The Effect of Combining Isometric Handgrip Exercise with Sundanese Degung Instrumental Music on Blood Pressure Changes in Elderly People with Hypertension
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/bik.v17i1.3209Keywords:
Blood pressure, Sundanese, Song, Degung, Hypertension, Isometric handgrip ExerciseAbstract
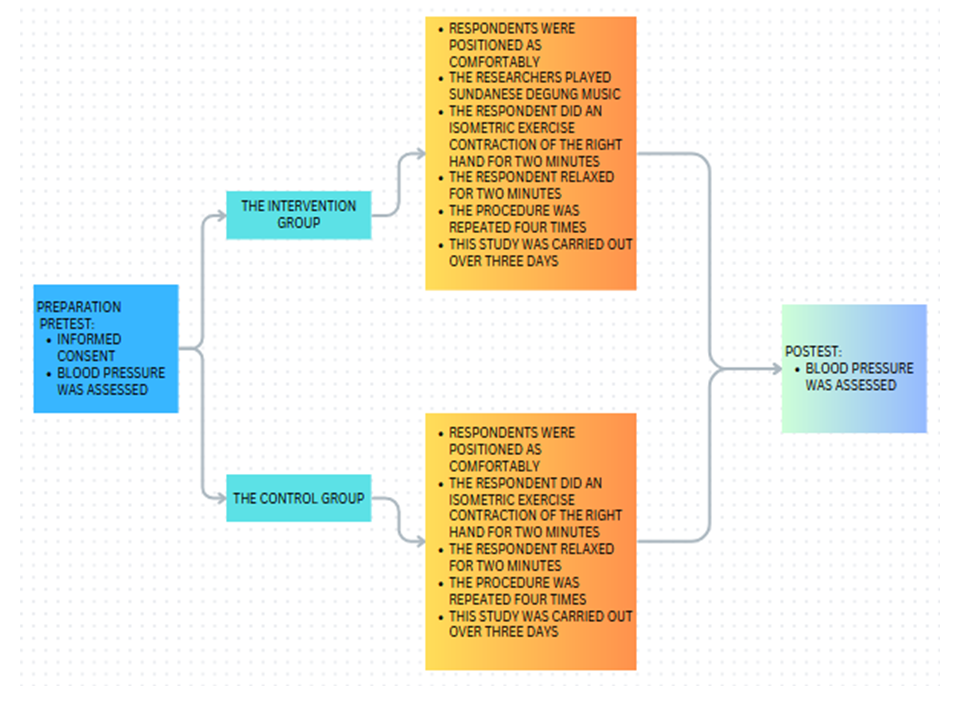
Hypertension is defined as a condition that blood pressure is more than 140/90 mmHg. Because the aging process causes blood vessels to stiffen and the elasticity of the ventricular walls to decrease, the elderly are categorized as a health susceptible category. This disorder can lead to hypertension, which can have catastrophic effects such as stroke and even death. The purpose of this study was to determine isometric handgrip exercise (IHE) therapy accompanied by degung instrumental music affects blood pressure changes in elderly people with hypertension. A quantitative design with a quasi-experimental approach, pretest and post-test methodologies, and a control group was used for the study. The sample strategy employed in this study will be non-probability sampling (purposive sampling). 59 samples were collected and divided into intervention and control groups. This study lasted 2 × 2 minutes, was interrupted by 3 minutes of rest, and was conducted on three consecutive days. The result of study showhed that the Sig (2-tailed) value was 0.00, indicating that there is an influence between the Isometric Handgrip Exercise intervention accompanied by Sundanese degung instrumental music on blood pressure changes in elderly people with hypertension. The IHE intervention accompanied by Sundanese degung instrumental music is recommended as IHE in decreasing blood pressure in hypertension patients
Downloads
References
Carlson, D. J., & et.al. (2016). The efficacy of isometric resistance training utilizing handgrip exercise for blood pressure management: A randomized trial. Medicine (United States), 95(52). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000005791 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000005791
Choirillaily, S., & et.al. (2020). Isometric Handgrip Exercise Lowers Blood Pressure in Hypertension Sufferers. Jurnal Keterapian Fisik, Volume 5, 62–146.
Enisah, E., Ernawati, D., Hendrawati, D., Rahayu, D., & Rachmawati, E. (2021). Systematic Review: Isometric Handgrip Exercise In Elderly With Hypertension. Pancasakti Journal Of Public Health Science And Research, 1(2), 81–91. https://doi.org/10.47650/pjphsr.v1i2.242 DOI: https://doi.org/10.47650/pjphsr.v1i2.242
Gede, P., & et.al, &. (2020). Literature Review : Pemberian Terapi Musik Terhadap Tekanan Darah Pada Lansia Dengan Hipertensi ( Literature Review : Providing of Music Therapy on Blood Pressure in Elderly with Hypertension ). 1–12.
Handayani, K. P., Johan, A., & Ropyanto, C. B. (2018). The influence of sundanese zither (KACAPI) music therapy on anxiety levels in pre-cardiac catheterization patients. Belitung Nursing Journal, 4(2), 256–262. https://doi.org/10.33546/bnj.125 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33546/bnj.125
John, L. (2021). The validity and reliability of ratings of perceived exertion (RPE) in isometric exercise training for the reductions of arterial blood pressure.
Kühlmann, A. Y. R., & et.al. (2016). Systematic review and meta-analysis of music interventions in hypertension treatment: A quest for answers. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 16(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-016-0244-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-016-0244-0
Kunutsor, S. K., Mäkikallio, T. H., Voutilainen, A., Hupin, D., & Laukkanen, J. A. (2021). Normalized handgrip strength and future risk of hypertension: findings from a prospective cohort study. Scandinavian Cardiovascular Journal, 55(6), 336–339. https://doi.org/10.1080/14017431.2021.1983206 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14017431.2021.1983206
Lea, J. W. D. (2021). The validity and reliability of ratings of perceived exertion (RPE) in isometric exercise training for the reductions of arterial blood pressure. Canterbury Christ Church University (United Kingdom).
Loaiza-Betancur, & et.al. (2020). Is Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Exercise an Efficient Alternative in Lifestyle Blood Pressure Management? A Systematic Review. Sports Health, 12(5), 470–477. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738120943882 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738120943882
Maisi, S., & et.al. (2017). Effectiveness of Lavender Aromatherapy and Classical Music Therapy in Lowering Blood Pressure in Pregnant Women With Hypertension. Belitung Nursing Journal, 3(6), 750–756. https://doi.org/10.33546/bnj.301 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33546/bnj.301
Mayasari, A. C., & et.al. (2022). Relationship between Family Support and Elderly Independence in Fulfilling Daily Activities. Malaysian Journal of Medical Research, 06(04), 15–19. https://doi.org/10.31674/mjmr.2022.v06i04.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31674/mjmr.2022.v06i04.003
Salami, S., Dewi, I. P., & Sajodin, S. (2018). Implementasi Fungsi Keluarga Dan Self Care Behavior Lansia Hipertensi Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Cijagra Lama Bandung. Jurnal Keperawatan ’Aisyiyah, 4(2), 79–85. https://doi.org/10.33867/jka.v4i2.45 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33867/jka.v4i2.45
Shah, S. A., & et.al. (2022). Factors Associated with Handgrip Strength Among Older Adults in Malaysia. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, 15, 1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S363421 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S363421
Tzourio, C. (2019). Hypertension, cognitive decline, and dementia: An epidemiological perspective. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 9(1), 61–70. https://doi.org/10.31887/dcns.2007.9.1/ctzourio DOI: https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2007.9.1/ctzourio
Widiastuti, A., Ulkhasanah, M. E., & Irawan, A. (2021). Isometric Handgrip Exercise Terhadap Tekanan Darah dan Nadi Pada Hipertensi: Literatur Review. Coping: Community of Publishing in Nursing; Vol 9 No 6 (2021): Desember 2021, 9(6), 663–671. https://doi.org/10.24843/coping.2021.v09.i06.p05
Yulinda, N., & Kusumawardani, L. H. (2023). Effect of Complementary Therapy Combination of Progressive Muscle Relaxation and Music Therapy ( RESIK ) to Lower Blood Pressure in the Elderly. 34–40. https://doi.org/10.33221/jiiki.v13i01.2260 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33221/jiiki.v13i01.2260
Zainuddin, R. N., & Labdullah, P. (2020). Efektivitas Isometric Handgrip Exercise dalam Menurunkan Tekanan Darah pada Pasien Hipertensi. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan Sandi Husada, 12(2), 615–624. https://doi.org/10.35816/jiskh.v12i2.364 DOI: https://doi.org/10.35816/jiskh.v12i2.364
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Sajodin Sajodin, Nandang, Riscka

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


















