Understanding High School Students’ Errors in solving Mathematics Problems: A Phenomenological Research
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v7i1.24005Keywords:
cognition domain, educational intervention, education policies, educational standars, learning engagement, mathematical problem solving, phenomenology research, technology-assisted learning modelAbstract
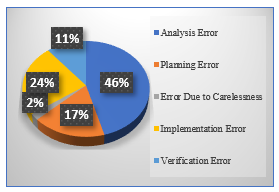
This research aims to understand a phenomenon regarding high school students’ errors in solving mathematics problems using a qualitative approach with phenomenology as the analysis framework. Data were collected through tests, classroom observations, documentation (students’ answer sheets, list of attendees, and students’ score lists), and unstructured phenomenological interviews with four purposively selected participants who met the selection criteria. The researchers used the mathematical problem-solving (MPS) model by Rott-Specht-Knipping and Aguas’ phenomenological data analysis steps using the NVIVO 12 software to analyze the students’ MPS process and identify their errors and the factors contributing to these errors. Errors were predominantly found in problems solved without engaging in the exploration phase. Analysis errors were the most common, while errors due to carelessness were the rarest. Factors contributing to these errors were identified across five domains: MPS Ability (MPSA), cognition, affection, motivation, and self-awareness. This research provides valuable insights into student errors in MPS for researchers and educators, particularly teachers, and provides recommendations for mathematics education policies and future research.
Downloads
References
Aagaard, J. (2017). Introducing postphenom-enological research: a brief and selective sketch of phenomenological research methods. International Journal of Quali-tative Studies in Education, 30(6), 519–533. https://doi.org/10.1080/09518398.2016.1263884
Adinda, A., Purwanto, P., Parta, I. N., & Chandra, T. D. (2021). Investigation Of Students’ Metacognitive Awareness Failures About Solving Absolute Value Problems in Mathematics Education. Eurasian Journal of Educational Re-search, 2021(95). https://doi.org/10.14689/ejer.2021.95.2
Aguas, P. (2022). Fusing Approaches in Ed-ucational Research: Data Collection and Data Analysis in Phenomenological Re-search. The Qualitative Report. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2022.5027
Alexander, I. W. (1970). What is Phenome-nology? Journal of the British Society for Phenomenology, 1(1), 3–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071773.1970.11006091
Anderson, J. R., Lee, H. S., & Fincham, J. M. (2014). Discovering the structure of mathematical problem solving. Neu-roImage, 97, 163–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.031
Bartholomew, T. T., Joy, E. E., Kang, E., & Brown, J. (2021). A choir or cacopho-ny? Sample sizes and quality of convey-ing participants’ voices in phenomeno-logical research. Methodological Innova-tions, 14(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/20597991211040063
Blakemore, S. J., & Frith, C. (2003). Self-awareness and action. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 13(2), 219–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-4388(03)00043-6
Böswald, V., & Schukajlow, S. (2023). I val-ue the problem, but I don’t think my stu-dents will: preservice teachers’ judg-ments of task value and self-efficacy for modelling, word, and intramathematical problems. ZDM - Mathematics Educa-tion, 55(2), 331–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-022-01412-z
BSKAP. (2022). Copy of Appendix I of the Decree of the Head of the Educational Standards, Curriculum and Assessment Agency of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Research and Technology Number 033/H/Kr/2022 concerning Learning Achievements in Early Child-hood Education, Basic Education Levels and Secondary Education Levels in Merdeka Curriculum (p. 133). https://kurikulum.kemdikbud.go.id/rujukan
Carter, N., Bryant-Lukosius, D., DiCenso, A., Blythe, J., & Neville, A. J. (2014). The Use of Triangulation in Qualitative Research. Oncology Nursing Forum, 41(5), 545–547. https://doi.org/10.1188/14.ONF.545-547
Cleary, T. J., & Chen, P. P. (2009). Self-regulation, motivation, and math achievement in middle school: Variations across grade level and math context. Journal of School Psychology, 47(5), 291–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2009.04.002
Clements, M. A. (1982). Careless Errors Made by Sixth-Grade Children on Writ-ten Mathematical Tasks. Journal for Re-search in Mathematics Education, 13(2), 136. https://doi.org/10.2307/748360
Darmawan, E., & Suparman, S. (2019). Design of Mathematics Learning Media based on Discovery Learning to Improve Problem Solving Ability. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 1(2), 20-28. doi:https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v1i2.7564
DeBellis, V. A., & Goldin, G. A. (2006). Affect and Meta-Affect in Mathematical Problem Solving: a Representational Perspective. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 63(2), 131–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-006-9026-4
Demetriou, A., & Kazi, S. (2006). Self-awareness in g (with processing efficien-cy and reasoning). Intelligence, 34(3), 297–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2005.10.002
Díaz, V., Aravena, M., & Fores, G. (2020). Solving Problem Types Contextualized to the Quadratic Function and Error Analysis: A Case Study. Eurasia Jour-nal of Mathematics, Science and Tech-nology Education, 16(11), em1896. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/8547
Dwita, A., & Retnawati, H. (2022). Students’ errors in solving mathematical problems. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2575. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0107794
Eggen, P. D., & Kauchak, D. P. (1996). Strategy for Teacher: Teaching Content and Thinking Skills. Allyn & Bacon.
Etikan, I. (2016). Comparison of Convenience Sampling and Purposive Sampling. American Journal of Theoretical and Applied Statistics, 5(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajtas.20160501.11
Fatimah, Ms., Nurhidayah, Ms., Ahmad, H., Febryanti, Ms., & P., M. A. (2019). Ef-fect of Motivation and Gender on Prob-lem-solving in Student Mathematics. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Advanced Multidiscipli-nary Research (ICAMR 2018). https://doi.org/10.2991/icamr-18.2019.26
Furinghetti, F., & Morselli, F. (2009). Every unsuccessful problem solver is unsuc-cessful in his or her own way: affective and cognitive factors in proving. Educa-tional Studies in Mathematics, 70(1), 71–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-008-9134-4
García, T., Boom, J., Kroesbergen, E. H., Núñez, J. C., & Rodríguez, C. (2019). Planning, execution, and revision in mathematics problem solving: Does the order of the phases matter? Studies in Educational Evaluation, 61, 83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2019.03.001
García, T., Rodríguez, C., González-Castro, P., González-Pienda, J. A., & Torrance, M. (2016). Elementary students’ meta-cognitive processes and post-performance calibration on mathematical problem-solving tasks. Metacognition and Learning, 11(2), 139–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-015-9139-1
Groenewald, T. (2004). A Phenomenological Research Design Illustrated. Internation-al Journal of Qualitative Methods, 3(1), 42–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/160940690400300104
Hardini, R., Prahmana, R., Akib, I., & Shahrill, M. (2021). Learning Social Arithmetic of Low-Ability Student through the Context of Snacks and Money. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 4(1), 21-33. doi:https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v4i1.14308
Hasan, N., Subanji, S., & Sukorianto, S. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Kelas VIII dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Cerita Terkait Teorema Pythagoras. Jurnal Pendidikan: Teori, Penelitian, Dan Pengembangan, 4(4), 468. https://doi.org/10.17977/jptpp.v4i4.12264
Howard, D. C. P. (1994). Human‐computer interactions: a phenomenological exami-nation of the adult first‐time computer experience. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, 7(1), 33–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/0951839940070103
Irhamna, I., Amry, Z., & Syahputra, H. (2020). Contribution of Mathematical Anxiety, Learning Motivation and Self-Confidence to Student’s Mathematical Problem Solving. Budapest International Research and Critics in Linguistics and Education (BirLE) Journal, 3(4), 1759–1772. https://doi.org/10.33258/birle.v3i4.1343
Kalkan, F., & Dağlı, E. (2021). Views of sec-ondary school students on ideal teacher qualifications: A phenomenological anal-ysis. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE), 10(1), 317. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v10i1.20565
Karaali, G. (2015). Metacognition in the Classroom: Motivation and Self-Awareness of Mathematics Learners. PRIMUS, 25(5), 439–452. https://doi.org/10.1080/10511970.2015.1027837
(Ken) Clements, M. A. (1980). Analyzing children’s errors on written mathematical tasks. Educational Studies in Mathemat-ics, 11(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369157
Khusnani, A., Husein, R., Jufriansah, A., Thalo, O., Rahmawati, K., Fitri, M., & Adina, C. (2023). Identification of Understanding of Disaster Preparedness in the School Environment. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 5(3), 233-248. doi:https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v5i3.22974
Kingsdorf, S., & Krawec, J. (2014). Error Analysis of Mathematical Word Problem Solving Across Students with and with-out Learning Disabilities. Learning Dis-abilities Research & Practice, 29(2), 66–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/ldrp.12029
Krawec, J. L. (2014). Problem Representation and Mathematical Problem Solving of Students of Varying Math Ability. Jour-nal of Learning Disabilities, 47(2), 103–115. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219412436976
Kurniawan, D., Astalini, A., Darmaji, D., Tanti, T., & Maryani, S. (2022). Innovative Learning: Gender Perception of e-Module Linear Equations in Mathematics and Physics. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 4(2), 92-106. doi:https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v4i2.16610
Kwon, K., & Jonassen, D. H. (2011). The Influence of Reflective Self-Explanations on Problem-Solving Performance. Jour-nal of Educational Computing Research, 44(3), 247–263. https://doi.org/10.2190/EC.44.3.a
Leong, Y. H., Dindyal, J., Toh, T. L., Quek, K. S., Tay, E. G., & Lou, S. T. (2011). Teacher preparation for a problem-solving curriculum in Singapore. ZDM, 43(6–7), 819–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-011-0356-z
Lestari, A. R. A., Minggi, I., & Qadry, I. K. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan dalam Me-nyelesaikan Soal Cerita Materi Bangun Ruang Sisi Datar Berdasarkan Prosedur Newman. SIGMA (Suara Intelektual Gaya Mtematika), 11(2), 122–129.
Liu, D. W. Y., & Winder, B. (2014). Explor-ing foreign undergraduate students’ ex-periences of university. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Educa-tion, 27(1), 42–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/09518398.2012.736643
Lopez, V., & Whitehead, D. (2014). Sampling data and data collection in qualitative re-search. In Nursing and Midwifery Re-search (3rd ed.). Elsevier.
Lukman, L., Marsigit, M., Istiyono, E., Kartowagiran, B., Retnawati, H., Kistoro, H. C. A., & Putranta, H. (2021). Effective teachers’ personality in strengthening character education. Inter-national Journal of Evaluation and Re-search in Education (IJERE), 10(2), 512. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v10i2.21629
Milazoni, T. R., Maison, M., & Nizlel, N. (2022). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Cerita Matematika Berdasarkan Teori Pemrosesan Informa-si dan Pemberian Scaffolding. AKSIO-MA: Jurnal Program Studi Pendidikan Matematika, 11(1), 654–666. https://doi.org/10.24127/ajpm.v11i1.4705
Muis, K. R., Psaradellis, C., Lajoie, S. P., Di Leo, I., & Chevrier, M. (2015). The role of epistemic emotions in mathematics problem solving. Contemporary Educa-tional Psychology, 42, 172–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2015.06.003
NCTM. (2000). Principles and Standards for School Mathematics. NCTM.
Novak, E., & Tassell, J. L. (2017). Studying preservice teacher math anxiety and mathematics performance in geometry, word, and non-word problem solving. Learning and Individual Differences, 54, 20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2017.01.005
Özcan, Z. Ç., & Eren Gümüş, A. (2019). A modeling study to explain mathematical problem-solving performance through metacognition, self-efficacy, motivation, and anxiety. Australian Journal of Edu-cation, 63(1), 116–134. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004944119840073
Pavlin-Bernardić, N., Rovan, D., & Pavlović, J. (2017). Academic Cheating in Mathe-matics Classes: A Motivational Perspec-tive. Ethics & Behavior, 27(6), 486–501. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508422.2016.1265891
Pólya, G. (2004). How to solve it: A new as-pect of mathematical method (Vol. 5). Princeton university press.
Pomalato, S. W. D., Ili, L., Ningsi, B. A., Fadhilaturrahmi, F., Hasibuan, A. T., & Primayana, K. H. (2020). Student Error Analysis in Solving Mathematical Prob-lems. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(11), 5183–5187. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.081118
Priyani, H. A., & Ekawati, R. (2018). Error analysis of mathematical problems on TIMSS: A case of Indonesian secondary students. IOP Conference Series: Mate-rials Science and Engineering, 296, 012010. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/296/1/012010
Pugalee, D. K. (2001). Writing, Mathematics, and Metacognition: Looking for Connec-tions Through Students’ Work in Math-ematical Problem Solving. School Sci-ence and Mathematics, 101(5), 236–245. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1949-8594.2001.tb18026.x
Radatz, H. (1979). Error Analysis in Mathe-matics Education. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 10(3), 163. https://doi.org/10.2307/748804
Radatz, H. (1980). Students’ Errors in the Mathematical Learning Process: A Sur-vey. For the Learning of Mathematics, 1(1), 16–20. https://www.jstor.org/stable/40247696
Retnawati, H. (2016). Analisis Kuantitatif Instrumen Penelitian (First). Parama Publishing. www.nuhamedika.gu.ma
Rhodes, F. (1987). Carelessness? The Math-ematical Gazette, 71(458), 285–292. https://doi.org/10.2307/3617047
Rofi’ah, N., Ansori, H., & Mawaddah, S. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Cerita Matematika Berdasarkan Langkah Penyelesaian Pol-ya. EDU-MAT: Jurnal Pendidikan Ma-tematika, 7(2), 120. https://doi.org/10.20527/edumat.v7i2.7379
Rott, B., Specht, B., & Knipping, C. (2021). A descriptive phase model of problem-solving processes. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 53(4), 737–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01244-3
Schoenfeld, A. H. (1985). Mathematical problem solving. Academic Press.
Solso, R. L. (1995). Cognitive Psychology. Allyn & Bacon.
Son, A. L., Darhim, & Fatimah, S. (2019). An analysis to student error of algebraic problem solving based on polya and newman theory. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1315(1), 012069. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1315/1/012069
Svenson, I. F., Lawrence, J. A., & Willis, S. G. (1983). Distance university students’ processing of mathematics exercises. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 14(1), 73–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00704703
Sweller, J. (1988). Cognitive load during problem solving: Effects on learning. Cognitive Science, 12(2), 257–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/0364-0213(88)90023-7
Trezise, K., & Reeve, R. A. (2014). Cogni-tion-emotion interactions: patterns of change and implications for math prob-lem solving. Frontiers in Psychology, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00840
Ulya, H. (2015). Hubungan Gaya Kognitif Dengan Kemampuan Pemecahan Masa-lah Matematika Siswa. Jurnal Konseling Gusjigang, 1(2). https://doi.org/10.24176/jkg.v1i2.410
Vagle, M. D. (2009). Validity as intended: ‘bursting forth toward’ bridling in phe-nomenological research. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Educa-tion, 22(5), 585–605. https://doi.org/10.1080/09518390903048784
Veloo, A., Krishnasamy, H. N., & Wan Ab-dullah, W. S. (2015). Types of Student Errors in Mathematical Symbols, Graphs and Problem-Solving. Asian Social Sci-ence, 11(15). https://doi.org/10.5539/ass.v11n15p324
Verschaffel, L., Greer, B., & Corte, E. (2000). Making sense of word problems. Swets and Zeitlinger.
Verschaffel, L., Schukajlow, S., Star, J., & Van Dooren, W. (2020). Word problems in mathematics education: a survey. ZDM, 52(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-020-01130-4
Wa-Mbaleka, S. (2020). The Researcher as an Instrument. In A. P. Costa, L. P. Reis, & A. Moreira (Eds.), Computer Supported Qualitative Research (Vol. 1068). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31787-4
White, A. L. (2005). Active Mathematics In Classrooms: Finding Out Why Children Make Mistakes-And Then Doing Some-thing To Help Them. Square One, 15(4).
Yazıcı, S., & Fidan, N. K. (2020). Value pref-erences and requirements of the students attending the regional boarding second-ary schools. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE), 9(3), 635. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v9i3.20539
Yüksel, P., & Yıldırım, S. (2015). Theoretical Frameworks, Methods, and Procedures for Conducting Phenomenological Stud-ies. Turkish Online Journal of Qualita-tive Inquiry, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.17569/tojqi.59813
Submitted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ahmad Naufal Aljura, Heri Retnawati, Hutkemri Zulnaidi, Vianney Mbazumutima

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.












