Optimization of Gel Formulation and Antibacterial Activity against Cutibacterium acnes from Combined Extracts of Caesalpinia sappan and Carthamus tinctorius Using Simplex Lattice Design
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23917/pharmacon.v22i2.13175Keywords:
Antibacterial Activity; Caesalpinia sappan; Carthamus tinctorius; gel formulation; Cutibacterium acnesAbstract
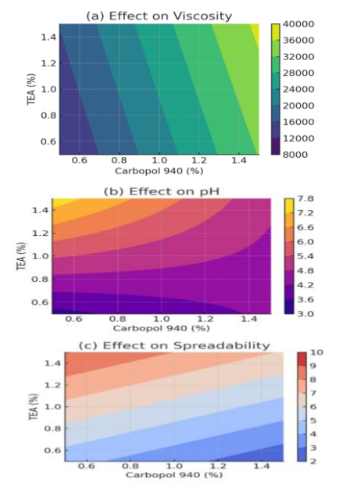
Acne vulgaris remains a common dermatological disorder in which Cutibacterium acnes plays a central role, while concerns over antibiotic resistance highlight the need for safe natural alternatives. This study aimed to develop and optimize a topical gel formulation containing combined extracts of Caesalpinia sappan and Carthamus tinctorius with antibacterial activity against C. acnes. An experimental design was employed using the Simplex Lattice Design (SLD) method to optimize the proportions of Carbopol 940 and triethanolamine as gelling and stabilizing agents. The prepared gels were evaluated for physical characteristics, stability, hedonic properties, and antibacterial activity using the agar diffusion method. The optimized formulation, with a desirability value of 0.931, demonstrated appropriate viscosity, spreadability, and pH within the physiological range. Stability testing through six freeze–thaw cycles confirmed no significant changes in organoleptic or physicochemical parameters. Hedonic evaluation indicated good acceptance regarding odor, texture, and non-irritating properties, though color preference was slightly lower. Antibacterial assays showed that both the optimized gel and combined extracts produced strong inhibition zones against C. acnes, comparable to clindamycin as a positive control. These findings confirm that the combination of C. sappan and C. tinctorius extracts, when optimized through statistical design, can yield a stable and effective herbal gel with strong antibacterial activity. This research highlights the potential of integrating traditional medicinal plants with modern formulation approaches to develop safe, natural, and sustainable alternatives for acne management.
Downloads
References
Almasaudi, S. (2021). The antibacterial activities of honey. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(4), 2188–2196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.10.017
Bai, H., Yang, J., & Wang, R. (2025). Carthamus tinctorius L.: A comprehensive review of its ethnomedicine, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 16, 1609299. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1609299
Beig, M., Shirazi, O., Ebrahimi, E., Banadkouki, A. Z., Golab, N., & Sholeh, M. (2024). Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Cutibacterium acnes isolates: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance, 39, 82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2024.07.005
Carballido, F., Philippe, A., Maitre, M., Lauze, C., Chanssard, N., Garidou, L., Duplan, H., & Tan, J. (2024). A dermocosmetic product containing the sap of oat plantlets and Garcinia mangostana extract improves the clinical signs of acne. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.19876
Cavallo, I., Sivori, F., Truglio, M., De Maio, F., Lucantoni, F., Cardinali, G., & al, et. (2022). Skin dysbiosis and Cutibacterium acnes biofilm in inflammatory acne lesions of adolescents. Scientific Reports, 12, 21104. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-25614-7
Daud, N. S., & Suryanti, E. (2017). Formulasi Emulgel Antijerawat Minyak Nilam (Patchouli oil) Menggunakan Tween 80 dan Span 80 sebagai Pengemulsi dan HPMC sebagai Basis Gel. Jurnal Mandala Pharmacon Indonesia, 3(2), 90–95. https://doi.org/10.35311/jmpi.v3i02.3
Deka, T. (2022). Box-Behnken Design Approach to Develop Nano-Vesicular Herbal Gel for the Management of Skin Cancer in Experimental Animal Model. International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics, 14(6), 19. https://doi.org/10.22159/IJAP.2022V14I6.45867
Dixit, G. (2021). Formulation and evaluation of herbal gel for management of mouth ulcers. Indian Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 8(3), 139–143. https://doi.org/10.18231/J.IJPP.2021.039
Febriyenti, Suharti, N., Lucida, H., Husni, E., & Sedona, O. (2018). 178-674-5-Pb. Sains Farmasi Dan Klinis, 5(1), 23–27.
Hansur, L., Aras, D. U., & Dwijayanti, E. (2024). Potential of Hydroxysafflor yellow A, the main compound of Kasumba Turate (Carthamus tinctorius) as Anti-Inflammatory in Lung, Liver and Cardiac Tissues: A Literature Review. Pharmacon: Jurnal Farmasi Indonesia, 21(2). https://doi.org/10.23917/pharmacon.v21i2.4908
Hayat, M., Nawaz, A., Chinnam, S., Muzammal, M., Latif, M. S., Yasin, M., Ashique, S., Zengin, G., & Farid, A. (2023). Formulation development and optimization of herbo synthetic gel: In vitro biological evaluation and in vivo wound healing studies. Process Biochemistry, 130, 116–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2023.04.010
Kaya, Y., Kobya, V., Mardani, A., & Assaad, J. J. (2024). Effect of modified Triethanolamine on grinding efficiency and performance of cementitious materials. Talanta Open, 9, 100293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talo.2024.100293
Lestari, F. A., Hajrin, W., & Hanifa, N. I. (2020). Optimasi Formula Krim Ekstrak Daun Katuk (Sauropus androgynus) Variasi Konsentrasi Asam Stearat, Trietanolamin, dan Gliserin. Jurnal Kefarmasian Indonesia, 10(2), 110–119. https://doi.org/10.22435/jki.v10i2.2496
Litovin, H., & Noveski, R. (2022a). Challenges and best practices in phytopharmaceutical production. Macedonian Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 68(Suppl 2), 117–118. https://doi.org/10.33320/maced.pharm.bull.2022.68.04.052
Mayslich, C., Grange, P. A., & Dupin, N. (2021). Cutibacterium acnes as an Opportunistic Pathogen: An Update of Its Virulence-Associated Factors. Microorganisms, 9(2), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020303
Nahdhia, N., Hendradi, E., & Rijal, M. A. S. (2025). Design and optimization of nanoemulsion system by simplex lattice design method to improve solubility of topical diclofenac sodium. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 18(5), 2237–2243. https://doi.org/10.52711/0974-360X.2025.00320
Olmos, D., & González-Benito, J. (2021). Polymeric Materials with Antibacterial Activity: A Review. Polymers, 13(4), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040613
Pattananandecha, T., Apichai, S., Julsrigival, J., Ogata, F., Kawasaki, N., & Saenjum, C. (2022). Antibacterial Activity against Foodborne Pathogens and Inhibitory Effect on Anti-Inflammatory Mediators’ Production of Brazilin-Enriched Extract from Caesalpinia sappan Linn. Plants, 11(13), 1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11131698
Pratiwi, G., Ramadhiani, A. R., Shiyan, S., & Chabib, L. (2024). Combination Simplex Lattice Design Modelling with Chemometrics Analysis for Optimization Formula Self-Nano Emulsion Loaded Quercetin. Biomedicines Research International, 14(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC141.014
Ramadhani, R. A., Riyadi, D. H. S., Triwibowo, B., & Kusumaningtyas, R. D. (2017). Review Pemanfaatan Design Expert untuk Optimasi Komposisi Campuran Minyak Nabati sebagai Bahan Baku Sintesis Biodiesel. Jurnal Teknik Kimia Dan Lingkungan, 1(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.33795/jtkl.v1i1.5
Rozas, M., de Ruijter, A. H., Fabrega, M. J., Zorgani, A., Guell, M., Paetzold, B., & Brillet, F. (2021). From Dysbiosis to Healthy Skin: Major Contributions of Cutibacterium acnes to Skin Homeostasis. Microorganisms, 9(3), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030628
Safitri, F. I., Nawangsari, D., & Febrina, D. (2021). Overview: Application of Carbopol 940 in Gel. Advances in Health Sciences Research, International Conference on Health and Medical Sciences (AHMS 2020). https://doi.org/10.2991/ahsr.k.210127.018
Shmakov, S. L., Babicheva, T. S., Kurochkina, V. A., Lugovitskaya, T. N., & Shipovskaya, A. B. (2023). Structural and Morphological Features of Anisotropic Chitosan Hydrogels Obtained by Ion-Induced Neutralization in a Triethanolamine Medium. Gels, 9(11), 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110876
Sindhu, R. K., Gupta, R., Wadhera, G., & Kumar, P. (2022). Modern Herbal Nanogels: Formulation, Delivery Methods, and Applications. Gels, 8(2), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8020097
Singh, V. K., Sahoo, D., Agrahari, K., Khan, A., Mukhopadhyay, P., Chanda, D., & Yadav, N. P. (2023). Anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-psoriatic potential of apigenin in RAW 264.7 cells, HaCaT cells and psoriasis like dermatitis in BALB/c mice. Life Sciences, 328, 121909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121909
Syamsunarno, M. R. A. A., Safitri, R., & Kamisah, Y. (2021). Protective Effects of Caesalpinia sappan Linn. And Its Bioactive Compounds on Cardiovascular Organs. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12, 725745. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.725745
Vij, T., Prashant Anil, P., Shams, R., Dash, K. K., Kalsi, R., Pandey, V. K., Harsányi, E., Kovács, B., & Shaikh, A. M. (2023). A Comprehensive Review on Bioactive Compounds Found in Caesalpinia sappan. Molecules, 28(17), 6247. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176247
Wekalao, J., Premalatha, S., Prabakaran, P., & Rathish, C. R. (2025). Graphene-integrated Multiresonator Architecture with Machine Learning Enhancement for Enhanced Isoquercitrin Detection System in Phytopharmaceutical Formulations. Plasmonics.
Yan, Y., Li, X., Zhang, C., Lv, L., Gao, B., & Li, M. (2021). Research Progress on Antibacterial Activities and Mechanisms of Natural Alkaloids: A Review. Antibiotics, 10(3), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030318
Yusuf, A. L., Nugraha, D., Wahlanto, P., Indriastuti, M., Ismail, R., & Himah, F. A. (2022). Formulasi Dan Evaluasi Sediaan Gel Ekstrak Buah Pare (Momordica Charantia L.) Dengan Variasi Konsentrasi Carbopol 940. Pharmacy Genius, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.56359/pharmgen.v1i01.149