A Review of Methodological Standards and Current Practices in Hemolytic Toxicity Testing of Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/pharmacon.v22i2.13229Keywords:
Hemocompatibility, Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems, Hemolytic toxicity testingAbstract
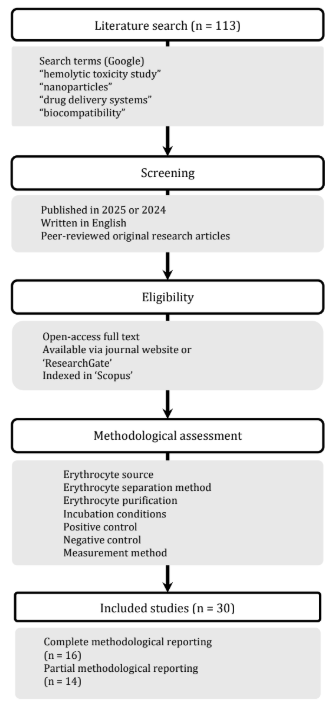
Hemolytic toxicity testing is a fundamental component of hemocompatibility assessment for nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems (N-DDSs), as erythrocyte integrity reflects blood safety prior to clinical application. Despite its critical role, experimental procedures vary across the literature. Essential methodological details are frequently omitted, hindering reproducibility and standardization. This variability urges the need for a consolidated reference that examines both current practices and established guidelines. This narrative review aims to provide a structured overview of hemolytic toxicity testing methodologies applied to N-DDSs, with particular emphasis on procedural parameters and their alignment with ASTM and ISO standards. Literature was identified through Google search and open access Scopus-Indexed journals primarily covering publications from 2025 and supplemented with earlier studies to provide historical context. Articles were selected based on relevance to seven methodological parameters which were erythrocyte source, methods of erythrocyte separation and purification, incubation conditions, positive and negative controls, measurement method. Analysis of 30 publications revealed human erythrocytes were the predominant model, with phosphate buffered saline and detergent-like substances were most commonly used negative and positive controls, respectively. Centrifugation controls were inconsistently reported, while incubation was typically run at 37oC, with varying durations depending on the nanoparticle system. Variability was also observed in approaches used to quantify free hemoglobin. Overall, while hemolytic toxicity studies continue to rely on ASTM and ISO guidelines, greater methodological details and standardization would enhance the reliability and reproducibility of hemocompatibility assessments in nanoparticle drug delivery research.
Downloads
References
Ansary, A., Osman, A., & El-Khouly, M. E. (2025). Doxorubicin-loaded pH-responsive porphyrin-derived carbon dots as a promising biocompatible drug delivery system for effective chemotherapy of breast cancer. RSC Advances, 15(9), 6457–6473. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ra09058f
Aroonthongsawat, P., Manocheewa, S., Srisawat, C., Punnakitikashem, P., & Suwanwong, Y. (2025). Enhancement of the in vitro anti-leukemic effect of the histone deacetylase inhibitor romidepsin using Poly-(D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles as a drug carrier. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2025.107043
ASTM International. (2013). ASTM F756-13: Standard Practice for Assessment of Hemolytic Properties of Materials.
ASTM International. (2000). ASTM F756-00; Standard Practice for Assessment of Hemolytic Properties of Materials.
ASTM International. (2008). ASTM F756-08: Standard Practice for Assessment of Hemolytic Properties of Materials Designation .
Azevedo, N. C. L., de Medeiros, A. M. Z., da Silva, G. H., Brito, M. L., Faria, J. M. L., Delite, F. S., Paula, A. J., & Martinez, D. S. T. (2024). Biocorona Formation and Hemolytic Effects of Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanoparticles. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 35(12). https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20240148
Ben Amor, A., Hemmami, H., Gherbi, M. T., Seghir, B. Ben, Zeghoud, S., Gharbi, A. H., Chenna, D., Ben Amor, I., Alsaeedi, H., Cornu, D., Bechelany, M., & Barhoum, A. (2025). Synthesis of spherical carbon nanoparticles from orange peel and their surface modification with chitosan: Evaluation of optical properties, biocompatibility, antioxidant and anti-hemolytic activity. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 15(7), 11345–11358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-024-06291-w
Bernier, A., Tobias, T., Nguyen, H., Kumar, S., Smith, C. W., Sunasee, R., Ckless, K., Tuga, B., & Imtiaz, Y. (2021). Vascular and blood compatibility of engineered cationic cellulose nanocrystals in cell-based assays. Nanomaterials, 11(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082072
Canham, P. B., & Burton, A. C. (1968). Distribution of size and shape in populations of normal human red cells. Circulation Research, 22(3), 405–422. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.22.3.405
Chahardoli, A., Qalekhani, F., Hajmomeni, P., Shokoohinia, Y., & Fattahi, A. (2025). Enhanced hemocompatibility, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties of biomolecules stabilized AgNPs with cytotoxic effects on cancer cells. Scientific Reports, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-82349-z
Chan, H. W., Sheung, P. W., Tsao, S. T. M., Wu, C. Y., & Chuang, H. Y. (2025). Gold nanoparticle-loaded macrophages enhance radiotherapy via immune remodeling in oral cancer. Materials Today Bio, 33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102029
Chaurasiya, S., M, V. M., Jangid, A. K., Medicherla, K., Pooja, D., & Kulhari, H. (2025). Synthesis and Evaluation of PEG Derivatized Nanostructures as Potential Delivery Carrier for Hydrophobic Drugs. Nano Trends, 100149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nwnano.2025.100149
Christodoulou, E., Tsimpolis, A., Theodorakis, K., Axypolitou, S., Tsamesidis, I., Kontonasaki, E., Pavlidou, E., & Bikiaris, D. N. (2025). Biodegradable Zwitterionic PLA-Based Nanoparticles: Design and Evaluation for pH-Responsive Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery. Polymers, 17(18), 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182495
Crawford, L., Wyatt, M., Bryers, J., & Ratner, B. (2021). Biocompatibility Evolves: Phenomenology to Toxicology to Regeneration. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 10(11). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202002153
de La Taille, T., Sarfati, P., Aid, R., Fournier, L., Pavon-Djavid, G., Chaubet, F., & Chauvierre, C. (2025). Microemulsion-Inspired Polysaccharide Nanoparticles for an Advanced Targeted Thrombolytic Treatment. ACS Nano, 19(2), 2944–2960. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.4c17049
De Menezes, Y. A. S., Félix-Silva, J., Da Silva-Júnior, A. A., Rebecchi, I. M. M., De Oliveira, A. S., Uchoa, A. F., & De F. Fernandes-Pedrosa, M. (2014). Protein-rich fraction of cnidoscolus urens (L.) arthur leaves: Enzymatic characterization and procoagulant and fibrinogenolytic activities. Molecules, 19(3), 3552–3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19033552
Deng, H., Xu, M., Liu, H., & Gao, H. (2022). Clinical analysis of the characteristics of patients diagnosed with hemolytic anemia induced by hepatitis E viral infection. ILIVER, 1(2), 117–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iliver.2022.05.001
Dobrovolskaia, M. A., Clogston, J. D., Neun, B. W., Hall, J. B., Patri, A. K., & McNeil, S. E. (2008). Method for analysis of nanoparticle hemolytic properties in vitro. Nano Letters, 8(8), 2180–2187. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0805615
Dubach, I. L., Buzzi, R. M., Schaer, D. J., & Vallelian, F. (2025). Patterns of hemolysis, erythropoiesis, and iron distribution define unique disease trajectories in three mouse models of genetic anemia. Experimental Hematology, 147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2025.104787
Dvanajscak, Z., Walker, P. D., Cossey, L. N., Messias, N. C., Boils, C. L., Kuperman, M. B., & Larsen, C. P. (2019). Hemolysis-associated hemoglobin cast nephropathy results from a range of clinicopathologic disorders. Kidney International, 96(6), 1400–1407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.08.026
Ebrahimi, S., & Bagchi, P. (2022). A computational study of red blood cell deformability effect on hemodynamic alteration in capillary vessel networks. Scientific Reports, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08357-z
Huang, L., Guo, W., Zhao, T., Feng, Y., Li, Y., An, Q., Li, C., Tian, Y., Zhang, H., Zhou, C., Sun, Y., He, C., Niu, Z., Shen, H., & Xiang, B. (2025). Microfluidic fabrication of lipid nanoparticles for co-delivery of siRNA and hydroxychloroquine: An engineered theranostic platform for enhanced breast cancer treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.160172
Ilhami, F. B., Puspitarini, S., Fitriana, Rahmawati, A., Mayasari, N. R., & Herliniati, H. (2025). Protective layer β-cyclodextrin within peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) shells’ nanoparticles enhances intracellular stable fluorescence for bioimaging applications: An in vitro and in silico study. Plant Nano Biology, 11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plana.2025.100135
International Organization for Standardization (ISO). (n.d.). ISO/TR 7406: Biological evaluation of medical devices—Guidance for hemocompatibility testing.
Islamzada, E., Matthews, K., Lamoureux, E. S., Duffy, S. P., Scott, M. D., & Ma, H. (2022). Degradation of red blood cell deformability during cold storage in blood bags. EJHaem, 3(1), 63–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/jha2.343
Jeong, J. H., Sugii, Y., Minamiyama, M., & Okamoto, K. (2006). Measurement of RBC deformation and velocity in capillaries in vivo. Microvascular Research, 71(3), 212–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2006.02.006
Kasprzyk, M., Opiła, G., Hinz, A., Stankiewicz, S., Bzowska, M., Wolski, K., Dulińska-Litewka, J., Przewoźnik, J., Kapusta, C., & Karewicz, A. (2025). Hyaluronic Acid-Coated SPIONs with Attached Folic Acid as Potential T2 MRI Contrasts for Anticancer Therapies. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 17(6), 9059–9073.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c20101
Kuck, L., Frappa, F. A., McNamee, A. P., & Simmonds, M. J. (2025). Storage temperature and anticoagulant choice determine the short-term stability of blood rheological parameters. Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation. https://doi.org/10.1177/13860291251376503
Luan, H., Peng, C., Yasin, P., Shang, Q., Xiang, W., & Song, X. (2025). Mannosamine-Engineered Nanoparticles for Precision Rifapentine Delivery to Macrophages: Advancing Targeted Therapy Against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 19, 2081–2102. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S505682
Ma, L., Zhou, W., Ma, X., Li, X., Zhang, Q., Ma, W., Chen, N., Zhou, X. T., & Tang, X. H. (2025). Preparation and property evaluation of oral colon targeted protein delivery system with sodium alginate and chitosan. Scientific Reports, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-04983-5
Mayerhöfer, T. G., Pahlow, S., & Popp, J. (2020). The Bouguer‐Beer‐Lambert Law: Shining Light on the Obscure. ChemPhysChem, 21(18), 2029–2046. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.202000464
Mazzarino, L., Loch-Neckel, G., dos Santos Bubniak, L., Ourique, F., Otsuka, I., Halila, S., Curi Pedrosa, R., Santos-Silva, M. C., Lemos-Senna, E., Curti Muniz, E., & Borsali, R. (2015). Nanoparticles Made From Xyloglucan-Block-
Polycaprolactone Copolymers: Safety Assessment for Drug Delivery. Toxicological Sciences, 147(1), 104–115. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfv114
Medeiros, T. S., Bezerra de Lima, L. E., Alves-Pereira, E. L., Alves-Silva, M. F., Dourado, D., Fernandes-Pedrosa, M. de F., Figueiredo, R. C. B. Q. de, & da Silva-Junior, A. A. (2025). Cationic and anionic PLGA-cholesterol hybrid nanoparticles as promising platforms to enhance the trypanocidal efficacy of benznidazole and drug delivery in Trypanosoma cruzi-
infected cells. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117782
Na, R., Jing, J., Yang, H., Li, Y., Yuan, X., Sun, X., Han, J., Wang, J., Tong, Z., He, G., & Ye, W. (2025). Formulation and Evaluation of VCAM-1-Targeted Methotrexate Lipid Nanoparticles for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 20, 10977–10998. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S532163
Neun, B. W., Ilinskaya, A. N., & Dobrovolskaia, M. A. (2018). Updated Method for In Vitro Analysis of Nanoparticle Hemolytic Properties. In Scientia Pharmaceutica (Vol. 79, Issue 3, pp. 91–102). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7352-1_9
Ngcamu, A. N., Nwabuife, J. C., Ndimande, N. P., Gabela, S., Ghazi, T., Sekhoacha, M. P., & Faya, M. A. (2025). Novel folic acid-functionalized smart Eicosapentaenoic acid liposomes for the targeted delivery of quercetin against cancer. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2025.107358
Peng, C., Luan, H., Shang, Q., Xiang, W., Yasin, P., & Song, X. (2025). Mannosamine-Modified Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-Polyethylene Glycol Nanoparticles for the Targeted Delivery of Rifapentine and Isoniazid in Tuberculosis Therapy. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 36(5), 1021–1033. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5c00062
Qian, H., Lv, J., & Hu, X. (2025). Development and evaluation of curcumin nano-niosomes for glioma-targeted therapy. Scientific Reports, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-95348-5
Rojas-Mancilla, E., Oyarce, A., Verdugo, V., Zheng, Z., & Ramírez-Tagle, R. (2015). The cluster [Re6Se8I6]3− induces low hemolysis of human erythrocytes in vitro: Protectives effect of albumin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(1), 1728–1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16011728
Salimi, S., Motalleb, G., Dehghani, H., Rahdar, A., Dastjerdi, K., Velasco, B., & Taboada, P. (2025). Anticancer effect of tamoxifen and Fe3O4@SiO2@Cu hybrid NPs on malignant human breast cancer cell (MCF-7). Journal of Molecular Liquids, 429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2025.127570
Shafique, S., Irshad, A., Ishtiaq, U., Mhamdi, L., Sharif, S., Jawad, R., Martin, P., M’Hamdi, N., Arshad, S., & Bejaoui, B. (2025). Reimagine breast cancer treatment: MgO-IDA nanocomposites: A promising strategy for precision medicine targeting MCF-7 cells. Results in Chemistry, 17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2025.102660
Shakeel, V., Hussain Gul, I., John, P., & Bhatti, A. (2024). Biocompatible gelatin-coated ferrite nanoparticles: A magnetic approach to advanced drug delivery. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 32(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102066
Shakibaie, M., Hosseininasab, S. S., Riahi-Madvar, S., Adeli-Sardou, M., Jabari-Morouei, F., & Forootanfar, H. (2025). The potential of novel arsenic nanoparticles containing metformin (MTF@As NPs): a study on their antioxidant and cytotoxic properties. BMC Chemistry, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-025-01419-z
Sharifi, F., Ebrahimnejad, P., Mohammadi, H., Abasi, M., Asare-Addo, K., & Nokhodchi, A. (2025). Unlocking Curcumin’s potential: Nano-encapsulation in mPEG-chitosan/hyaluronic acid complexes for enhanced therapeutic impact in colon cancer. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2025.106894
Sherwood, L. (2016). Human Physiology: From Cells tp Systems (Ninth).
Shi, H., Wang, B., Shi, Z., Ma, H., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, Y., Xia, N., Wu, C., & Gao, Y. (2025). Paclitaxel-Ang-2-functionalized bionic mesoporous selenium nanoparticles for targeted therapy of glioma. Pharmacological Research, 216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107783
Sohail, S., Zeb, A., Alamri, A. H., Fatease, A. Al, Lahiq, A. A., Alruwaili, N. K., Khan, S., & Din, F. ud. (2025). Novel biocompatible multifunctional porous magnetic nanoclusters for the targeted delivery of lenvatinib towards hepatocellular carcinoma. Materials Advances, 6(5), 1769–1787. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ma01101e
Ullah, I., Kamal, A., Saba, M., Ara, U., Touhami, D., Wahab, A., Maqbool, T., Nazish, M., Alrefaei, A. F., & Lackner, M. (2025). Chlorophyllum molybdites-synthesized manganese oxide nanoparticles (MnO-NPs): morphology, biocompatibility, and anticancer properties against liver cancer (HepG2) cell line. Scientific Reports, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-93818-4
US FDA. (2023). Use of International Standard ISO 10993-1, “Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 1: Evaluation and testing within a risk management process.” https://www.fda.gov/media/85865/download
Uyuklu, M., Cengiz, M., Ulker, P., Hever, T., Tripette, J., Connes, P., Nemeth, N., Meiselman, H. J., & Baskurt, O. K. (2009). Effects of storage duration and temperature of human blood on red cell deformability and aggregation. Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation, 41(4), 269–278. https://doi.org/10.3233/CH-2009-1178
van Kampen, E. J., & Zijlstrat, W. G. (1983). Spectrophotometry of Hemoglobin and Hemoglobin Derivatives. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry (Vol. 23, pp. 199–257). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2423(08)60401-1
Yaghoubi, A., Ramazani, A., Sillanpaa, M., Ghasemzadeh, H., & Mohammadi, E. (2025). Biocompatible porous PAM/CNT nanocomposite hydrogel films for sustained drug delivery and cancer therapy. Scientific Reports, 15(1), 22387. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-05473-4
Yedgar, S., Barshtein, G., & Gural, A. (2022). Hemolytic Activity of Nanoparticles as a Marker of Their Hemocompatibility. In Micromachines (Vol. 13, Issue 12). MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122091
Zhaisanbayeva, B. A., Mun, E. A., Ulmanova, L., Zhunissova, Z., Umbayev, B., Olzhayev, F., Vorobjev, I. A., Hortelano, G., & Khutoryanskiy, V. V. (2024). In vitro and in vivo toxicity of thiolated and PEGylated organosilica nanoparticles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 652, 123852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.123852
Zheng, C., Li, S., Mueller, J., Chen, C., Lyu, H., Yuan, G., Zamalloa, A., Adofina, L., Srinivasan, P., Menon, K., Heaton, N., Immenschuh, S., Silva, I., Rausch, V., Hammad, S., Dooley, S., Chokshi, S., Riva, A., He, S., & Mueller, S. (2025). Evidence for alcohol-mediated hemolysis and erythrophagocytosis. Redox Biology, 85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2025.103742