Genomics and Network Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Shigella flexneri from Raw Vegetables in Bangladesh for Risk Assessment and Targeted Therapeutic Intervention
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/pharmacon.v22i2.13565Keywords:
Shigella flexneri, Dissemination, Multidrug-resistant, Raw vegetables, BangladeshAbstract
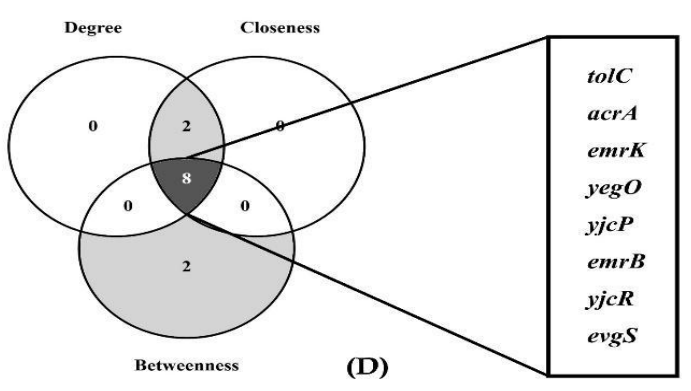
Shigella flexneri increasingly poses a threat to public health in developing nations through the dissemination of multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains via contaminated raw vegetables in urban agriculture systems. Despite extensive characterization of clinical isolates, the mechanistic insights and therapeutic vulnerabilities of food-borne S. flexneri strains from Bangladesh remain underexplored. Therefore, this study aimed to characterize MDR S. flexneri from Bangladeshi raw vegetables retrieved from the NCBI genome database and identify core and essential antibiotic-resistant genes as prioritized therapeutic targets. Whole-genome sequences of four S. flexneri strains isolated from tomatoes and green chilies across Gazipur and Dhaka were retrieved from NCBI GenBank and analyzed through comparative genomics to identify core genes and resistance determinants. Networks were constructed using the STRING database, followed by centrality-based topology analysis to identify hub genes that cross-referenced with the KEGG database and the Database of Essential Genes. Comparative analysis revealed 4273 core genes and 44 antibiotic resistance genes across all strains. Network topology analysis identified eight hub genes (tolC, acrA, emrK, yegO, yjcP, emrB, yjcR, evgS) based on degree, closeness, and betweenness centrality metrics. Five hub genes (tolC, acrA, emrK, emrB, evgS) were classified as essential for bacterial survival, representing critical nodes in efflux-mediated resistance and two-component regulatory systems. These essential hub genes constitute high-priority therapeutic targets whose disruption could compromise multidrug resistance mechanisms and bacterial viability in food-borne S. flexneri. Additionally, to mitigate their dissemination, raising public awareness on MDR pathogens from raw vegetables is recommended.
Downloads
References
Ahmed, S., Chowdhury, M. I. H., Sultana, S., Alam, S. S., Marzan, M., & Islam, M. A. (2023). Prevalence of Antibiotic-Resistant Shigella spp. in Bangladesh: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 44,519 Samples. Antibiotics, 12(5), 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIBIOTICS12050817/S1
Alcock, B. P., Huynh, W., Chalil, R., Smith, K. W., Raphenya, A. R., Wlodarski, M. A., Edalatmand, A., Petkau, A., Syed, S. A., & Tsang, K. K. (2023). CARD 2023: expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), D690–D699.
Ananna, N. F., Akter, A., Amin, Md. Al, Islam, K. M. T., & Mahmud, S. (2024). Ligand-based pharmacophore modeling targeting the fluoroquinolone antibiotics to identify potential antimicrobial compounds. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Reports, 1, 100021. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CSBR.2024.100021
Ayele, B., Beyene, G., Mekonnen, Z., Esmael, A., Ayele, A., Alemayehu, D. H., & Beyene, G. T. (2025). Whole genome sequencing analysis of antibiotic resistant genes of Shigella species: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS ONE, 20(10), e0334701. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0334701
Azmi, I. J., Khajanchi, B. K., Akter, F., Hasan, T. N., Shahnaij, M., Akter, M., Banik, A., Sultana, H., Hossain, M. A., Ahmed, M. K., Faruque, S. M., & Talukder, K. A. (2014). Fluoroquinolone Resistance Mechanisms of Shigella flexneri Isolated in Bangladesh. PLOS ONE, 9(7), e102533. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0102533
Berger, I., & Loewy, Z. G. (2024). Antimicrobial Resistance and Novel Alternative Approaches to Conventional Antibiotics. Bacteria 2024, Vol. 3, Pages 171-182, 3(3), 171–182. https://doi.org/10.3390/BACTERIA3030012
Cline, M. S., Smoot, M., Cerami, E., Kuchinsky, A., Landys, N., Workman, C., Christmas, R., Avila-Campilo, I., Creech, M., & Gross, B. (2007). Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nature Protocols, 2(10), 2366–2382.
Freed, N. E., Bumann, D., & Silander, O. K. (2016). Combining Shigella Tn-seq data with gold-standard E. coli gene deletion data suggests rare transitions between essential and non-essential gene functionality. BMC Microbiology 2016 16:1, 16(1), 203-. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12866-016-0818-0
Gharpure, R., Marsh, Z. A., Tack, D. M., Collier, S. A., Strysko, J., Ray, L., Payne, D. C., & Garcia-Williams, A. G. (2021). Disparities in Incidence and Severity of Shigella Infections Among Children—Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet), 2009-2018. Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, 10(7), 782–788. https://doi.org/10.1093/JPIDS/PIAB045
Hossain, M. A., Al Amin, M., Khan, M. A., Refat, M. R. R., Sohel, M., Rahman, M. H., Islam, A., & Hoque, M. N. (2024). Genome-Wide Investigation Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets in Shigella spp. BioMed Research International, 2024(1), 5554208. https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/5554208
Islam, Md. S., Pramanik, P. K., Rana, Md. L., Ullah, Md. A., Neloy, F. H., Ramasamy, S., Schreinemachers, P., Oliva, R., & Rahman, Md. T. (2024). Draft genome sequence of antibiotic-resistant Shigella flexneri MTR_GR_V146 strain isolated from a tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) sample collected from a peri-urban area of Bangladesh. Microbiology Resource Announcements, 13(4). https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.00099-24
Jin, Q., Yuan, Z., Xu, J., Wang, Y., Shen, Y., Lu, W., Wang, J., Liu, H., Yang, J., Yang, F., Zhang, X., Zhang, J., Yang, G., Wu, H., Qu, D., Dong, J., Sun, L., Xue, Y., Zhao, A., … Yu, J. (2002). Genome sequence of Shigella flexneri 2a: insights into pathogenicity through comparison with genomes of Escherichia coli K12 and O157. Nucleic Acids Research, 30(20), 4432–4441. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKF566
Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Matsuura, Y., & Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. (2025). KEGG: biological systems database as a model of the real world. Nucleic Acids Research, 53(D1), D672–D677. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKAE909
Kar, A., Ahmed, P., Sakib, N., Shibly, A. Z., Zohora, F. T., Dutta, A., Somadder, P. D., & Rahman, M. M. (2025). Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern of Shigella Spp. and Assessed Their Pathogenic Potential Using the Caenorhabditis elegans Infection Model Associated with Acute Diarrheal Patients in Tangail, Bangladesh. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease.
Kim, J., & Ahn, J. (2022). Emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant foodborne pathogens from farm to table. Food Science and Biotechnology, 31(12), 1481–1499. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10068-022-01157-1/METRICS
Lu, T., Das, S., Howlader, D. R., Picking, W. D., & Picking, W. L. (2024). Shigella Vaccines: The Continuing Unmet Challenge. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, Vol. 25, Page 4329, 25(8), 4329. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS25084329
Luo, H., Lin, Y., Liu, T., Lai, F.-L., Zhang, C.-T., Gao, F., & Zhang, R. (2021). DEG 15, an update of the Database of Essential Genes that includes built-in analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(D1), D677–D686.
Nisa, I., Qasim, M., Yasin, N., Ullah, R., & Ali, A. (2020). Shigella flexneri: an emerging pathogen. Folia Microbiologica, 65(2), 275–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12223-020-00773-W/METRICS
Page, A. J., Cummins, C. A., Hunt, M., Wong, V. K., Reuter, S., Holden, M. T. G., Fookes, M., Falush, D., Keane, J. A., & Parkhill, J. (2015). Roary: rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics, 31(22), 3691–3693. https://doi.org/10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTV421
Pasqua, M., Grossi, M., Scinicariello, S., Aussel, L., Barras, F., Colonna, B., & Prosseda, G. (2019). The MFS efflux pump EmrKY contributes to the survival of Shigella within macrophages. Scientific Reports 2019 9:1, 9(1), 2906-. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39749-3
Pruitt, K. D., Tatusova, T., & Maglott, D. R. (2005). NCBI Reference Sequence (RefSeq): a curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Research, 33(suppl_1), D501–D504. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKI025
Ranjbar, R., & Farahani, A. (2019). Shigella: Antibiotic-resistance mechanisms and new horizons for treatment. Infection and Drug Resistance, 12, 3137–3167. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S219755;PAGE:STRING:ARTICLE/CHAPTER
Saito, R., Smoot, M. E., Ono, K., Ruscheinski, J., Wang, P.-L., Lotia, S., Pico, A. R., Bader, G. D., & Ideker, T. (2012). A travel guide to Cytoscape plugins. Nature Methods, 9(11), 1069–1076.
Sassi, A., Basher, N. S., Kirat, H., Meradji, S., Ibrahim, N. A., Idres, T., & Touati, A. (2025). The Role of the Environment (Water, Air, Soil) in the Emergence and Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Antibiotics 2025, Vol. 14, Page 764, 14(8), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIBIOTICS14080764
Seemann, T. (2014). Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics, 30(14), 2068–2069. https://doi.org/10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTU153
Szklarczyk, D., Kirsch, R., Koutrouli, M., Nastou, K., Mehryary, F., Hachilif, R., Gable, A. L., Fang, T., Doncheva, N. T., & Pyysalo, S. (2023). The STRING database in 2023: protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), D638–D646.
Xiao, R., Huang, D., Du, L., Song, B., Yin, L., Chen, Y., Gao, L., Li, R., Huang, H., & Zeng, G. (2023). Antibiotic resistance in soil-plant systems: A review of the source, dissemination, influence factors, and potential exposure risks. Science of The Total Environment, 869, 161855. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2023.161855