Wet Cupping Therapy as A Complementary Intervention for Blood Glucose Reduction: Pre-Experimental Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/bik.v19i1.12526Keywords:
cupping therapy, blood glucose, Diabetes MellitusAbstract
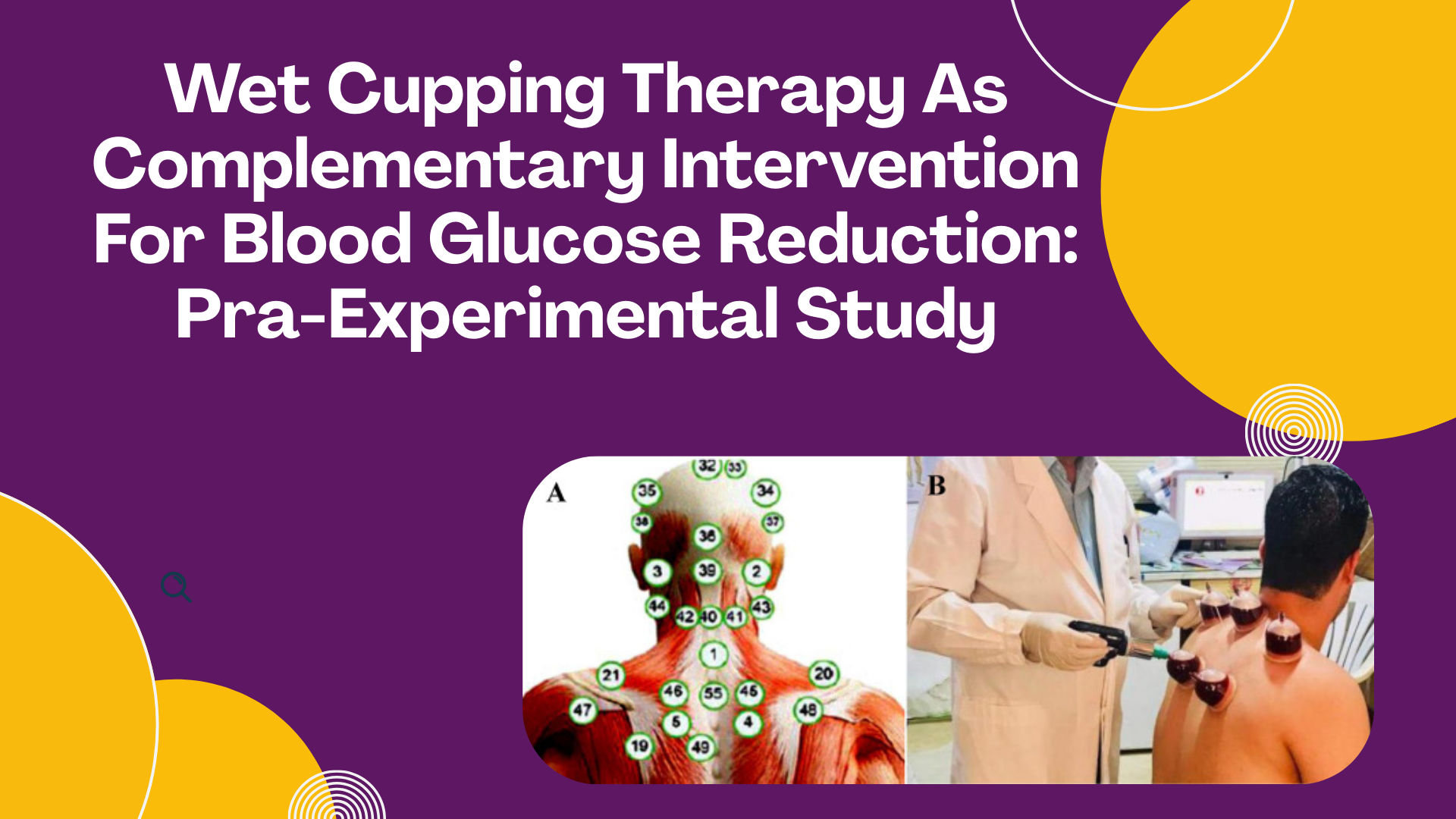
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease characterized by persistently elevated blood glucose levels and is a significant global public health problem. Wet cupping therapy is a complementary therapy that supports glycemic control, although community-based evidence is still very limited. This study was conducted to examine the short-term impact of wet cupping therapy on blood glucose levels in adults. This study used a pre-experimental, single-group pre-test-post-test design and was conducted in Wirobrajan Village, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, in April 2025. Thirty adults aged 26-45 years who were not receiving glucose-lowering medication were recruited using quota sampling. Blood glucose levels were measured before and immediately after one wet cupping therapy session. A paired-sample t-test with a significance level of p < 0.05 was used to look at the data. The mean blood glucose level dropped from 131 mg/dL before the intervention to 117 mg/dL after, a difference of 14.2 mg/dL. This drop was statistically significant (p = 0.0001). These findings indicate that wet cupping therapy significantly reduces short-term blood glucose levels in adults. Wet cupping therapy can be considered a complementary intervention for glycemic control. However, further randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Downloads
References
ADA. (2024). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 46(Supplement 1), S1–S291. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc23-Sintesi
Al-Bedah, A. M. N., Khalil, M. K. M., Elolemy, A. T., & Hussein, A. A. (2022a). Hijama (wet cupping therapy): Indications, safety, and evidence-based perspective. Journal of Integrative Medicine, 20(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joim.2021.10.003
Al-Bedah, A. M. N., Khalil, M. K. M., Elolemy, A. T., & Hussein, A. A. (2022b). Hijama (wet cupping therapy): Indications, safety, and evidence-based perspective. Journal of Integrative Medicine, 20(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joim.2021.10.003
Association, W. M. (2022). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAM A, 327(7), 637–644. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.1610
Boddy, C., & Boddy, J. (2023). Sampling in health research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 32(1–2), 12–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.16225
Bukhari, M. I. (n.d.). Shahih al-Bukhari. Hadith No. 5683.
Chow, S. C., Shao, J., Wang, H., & Lokhnygina, Y. (2018). Sample size calculations in clinical research (3rd ed.). Chapman dan Hall/CRC. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315183084
Ebrahim, N., Hashem, M., & El-Masry, R. (2018). Therapeutic effects of wet cupping therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Advanced Research, 8(6), 687–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.09.001
El Sayed, N., Mostafa, R., & Farouk, H. (2021). Wet cupping therapy for blood glucose regulation: Evidence from clinical studies. Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine, 18(1), 12–20. https://doi.org/10.1515/jcim-2020-0215
Farhadi, K., Schwebel, D. C., Saeb, M., Choubsaz, M., Mohammadi, R., & Ahmadi, A. (2016). The effectiveness of wet cupping for nonspecific low back pain in Iran: A randomized controlled trial. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 24, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.ctim.2016.02.007
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A., & Lang, A. G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41(4), 1149–1160. https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149
Gray, J. R., Grove, S. K., & Sutherland, S. (2023). The practice of nursing research: Appraisal, synthesis, and generation of evidence. Elsevier., 9th ed.
Guyton, A. C., & Hall, J. E. (2021). Textbook of medical physiology. Elsevier., (14th ed.).
ITBI. (2020). Ikatan Terapis Bekam Indonesia(ITBI).
Kim, J. I., Lee, M. S., Lee, D. H., & Ernst, E. (2019). Cupping for treating pain: A systematic review. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 1–10. https://doi.org/ 10.1155 2019/8478291
Li-Kung Wu, Yi-Chen Chen, C.-S. H. (2024). The efficacy and safety of cupping as complementary and alternative therapy for metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 102(13), e33341. https://doi.org/10.1097 /MD.0000000000033341
Li, H., Wang, J., & Zhang, X. (2022). Wet cupping therapy and glycemic control: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8823902
Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., & Li, Q. (2022). Efficacy and safety of wet cupping therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice, 49, 101651. https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.ctcp.2022.101651
Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., & L. (2022). Efficacy and safety of wet cupping therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice, 46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctcp.2022.101651
Nik Husain, R., Mohd Hairon, S., Mohd Zain, R. (2020). The effects of wet cupping therapy on fasting blood sugar, renal function parameters, and endothelial function: A single-arm intervention study. Oman Medical Journal, 35(2), e108. https://doi.org/10.5001/omj.2020.26
Polit, D. F., & Beck, C. T. (2021). Generating and assessing evidence for nursing practice. Wolters Kluwer. Nursing Research, (11th ed.).
Qureshi, N. A., Ali, G. I., & Alqahtani, A. (2020). Integration of cupping therapy within modern medicine: Current evidence and future perspective. Integrative Medicine Research, 9(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imr.2020.100449
Sherwood, L. (2020). Human physiology: From cells to systems. Cengage Learning., (10th ed.).
Syaikhu. (2008). Mukjizat pengobatan bekam Nabi: Studi ilmiah dan praktik bekam kesehatan Islam. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Thibbun Nabawi.
Tao, J., Zhao, P., Mo, T., Zhao, R., Yang, N., Lee, M. S., Liu, J., & Cao, H. (2020). Key elements that determine the efficacy of cupping therapy: A bibliometric analysis and review of clinical studies. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medical Sciences, 7(4), 345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcms.2020.11.001
Wu, L.-K., Chen, Y.-C., Hung, C.-S., et al. (2023). The efficacy and safety of cupping as complementary and alternative therapy for metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 102(13), e33341. https://doi.org/10.1097 /MD.0000000000033341
Wulandari, R. (2015). Pengaruh terapi bekam terhadap penurunan glukosa darah di Karangmalaya Sragen. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan, 6(2), 25–32.
Xiong, J., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, X. (2021). Effects of cupping therapy on anxiety and quality of life: A meta-analysis. Journal of Integrative Medicine, 19(4), 316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.joim.2021.04.005
Zhang, L., Zheng, Y., & Qiao, Y. (2021a). Effect of cupping therapy on blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9945631
Zhang, L., Zheng, Y., & Qiao, Y. (2021b). Effect of cupping therapy on blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9945631
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Mahfud Mahfud, R. Jaka Sarwadhamana, Dihan Fahry Muhammad, Allama Zaki Almubarok, Arroyan Arroyan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


















