Validating a TPCK-S Instrument for Hologram-Based Mathematics Teaching
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v7i3.12119Keywords:
complex learning cycles, educational innovations, hologram technology, immersive technology in education, performative skill assessment, teacher pedagogical competence, technology integrationAbstract
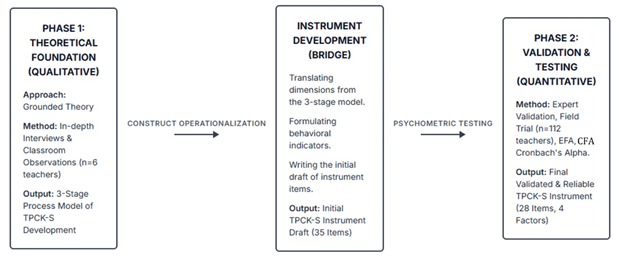
The successful use of 3D holograms in teaching geometry depends greatly on teachers’ practical skills. However, there remains a substantial gap in understanding how these skills are developed and how they can be reliably assessed. This study, carried out with mathematics teachers in Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia, seeks to address this issue by (1) proposing a theoretical model for the development of Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge and Skills (TPCK-S), and (2) creating and validating an instrument to measure this construct. Following a sequential exploratory mixed-methods design, a theoretical model was first built through a grounded theory study with six junior high school mathematics teachers. Building on this model, an instrument was then empirically validated with a sample of 112 junior high school teachers through the combined use of Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) and Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA). The findings revealed a three-stage TPCK-S development model consisting of Technical Familiarization, Pedagogical Experimentation, and Fluent Integration. In addition, the validated 28-item instrument demonstrated a solid four-factor structure, with confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) showing good model fit and internal consistency reliability reaching an excellent level (α = 0.91). Overall, this study contributes a rigorously tested TPCK-S instrument that can serve as a valuable diagnostic tool to support and strengthen teacher professional development in the digital era.
Downloads
References
Angeli, C., & Valanides, N. (2009). Epistemological and methodological issues for the conceptualization, development, and assessment of ICT-TPCK: Advances in technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPCK). Computers and Education, 52(1), 154–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2008.07.006
Avila-Garzon, C., Bacca-Acosta, J., Kinshuk, , Duarte, J., & Betancourt, J. (2021). Augmented Reality in Education: An Overview of Twenty-Five Years of Research. Contemporary Educational Technology, 13(3), 1–29. https://doi.org/10.30935/cedtech/10865
Balalle, H. (2025). Learning beyond realities: exploring virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality in higher education—a systematic literature review. Discover Education, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-025-00559-7
Budiningsih, I., Soehari, T. D., & Supriyanto, E. (2022). Continuous learning for employee capacity developing in personal mastery at Bank Indonesia. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 61-77.
Byrne, B. M. (2001). Structural equation modeling with AMOS: Basic concepts (1st ed., Vol. 20). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Mahwah. N. J.
Cheng, Y. L., & Mix, K. S. (2014). Spatial Training Improves Children’s Mathematics Ability. Journal of Cognition and Development, 15(1), 2–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15248372.2012.725186
Corbin, J., & Strauss, A. (2014). Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. In Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory, 3rd ed. Sage Publications, Inc. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781452230153
Creswel, John W and Clark, & Plano, V. L. (2017). Designing and conducting mixed methods research. Sage publications.
Durdu, L., & Dag, F. (2017). Pre-Service Teachers’ TPACK Development and Conceptions through a TPACK-Based Course. Australian Journal of Teacher Education, 42(11), 150–171. https://doi.org/10.14221/ajte.2017v42n11.10
Ertmer, P. A., & Newby, T. J. (2013). Behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism: Comparing critical features from an instructional design perspective. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 26(2), 43–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/piq.21143
Harmadi, F., Maryani, I., Sukirman, S., & Montano, E. C. N. (2025). Digital Transformation: Exploring the Relationship Between Literacy, Motivation, and TPACK in Elementary Education. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 294-310.
Ishartono, N., binti Halili, S. H., Ningtyas, Y. D. W. K., Tonra, W. S., Kholid, M. N., Waluyo, M., & Djamilah, S. (2022). The Role of Instructional Design in Improving Pre-Service and In-Service Teacher’s Mathematics Learning Sets Skills: A Systematic Literature Review in Indonesian Context. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 13-31.
Joshi, S. C. (2023). TPACK and Teachers’ Self-Efficacy: A Systematic Review TPACK et l’auto-efficacité des enseignants: une revue systématique. Canadian Journal of Learning and Technology, 49(2).
Kadluba, A., Strohmaier, A., Schons, C., & Obersteiner, A. (2025). How much C is in TPACK? A systematic review on the assessment of TPACK in mathematics. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 118(2), 169–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-024-10357-x
Kaharuddin, A. (2024). Development of 3 Dimensional Hologram Media Based On TPCK’S (Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge and Skills) To Improve Students’ Science Skills In Geometry Learning. Universitas Negeri Makassar.
Kaharuddin, A., Arsyad, N., & Asdar. (2023). The Practicality of 3D Hologram Media in Geometry Learning. Himalayan Journal of Education and Literature, 04(02), 1–2. https://doi.org/10.47310/hjel.2023.v04i02.025
Khairunnisa Roslan, R., & Ahmad, A. (2017). 3D Spatial Visualisation Skills Training Application for School Students Using Hologram Pyramid. International Journal On Informatics Visualization, 1(4).
Khuluq, K., Veranita, A., & Ariyati, I. (2024). Optimizing Image Media on Mathematics Learning Outcomes for High Grade Students in Elementary Schools. Buletin KKN Pendidikan, 47-60.
Koh, J. H. L., & Chai, C. S. (2016). Seven design frames that teachers use when considering technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK). Computers and Education, 102, 244–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.09.003
Kosko, K. W. (2022). Pre-service teachers’ professional noticing when viewing standard and holographic recordings of children’s mathematics. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 17(4), em0706. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/12310
Li, M., Vale, C., Tan, H., & Blannin, J. (2024). A systematic review of TPACK research in primary mathematics education. Mathematics Education Research Journal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-024-00491-3
Malhotra, A. T. (2021). Role of Lesh’s model of multimodal representation in learning of mathematical concepts. International Journal of Reflective Research in Social Sciences, 4(2), 2581–5733. www.reflectivejournals.com
Mishra, P., & Koehler, M. J. (2006). Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge: A Framework for Teacher Knowledge. Teachers College Record, 108(6), 1017–1054. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9620.2006.00684.x
Moore, K. C., & Carlson, M. P. (2012). Students’ images of problem contexts when solving applied problems. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 31(1), 48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2011.09.001
Mullis, I. V. S., Martin, M. O., & Von Davier, M. (2021). TIMSS 2023 Assessment Frameworks. TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center.
Noroozi, O., & Sahin, I. (2023). Technology-Enhanced Learning Environments in Education. ISTES Organization Monument. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/378708056
Rusli Baharuddin, M., Baharuddin, H., & Beta, P. (2021). “Investigating Students Error When Solving Whole Number Problem”: Case in Procedural Error and Concept Error. Proceedings of the 1st Annual International Conference on Natural and Social Science Education (ICNSSE 2020), 111–115.
Ruthven, K. (2009). Towards a Naturalistic Conceptualisation of Technology Integration in Classroom Practice: the example of school mathematics. Éducation et Didactique, 3–1, 131–159. https://doi.org/10.4000/educationdidactique.434
Salloum, S. A., Alhumaid, K., Alfaisal, A. M., Aljanada, R. A., & Alfaisal, R. (2024). Adoption of 3D Holograms in Science Education: Transforming Learning Environments. IEEE Access, 12, 70984–70998. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3402549
Schmidt, D. A., Baran, E., Thompson, A. D., Mishra, P., Koehler, M. J., & Shin, T. S. (2009). Technological pedagogical content knowledge (Track): The development and validation of an assessment instrument for preservice teachers. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 42(2), 123–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2009.10782544
Tondeur, J., van Braak, J., Ertmer, P. A., & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A. (2017). Understanding the relationship between teachers’ pedagogical beliefs and technology use in education: a systematic review of qualitative evidence. Educational Technology Research and Development, 65(3), 555–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-016-9481-2
Utari, V. T., Maryani, I., Hasanah, E., Suyatno, S., Mardati, A., Bastian, N., ... & Reotutor, M. A. C. (2025). Exploring the Intersection of TPACK and Professional Competence: A Study on Differentiated Instruction Development within Indonesia’s Merdeka Curriculum. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 136-153.
Voogt, J., Fisser, P., Pareja Roblin, N., Tondeur, J., & van Braak, J. (2013). Technological pedagogical content knowledge - A review of the literature. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 29(2), 109–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2729.2012.00487.x
Yang, J. C., & Lin, Y. L. (2010). Development and Evaluation of an Interactive Mobile Learning Environment with Shared Display Groupware. Educational Technology & Society, 13(1), 195–207. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279670663
Yoo, Hawon and Jang, Jaehong and Oh, Hyunju and Park, & Innwoo. (2022). The potentials and trends of holography in education: A scoping review. Computers & Education, 104533.
Yoon, S. A., & Wang, J. (2014). Making the Invisible Visible in Science Museums Through Augmented Reality Devices. TechTrends, 58(1).
Submitted
Accepted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Andi Kaharuddin, Javier García García, Irma Magfirah, Yulismayanti Yulismayanti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.












