there were differences in compliance with diet (p = 0.001), activity (p = <0.001), treatment (p = <0.001), and education (p = 0.002) between the intervention group and the control group. Therefore, it can be concluded that SMC with the TTM approach has proven effective in improving compliance with type 2 diabetes patients—both compliance with diet, activity, treatment, and education.
Downloads
References
Abu-Saad, K., Murad, H., Barid, R., Olmer, L., Ziv, A., Younis-Zeidan, N., … Kalter-Leibovici, O. (2019). Development and efficacy of an electronic, culturally adapted lifestyle counseling tool for improving diabetes-related dietary knowledge: Randomized controlled trial among ethnic minority adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 21(10). https://doi.org/10.2196/13674 PubMed: 31621640
Anoop, K. R., & Kiron, S. S. (2021). Effect of Electronic Mode of Patient Counseling On Improving The Outcome of Treatment For Diabetes Mellitus In Rural Population of Kerala. European Journal of Biomedical and Phamaceutical Sciences, 8(3), 173–180. https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/J85XY
Bekele, H., Asefa, A., Getachew, B., & Belete, A. M. (2020). Barriers and Strategies to Lifestyle and Dietary Pattern Interventions for Prevention and Management of TYPE-2 Diabetes in Africa, Systematic Review. Journal of Diabetes Research, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7948712 PubMed: 32766315
Bossman, I. F., Dare, S., Oduro, B. A., Baffour, P. K., Hinneh, T. K., & Nally, J. E. (2021). Patients’ knowledge of diabetes foot complications and self-management practices in Ghana: A phenomenological study. PLoS ONE, 16(8 August), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256417 PubMed: 34432838
Cannata, F., Vadala, G., Russo, F., Papalia, R., Napoli, N., & Pozzilli, P. (2020). Beneficial Effects of Physical Activity in Diabetic Patients. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 5(70), 1–11. https://doi.org/doi:10.3390/jfmk5030070 PubMed: 33467285
Dunkel, A., von Storch, K., Hochheim, M., Zank, S., Polidori, M. C., & Woopen, C. (2024). Long‑Term Effects of Transtheoretical Model‑Based Lifestyle Intervention on Self‑efficacy and Self‑management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes — Randomised Controlled Trial. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 23(1), 519–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01290-6 PubMed: 39349794
Farahani, I., Laeer, S., Farahani, S., Schwender, H., & Laven, A. (2020). Blended learning: Improving the diabetes mellitus counseling skills of German pharmacy students. Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning, 12(8), 963–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cptl.2020.04.016 PubMed: 32564999
Galstyan, G. R., Valeeva, F. V., Motkova, S. I., Surkova, E. V., Savelyeva, L. V., Rudina, L. M., … Shestakova, M. V. (2021). Lifestyle modification program, LIFE is LIGHT, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: Results from a 48-week, multicenter, non-randomized, parallel-group, open-label study. Obesity Science and Practice, 7(4), 368–378. https://doi.org/10.1002/osp4.502 PubMed: 34401196
Hjelm, K., Bard, K., & Apelqvist, J. (2022). Gestational diabetes: Changed health beliefs in migrant women from five Asian countries living in Sweden: A prospective qualitative study. Primary Health Care Research and Development, 23(e2), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1463423621000785 PubMed: 35016742
Imeri, H., Toth, J., Arnold, A., & Barnard, M. (2022). Use of the transtheoretical model in medication adherence: A systematic review. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 18(5), 2778–2785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2021.07.008 PubMed: 34275751
Jalilian, M., Sarbarzeh, P. A., & Oubari, S. (2020). Factors related to severity of diabetic foot ulcer: A systematic review. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity, 13, 1835–1842. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S256243 PubMed: 32547145
Ji, L., Ma, J., Lu, W., Liu, J., Zeng, J., Yang, J., … Wang, Y. (2021). Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of teneligliptin monotherapy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise. Journal of Diabetes Investigation, 12(4), 537–545. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13389 PubMed: 32810383
Jiménez-Zazo, F., Romero-Blanco, C., Castro-Lemus, N., Dorado-Suárez, A., & Aznar, S. (2020). Transtheoretical model for physical activity in older adults: Systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249262
Kementerian Kesehatan. (2018). Riskesdas 2018. Jakarta: Kementrian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia.
Khan, M. (2024). Triplica Counseling for Diabetic Patient with Co-Existent Hepatitis: Public Health Awareness Glance. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 53(3), 744–746. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijph.v53i3.15160 PubMed: 38919302
Kusnanto, K., Arifin, H., & Widyawati, I. Y. (2020). A qualitative study exploring diabetes resilience among adults with regulated type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews, 14(6), 1681–1687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.08.035 PubMed: 32905940
Lee, S.-Y., Renner, S., Kovacic, M. B., & Lee, R. (2022). Food Literacy Education During Nutrition Counseling for Patients With Diabetes: In-Depth Interviews With Registered Dietitians/Registered Dietitians Nutritionists. Current Developments in Nutrition, 6, 848. https://doi.org/10.1093/cdn/nzac065.032
Medhat, M., Sabry, N., & Ashoush, N. (2020). Knowledge, attitude and practice of community pharmacists towards nutrition counseling. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy, 42(6), 1456–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-020-01106-0 PubMed: 32860597
Molavynejad, S., Miladinia, M., & Jahangiri, M. (2022). A randomized trial of comparing video telecare education vs. in-person education on dietary regimen compliance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a support for clinical telehealth Providers. BMC Endocrine Disorders, 22(116), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-022-01032-4 PubMed: 35501846
Niu, Y. L., Zhang, Y., Song, Z. Y., Zhao, C. Z., Luo, Y., Wang, Y., & Yuan, J. (2024). Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart versus Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 53(2), 313–322. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijph.v53i2.14916 PubMed: 38894842
Nkhoma, D. E., Soko, C. J., Banda, K. J., Greenfield, D., Li, Y. C., & Iqbal, U. (2021). Impact of DSMES app interventions on medication adherence in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Health and Care Informatics, 28(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjhci-2020-100291 PubMed: 33853862
Patnode, C. D., Redmond, N., Lacocca, M. O., & Henninger, M. (2022). Behavioral Counseling Interventions to Promote a Healthy Diet and Physical Activity for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Adults Without Known Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors. Update Evidence Report and Syatematic eview for the US Preventive Servic. Jama, 328(4), 367–374. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.10951 PubMed: 35881116
Peimani, M., Esfahani, Z., Bandarian, F., Esmaeili, S., Moghaddam, S. S., Namazi, N., … Larijani, B. (2024). The Burden of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Attributable Risk Factors in Iran, 1990–2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 53(4), 913–923. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijph.v53i4.15569 PubMed: 39444467
Pennington, C. G. (2021). Applying the Transtheoretical Model of Behavioral Change to Establish Physical Activity Habits. Journal of Education and Recreation Patterns, 2(1), 11–20. https://doi.org/10.53016/jerp.v2i1.6
Sanz-Cánovas, J., López-Sampalo, A., Cobos-Palacios, L., Ricci, M., Hernández-Negrín, H., Mancebo-Sevilla, J. J., … Bernal-López, M. R. (2022). Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Elderly Patients with Frailty and/or Sarcopenia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148677 PubMed: 35886528
Sarmadika, M., Mazandarani, A., Faramarzi, E., & Ehsani, A. (2022). The effect of dietary counseling and medical nutrition therapy on HbA1c levels in patients with diabetes in Imam Reza hospital of Tabriz, Iran. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 2(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2017
van Netten, J. J., Raspovic, A., Lavery, L. A., Monteiro-Soares, M., Paton, J., Rasmussen, A., … Bus, S. A. (2024). Prevention of foot ulcers in persons with diabetes at risk of ulceration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, 40(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3652 PubMed: 37243880
WHO. (2024). Diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes#tab=tab_1
Yang, J. J., Yu, D., Wen, W., Saito, E., Rahman, S., Shu, X. O., … Zheng, W. (2019). Association of Diabetes with All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in Asia: A Pooled Analysis of More Than 1 Million Participants. JAMA Network Open, 2(4), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.2696 PubMed: 31002328
Zhang, B., Kalampakorn, S., Powwattana, A., Sillabutra, J., & Liu, G. (2024). A Transtheoretical Model-Based Online Intervention to Improve Medication Adherence for Chinese Adults Newly Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes: A Mixed-Method Study. Journal of Primary Care and Community Health, 15, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/21501319241263657 PubMed: 39077970
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mulyaningsih Mulyaningsih, Noviana Ayu Ardika , Wahyuni, Hermawati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


















