Behavior of Indonesian Nurses Toward Non-Reported Needle Stick Injury in Saudi Arabia: A Phenomenological Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/bik.v16i2.1882Abstract
Non-reported needle stick injury (NSI) is still a major problem faced by nurses when working in health services in Saudi Arabia viewed from the perspective of occupational health and safety (OHS). Knowing the behavior of nurses in the workplace can have implications for the OHS culture. Objective: To explore the behavior of Indonesian nurses towards non-reported NSI in health services in Saudi Arabia. This study used a qualitative method with a phenomenological approach. The research subjects used typical case sampling of 12 Indonesian nurses who had work experience regarding NSI. In-depth interviews with structured questions were conducted with respondents following guidelines for data analysis using a seven step analysis by Colaizzi and Nvivo software. There were 13 categories from 4 themes found in this research about knowledge, behavior and skills also management of exposure and post exposure. The behavior of Indonesian nurses towards non-reported needle stick injury based on experience has been carried out even though the behavior, especially knowledge, attitude and skills policy on management of needle stick injury needs improvement.
Downloads
References
Abalkhail, A., Kabir, R., Elmosaad, Y. M., Alwashmi, A. S. S., Alhumaydhi, F. A., Alslamah, T., Almoammar, K. A., Alsalamah, Y. A., & Mahmud, I. (2022). Needle-Stick and Sharp Injuries among Hospital Healthcare Workers in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106342
Al-qahtani, S. M., Elzahrany, Y. R., Alahmed, M. A., Alanezi, S. L., Marei, R. O., Alqhtani, A. D., Alqahtani, R. S., & Kofi, M. (2022). Prevalence , Underreporting and Barriers of Needle Stick and Sharps Injuries ( NSSIs ) among Nurses at Primary Healthcare Centers , Riyadh , Saudi Arabia. 5(02), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.29011/2688-7460.100067
Al Shaikh, H. A., Al Mahdi, M. M., & Naik, B. R. (2019). Sharps injuries among health care workers in Al Ahsa region, Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Infection Control, 15(4). https://doi.org/10.3396/ijic.v15i4.017.19
Alfulayw, K. H., Al-Otaibi, S. T., & Alqahtani, H. A. (2021). Factors associated with needlestick injuries among healthcare workers: implications for prevention. BMC Health Services Research, 21(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07110-y
Alharazi, R., Almutary, H., Felemban, O., Alariany, A. S., Alshamrani, F. A., Hawsawi, E. H., & Alsulami, L. M. (2022). Prevalence of Needle Stick Injuries Among Nurses in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Nursing: Research and Reviews, Volume 12(December), 235–246. https://doi.org/10.2147/nrr.s376343
Alluhidan, M., Tashkandi, N., Alblowi, F., Omer, T., Alghaith, T., Alghodaier, H., Alazemi, N., Tulenko, K., Herbst, C. H., Hamza, M. M., & Alghamdi, M. G. (2020). Challenges and policy opportunities in nursing in Saudi Arabia. Human Resources for Health, 18(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12960-020-00535-2
Almasoud, M. (2021). Study on How to Established National Occupational Health and Safety at Institute in Saudi Arabia. In Gnana Sheela K (Ed.), New Visions in Science and Technology Vol. 2 (First Edit, Vol. 2, Issue September). BP International. https://doi.org/10.9734/bpi/nvst/v2
Alsabaani, A., Alqahtani, N. S. S., Alqahtani, S. S. S., Al-Lugbi, J. H. J., Asiri, M. A. S., Salem, S. E. E., Alasmari, A. A., Mahmood, S. E., & Alalyani, M. (2022). Incidence, Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Toward Needle Stick Injury Among Health Care Workers in Abha City, Saudi Arabia. Frontiers in Public Health, 10, 771190. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.771190
Andriani, L. (2018). Penerapan Universal Precaution Untuk Pencegahan Penularan Hiv-Aids. Jurnal Media Kesehatan, 7(1), 62–68. https://doi.org/10.33088/jmk.v7i1.225
Bouya, S., Balouchi, A., Rafiemanesh, H., Amirshahi, M., Dastres, M., Moghadam, M. P., Behnamfar, N., Shyeback, M., Badakhsh, M., Allahyari, J., Al Mawali, A., Ebadi, A., Dezhkam, A., & Daley, K. A. (2020). Global Prevalence and Device Related Causes of Needle Stick Injuries among Health Care Workers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Annals of Global Health, 86(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.5334/aogh.2698
Dessalines, S. (2021). Investigating the Effects of an Occupational Safety Course on Needlestick Injury Prevention and Incident Reporting for Emergency Department Registered Nurses: A Quality Improvement Project. Nicole Wertheim College of Nursing Student Projects., 1(2022), 165. https://digitalcommons.fiu.edu/cnhs-studentprojects/165
Fahruddin, A. (2022). Evaluation of Social Security System Implementation for Indonesian Nurses in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia : A Case Study. Jurnal Berita Ilmu Keperawtan, 15(285), 285–292. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.23917/bik.v15i2.17553
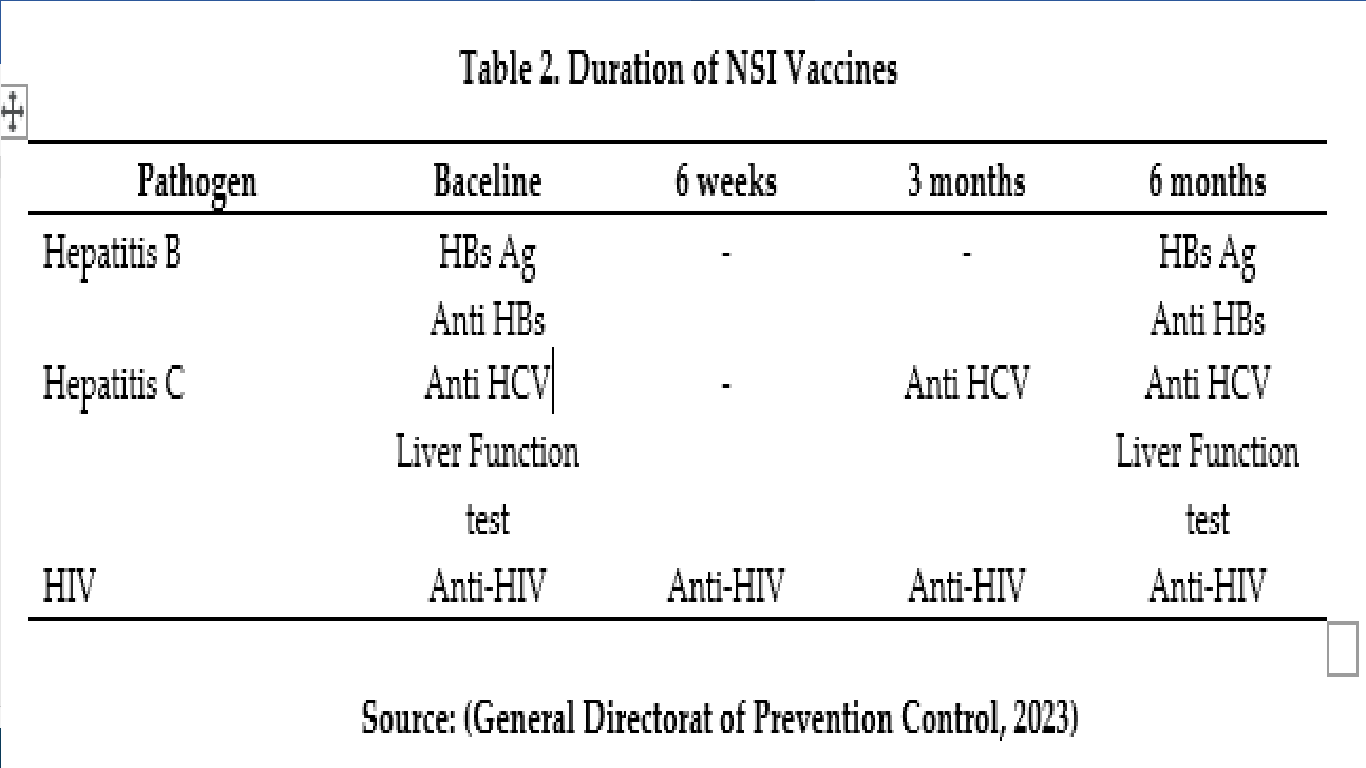
General Directorat of Prevention Control. (2023). BICSL. Ministry of Health of Saudi Arabia.
Goekcimen, K., Schwendimann, R., Pfeiffer, Y., Mohr, G., Jaeger, C., & Mueller, S. (2023). Addressing Patient Safety Hazards Using Critical Incident Reporting in Hospitals: A Systematic Review. Journal of Patient Safety, 19(1), e1–e8. https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000001072
Herlinawati, Hikmat, R., Indragiri, S., & Hidayat, R. A. (2021). Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kecelakaan Tertusuk Jarum Suntik pada Perawat. Health Care : Jurnal Kesehatan, 10(2), 230–238. https://doi.org/10.36763/healthcare.v10i2.143
Huang, H.-M., Chien, H.-C., Lin, W.-L., Chang, C.-H., Chang, M.-Y., Su, J.-Y., & Mu, P.-F. (2022). Prevention of needle-stick injury among nurses in an acute ward of a hospital: a best practice implementation project. JBI Evidence Implementation, 20(2), 134–143. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000294
Ismara Ima, K., Husodo, A., Prabandari, Y., & Hariyono, W. (2018). Mencegah Bahaya Tertusuk Jarum Suntik (NSI:Prevention) (Pertama). UNY Press.
Majdabadi, M. A., Yazdanirad, S., Yarahmadi, R., Abolghasemi, J., & Ebrahimi, H. (2022). The impact of emotional intelligence and personality traits on the occurrence of unsafe behaviors and needle stick injuries among the nurses. Heliyon, 8(6), e09584. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09584
Makeen, A. M., Alharbi, A. A., Mahfouz, M. S., Alqassim, A. Y., Ismail, A. A., Arishi, H. M., El-Setouhi, M. A., Horner, R. D., & Muaddi, M. A. (2022). Needlestick and sharps injuries among secondary and tertiary healthcare workers, Saudi Arabia. Nursing Open, 9(1), 816–823. https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.1136
Manal, A. G., Hamed, A., Shazra, A., & Duaa, A. Q. (2018). Investigating Healthcare Workers Experience after a Needle Stick Injury at a Tertiary Hospital in Makkah Region in Saudi Arabia : A Qualitative Assessment. Indian Journal, 7(4), 1–17. https://indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:ijmrhs&volume=7&issue=4&article=003
Morrow, R., Rodriguez, A., King, & Nigel. (2015). Colaizzi’s descriptive phenomenological method Original Citation. The Psychologist, 28(8), 643–644. http://eprints.hud.ac.uk/id/eprint/26984/
Qureshi, M. O., Chughtai, A., & Seale, H. (2021). Examining the discourse regarding the delivery of occupational health and safety training to healthcare workers: a review of pandemic plans of 23 countries. Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Control, 10(SUPPL 1), 22–23.
Sabaa, M. A., Hassan, A. M., Abd-Alla, A. K., Hegazy, E. E., & Amer, W. H. (2022). Needle-stick and sharps injuries: awareness, prevalence and risk factors of a global problem in healthcare workers at Tanta University Hospitals, Egypt. International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics : JOSE, 28(3), 1419–1429. https://doi.org/10.1080/10803548.2021.1901445
Utarini, A. (2022). Penelitian Kualitatif dalam Pelayanan Kesehatan (2nd ed.). UGM Press.
Veronesi, L., Giudice, L., Agodi, A., Arrigoni, C., Baldovin, T., Barchitta, M., Benedetti, T., Caggiano, G., Cannizzaro, S. G., De Giglio, O., D’Errico, M., Destri, S., Fiorentini, R., Gentile, L., Mannone, A., Mascipinto, S., Mercuri, M., Montagna, M. T., Novati, R., … Pasquarella, C. (2018). A multicentre study on epidemiology and prevention of needle stick injuries among students of nursing schools. Annali Di Igiene : Medicina Preventiva e Di Comunita, 30(5 Supple 2), 99–110. https://doi.org/10.7416/ai.2018.2254
Yang, H., Zhang, H., Lu, Y., Gu, Y., Zhou, J., & Bai, Y. (2022). A program to improve the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of needle stick and sharps injuries through bundled interventions among nurses: An KAP Mode-Based Approach to Intervention. Psychology, Health & Medicine, 27(5), 999–1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2020.1830132
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Akhir Fahruddin, Yayi Suryo Prabandari, Martinus Sutena, Nurul Uswatin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


















